Abstract
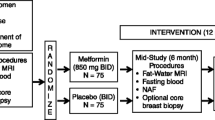
Metformin may exert anti-cancer effects through indirect (insulin-mediated) or direct (insulin-independent) mechanisms. We report results of a neoadjuvant “window of opportunity” study of metformin in women with operable breast cancer. Newly diagnosed, untreated, non-diabetic breast cancer patients received metformin 500 mg tid after diagnostic core biopsy until definitive surgery. Clinical (weight, symptoms, and quality of life) and blood [fasting serum insulin, glucose, homeostasis model assessment (HOMA), C-reactive protein (CRP), and leptin] attributes were compared pre- and post-metformin as were terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and Ki67 scores (our primary endpoint) in tumor tissue. Thirty-nine patients completed the study. Mean age was 51 years, and metformin was administered for a median of 18 days (range 13–40) up to the evening prior to surgery. 51 % had T1 cancers, 38 % had positive nodes, 85 % had ER and/or PgR positive tumors, and 13 % had HER2 overexpressing or amplified tumors. Mild, self-limiting nausea, diarrhea, anorexia, and abdominal bloating were present in 50, 50, 41, and 32 % of patients, respectively, but no significant decreases were seen on the EORTC30-QLQ function scales. Body mass index (BMI) (−0.5 kg/m2, p < 0.0001), weight (−1.2 kg, p < 0.0001), and HOMA (−0.21, p = 0.047) decreased significantly while non-significant decreases were seen in insulin (−4.7 pmol/L, p = 0.07), leptin (−1.3 ng/mL, p = 0.15) and CRP (−0.2 mg/L, p = 0.35). Ki67 staining in invasive tumor tissue decreased (from 36.5 to 33.5 %, p = 0.016) and TUNEL staining increased (from 0.56 to 1.05, p = 0.004). Short-term preoperative metformin was well tolerated and resulted in clinical and cellular changes consistent with beneficial anti-cancer effects; evaluation of the clinical relevance of these findings in adequately powered clinical trials using clinical endpoints such as survival is needed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Decensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, Cazzaniga M, Gennari A, Bonanni B, Gandini S (2010) Metformin and cancer risk in diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 3:1451–1461
Zhang ZJ, Zheng ZJ, Kan H, Song Y, Cui W, Zhao G, Kip KE (2011) Reduced risk of colorectal cancer with metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 34:2323–2328
Chlebowski RT, McTiernan A, Wactawski-Wende J, Manson JE, Aragaki AK, Rohan T, Ipp E, Kaklamani VG, Vitolins M, Wallace R, Gunter M, Phillips LS, Strickler H, Margolis K, Euhus DM (2012) Diabetes, metformin, and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Clin Oncol 30:2844–2852
Col NF, Ochs L, Springmann V, Aragaki AK, Chlebowski RT (2012) Metformin and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis and critical literature review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2170-x
Jiralerspong S, Palla SL, Giordano SH, Meric-Bernstam F, Liedtke C, Barnett CM, Hsu L, Hung MC, Hortobagyi GN, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2009) Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:3297–3302
Goodwin PJ, Pritchard KI, Ennis M, Clemons M, Graham M, Fantus IG (2008) Insulin-lowering effects of metformin in women with early breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 8:501–505
Duggan C, Irwin ML, Xiao L, Henderson KD, Smith AW, Baumgartner RN, Baumgartner KB, Bernstein L, Ballard-Barbash R, McTiernan A (2011) Associations of insulin resistance and adiponectin with mortality in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 29:32–39
Emaus A, Veierod MB, Tretli S, Finstad SE, Selmer R, Furberg A-S, Bernstein L, Schlichting E, Thune I (2010) Metabolic profile, physical activity, and mortality in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 121:651–660
Irwin ML, Duggan C, Wang CY, Smith AW, McTiernan A, Baumgartner RN, Baumgartner KB, Bernstein L, Ballard-Barbash R (2011) Fasting C-peptide levels and death resulting from all causes and breast cancer: the health, eating, activity, and lifestyle study. J Clin Oncol 29:47–53
Erickson K, Patterson RE, Flatt SW, Natarajan L, Parker BA, Heath DD, Laughlin GA, Saquib N, Rock CL, Pierce JP (2011) Clinically defined type 2 diabetes mellitus and prognosis in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 29:54–60
Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, Trudeau ME, Koo J, Taylor SK, Hood N (2012) Insulin- and obesity-related variables in early-stage breast cancer: correlations and time course of prognostic associations. J Clin Oncol 30:164–171
Belfiore A, Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, Vigneri R (2009) Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr Rev 230:586–623
Mulligan AM, O’Malley FP, Ennis M, Fantus IG, Goodwin PJ (2007) Insulin receptor is an independent predictor of a favorable outcome in early stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 106:39–47
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG, Sonenberg N, Pollak M (2006) Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:10269–10273
