Abstract
Background
Three-dimensional (3-D) stereoscopic vision is theoretically superior to two-dimensional (2-D) vision in endoscopic endonasal surgery. However, only few reports have quantitatively compared endoscopic performance under the two visual conditions. We introduced a newly designed stereoendoscopic system with a “dual-lens and single camera” for endoscopic endonasal surgery and objectively compared the performances under 3-D and high-definition 2-D visualizations on a dry laboratory model.
Methods
Thirty subjects without experience performing endoscopic surgery, computer-simulated training or any 3-D video system were recruited and divided into two groups (Group A and Group B) for performing two different tasks. The novel 4.7-mm-diameter stereoendoscope provided high-definition (HD) images. In Task 1, Group A started the task under the 3-D condition followed by the 2-D condition, and Group B vice versa. In Task 2, Group A started the task under the 2-D condition followed by the 3-D condition, and Group B vice versa. The performance accuracy and speed under the two visual conditions were analyzed.
Results
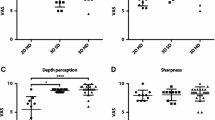
Significant improvement in performance accuracy and speed was seen under 3-D conditions in the both “3-D first” and “2-D first” subgroups during both tasks (P < .001). Regardless of order, the inaccuracy rate and performance time under 3-D conditions was significantly lower than that under 2-D conditions in each subject.
Conclusions
We demonstrated the advantage of 3-D visualization over 2-D visualization for inexperienced subjects. Further quantitative clinical studies are required to confirm whether stereoendoscopy actually provides benefits in clinical settings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birkett DH, Josephs LG, Este-McDonald J (1994) A new 3-D laparoscope in gastrointestinal surgery. Surg Endosc 8(12):1448–1451
Boyle E, Kennedy AM, Traynor O, Hill AD (2011) Training surgical skills using nonsurgical tasks–can Nintendo Wii™ improve surgical performance? J Surg Educ 68(2):148–154
Brown SM, Tabaee A, Singh A, Schwartz TH, Anand VK (2008) Three-dimensional endoscopic sinus surgery: feasibility and technical aspects. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 138(3):400–402
Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Esposito F, De Divitiis O, Messina A, De Divitiis E (2008) Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to the midline skull base: the evolving role of transsphenoidal surgery. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg 33:151–199
Chan AC, Chung SC, Yim AP, Lau JY, Ng EK, Li AK (1997) Comparison of two-dimensional vs three-dimensional camera systems in laparoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc 11(5):438–440
Chen G, Ling F (2010) A new plastic model of endoscopic technique training for endonasal transsphenoidal pituitary surgery. Chin Med J 123(18):2576–2579
Durrani AF, Preminger GM (1995) Three-dimensional video imaging for endoscopic surgery. Comput Biol Med 25(2):237–245
Fraser JF, Allen B, Anand VK, Schwartz TH (2009) Three-dimensional neurostereoendoscopy: subjective and objective comparison to 2D. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 52(1):25–31
Barkhoudarian G, Romero AD, Laws ER (2013) Evaluation of the Three-Dimensional Endoscope in Transsphenoidal Surgery. Neurosurgery DOI: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e31828ba962
Hanna GB, Shimi SM, Cuschieri A (1998) Randomised study of influence of two-dimensional versus three-dimensional imaging on performance of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Lancet 351(9098):248–251
Hofmeister J, Frank TG, Cuschieri A, Wade NJ (2001) Perceptual aspects of two-dimensional and stereoscopic display techniques in endoscopic surgery: review and current problems. Semin Laparosc Surg 8(1):12–24
Kassam A, Thomas AJ, Snyderman C, Carrau R, Gardner P, Mintz A, Kanaan H, Horowitz M, Pollack IF (2007) Fully endoscopic expanded endonasal approach treating skull base lesions in pediatric patients. J Neurosurg 106(2 Suppl):75–86
Kassam AB, Gardner PA, Snyderman CH, Carrau RL, Mintz AH, Prevedello DM (2008) Expanded endonasal approach, a fully endoscopic transnasal approach for the resection of midline suprasellar craniopharyngiomas: a new classification based on the infundibulum. J Neurosurg 108(4):715–728
Kennedy AM, Boyle EM, Traynor O, Walsh T, Hill AD (2011) Video gaming enhances psychomotor skills but not visuospatial and perceptual abilities in surgical trainees. J Surg Educ 68(5):414–420
Rosenberg BH, Landsittel D, Averch TD (2005) Can video games be used to predict or improve laparoscopic skills? J Endourol 19(3):372–376
Roth J, Singh A, Nyquist G, Fraser JF, Bernardo A, Anand VK, Schwartz TH (2009) Three-dimensional and 2-dimensional endoscopic exposure of midline cranial base targets using expanded endonasal and transcranial approaches. Neurosurgery 65(6):1116–1128
Shah RN, Leight WD, Patel MR, Surowitz JB, Wong YT, Wheless SA, Germanwala AV, Zanation AM (2011) A controlled laboratory and clinical evaluation of a three-dimensional endoscope for endonasal sinus and skull base surgery. Am J Rhinol Allergy 25(3):141–144
Tabaee A, Anand VK, Fraser JF, Brown SM, Singh A, Schwartz TH (2009) Three-dimensional endoscopic pituitary surgery. Neurosurgery 64(5 Suppl 2):288–293
Taffinder N, Smith SG, Huber J, Russell RC, Darzi A (1999) The effect of a second-generation 3D endoscope on the laparoscopic precision of novices and experienced surgeons. Surg Endosc 13(11):1087–1092
Votanopoulos K, Brunicardi FC, Thornby J, Bellows CF (2008) Impact of three-dimensional vision in laparoscopic training. World J Surg 32(1):110–118
Wasserzug O, Margalit N, Weizman N, Fliss DM, Gil Z (2010) Utility of a three-dimensional endoscopic system in skull base surgery. Skull Base 20(4):223–228
Wedmid A, Llukani E, Lee DI (2011) Future perspectives in robotic surgery. BJU Int 108(6 Pt 2):1028–1036
Yamauchi Y, Yamashita J, Morikawa O, Hashimoto R, Mochimaru R, Fukui Y, Uno H, Yokoyama K (2002) Surgical Skill Evaluation by Force Data for Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Training System. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2488:44–51
Acknowledgment
We thank MACHIDA Endoscope Co. Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan) and SHINKO OPTICAL Co. Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan) for allowing us to use their stereoendoscopic system for this study. We also thank the medical students who participated in this study.
Ethical standards
The authors declare that this work met all ethical standards for research and scientific publication.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawanishi, Y., Fujimoto, Y., Kumagai, N. et al. Evaluation of two- and three-dimensional visualization for endoscopic endonasal surgery using a novel stereoendoscopic system in a novice: a comparison on a dry laboratory model. Acta Neurochir 155, 1621–1627 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1757-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1757-2