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak M, Sonenberg N (2007) Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:10804–10812
Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 3.0, DCTD, NCI, NIH, DHHS March 31, 2003. http://ctep.cancer.gov. Publish Date: 9 August 2006
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetology 28:412–419
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, Fitzgibbons PL, Francis G, Goldstein NS, Hayes M et al (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:2784–2795
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, Dowsett M, Fitzgibbons PL, Hanna WM, Langer A et al (2007) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:118–145
Bloom HJ, Richardson WW (1957) Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer; a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer 11:359–377
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Dowsett M, Nielsen TO, A’Hern R et al (2011) Assessment of Ki67 in breast cancer: recommendations from the International Ki67 in Breast Cancer working group. J Natl Cancer Inst 103:1656–1664
Dowsett M, Dixon JM, Horgan K, Salter J, Hills M, Harvey E (2000) Antiproliferative effects of idoxifene in a placebo-controlled trial in primary human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6:2260–2267
Niraula S, Stambolic V, Dowling R, Ennis M, Chang M, Done S, Hallak S, Hood N, Leong W, Escallon J, Goodwin PJ (2010) Clinical and biologic effects of metformin in early stage breast cancer. Cancer Res 70(24 Suppl):104s
Frassoldati A, Maur M, Guarneri V, Nicolini M, Conte PF (2005) Predictive value of biologic parameters for primary chemotherapy in operable breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 6:315–324
Archer CD, Parton M, Smith IE et al (2003) Early changes in apoptosis and proliferation following primary chemotherapy for breast cancer. Br J Cancer 89:1035–1041
Tomic T, Botton T, Cerezo M et al (2011) Metformin inhibits melanoma development through autophagy and apoptosis mechanisms. Cell Death Dis 2:e199
Yasmeen A, Beauchamp MC, Piura E, Segal E, Pollak M, Gotlieb WH (2011) Induction of apoptosis by metformin in epithelial ovarian cancer: involvement of the Bcl-2 family proteins. Gynecol Oncol 121:492–498
Malki A, Youssef A (2011) Antidiabetic drug metformin induces apoptosis in human MCF breast cancer via targeting ERK signaling. Oncol Res 19:275–285
Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Deng XS, Alimova IN, Lind SE, Thor AD (2009) Metformin induces unique biological and molecular responses in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle 8:2031–2040
Wang LW, Li ZS, Zou DW, Jin ZD, Gao J, Xu GM (2008) Metformin induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 14:7192–7198
Li M, Liu J, Hu WL, Jia CH, Li HY, Wen ZH, Zou ZP, Bai XC, Luo SQ (2011) Effect of metformin on apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma cells in vitro and its mechanisms. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 31:1504–1508
Zakikhani M, Blouin MJ, Piura E, Pollak MN (2010) Metformin and rapamycin have distinct effects on the AKT pathway and proliferation in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123:271–279
Hadad S, Iwamoto T, Jordan L et al (2011) Evidence for biological effects of metformin in operable breast cancer: a pre-operative, window-of-opportunity, randomized trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128:783–794
Bonanni B, Puntoni M, Cazzaniga M, Pruneri G, Serrano D, Guerrieri-Gonzaga A, Gennari A, Trabacca MS, Galimberti V, Veronesi P, Johansson H, Aristarco V, Bassi F, Luini A, Lazzeroni M, Varricchio C, Viale G, Bruzzi P, Decensi A (2012) Dual effect of metformin on breast cancer proliferation in a randomized presurgical trial. J Clin Oncol 30:2593–2600
Ellis PA, Smith IE, Detre S, Burton SA, Salter J, A’Hern R, Walsh G, Johnston SR, Dowsett M (1998) Reduced apoptosis and proliferation and increased Bcl-2 in residual breast cancer following preoperative chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 48:107–116
Romero Q, Bendahl PO, Klintman M, Loman N, Ingvar C, Ryden L, Rose C, Grabau D, Borgquist S (2011) Ki67 proliferation in core biopsies versus surgical samples—a model for neo-adjuvant breast cancer studies. BMC Cancer 11:341
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Grant from Susan G. Komen for the Cure. Dr. Dowling is supported by a Banting Postdoctoral Fellowship from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Conflict of interest
Dr. Chang acknowledges funding from Hoffmann-LaRoche. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
Conduct of this study at Mount Sinai and Princess Margaret Hospitals was performed in compliance with the standards of the Ontario Cancer Research Ethics Board.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niraula, S., Dowling, R.J.O., Ennis, M. et al. Metformin in early breast cancer: a prospective window of opportunity neoadjuvant study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 135, 821–830 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2223-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2223-1