Abstract
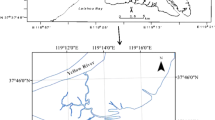
The deteriorating environmental conditions of Baiyangdian Lake have caused a wide public concern. Surface soils (0–20 cm) were collected at 10 sites of reed wetlands in raised fields of the Baiyangdian Lake. They were analyzed for total contents of trace elements to investigate their distribution and pollution levels in wetland soils of this region. Results showed that the mean contents of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn all exceeded their environmental background values of Hebei Province and had various degree of spatial variations. As, Cr and Ni contents exceeded considerably the probable effect levels. Multivariate analysis indicated that Cr, Cd, Ni, Cu, Pb and Zn had common sources and As had different sources for these trace elements. The average toxic units (TU) of trace elements in the Baiyangdian Lake followed the order As > Ni > Cr > Zn > Pb > Cu > Cd. As, Ni and Cr made the higher contributions to ΣTUs (i.e., 41.3 ± 7.2, 21.8 ± 4.1 and 16.2 ± 2.8 %, respectively). The potential ecological risk index of Cd \( \left( {E_{r}^{i} } \right) \) was 213.44, which was the highest value in the Baiyangdian Lake. The other trace elements had lower potential ecological risk indices (<40), following the order Cd > As > Cu > Pb = Ni > Cr > Zn. Potential toxicity response indices (RI) of trace elements for the whole lake region was 269.81, with a moderate potential toxicity response.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdu N, Abdulkadir A, Agbenin J, Buerkert A (2010) Vertical distribution of heavy metals in wastewater-irrigated vegetable garden soils of three West African cities. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 89:387–397
An Y, Kampbell DH (2003) Total, dissolved, and bioavailable metals at Lake Texoma marinas. Environ Pollut 122(2):253–259
Bai J, Cui B, Wang Q, Gao H, Ding Q (2009) Assessment of heavy metal contamination of roadside soils in Southwest China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23:341–347
Bai J, Cui B, Yang Z, Xu X, Ding Q, Gao H (2010a) Heavy metal contamination of cultivated wetland soils along a typical plateau lake from southwest China. Environ Earth Sci 59:1781–1788
Bai J, Yang Z, Cui B, Gao H, Ding Q (2010b) Some heavy metals distribution in wetland soils under different land use types along a typical plateau lake, China. Soil Tillage Res 106:344–348
Bai J, Cui B, Chen B, Zhang K, Deng W, Gao H, Xiao R (2011a) Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a typical plateau lake wetland, China. Ecol Model 222(2):301–306
Bai J, Huang L, Yan D, Wang Q, Gao H, Xiao R, Huang C (2011b) Contamination characteristics of heavy metals in wetland soils along a tidal ditch of the Yellow River Estuary, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25:671–676
Bai J, Xiao R, Cui B, Zhang K, Wang Q, Liu X, Gao H, Huang L (2011c) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from the young and old reclaimed regions in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environ Pollut 159:817–824
Baruthio F (1992) Toxic effects of chromium and its compounds. Biol Trace Elem Res 32(1):145–153
Brumelis G, Lapina L, Nikodemus O, Tabors G (2002) Use of the O horizon of forest soils in monitoring metal deposition in Latvia. Water Air Soil Pollut 135:291–309
Bustamante P, Bocher P, Cherel Y, Miramand P, Caurant F (2003) Distribution of trace elements in the tissues of benthic and pelagic fish from the Kerguelen Islands. Sci Total Environ 313:25–39
Cambardella CA, Moorman TB, Novak JM (1994) Carbon and nitrogen dynamics of soil organic matter fractions from cultivated grassland soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1501–1511
Cao H, Luan Z, Wang J, Zhang X (2009) Potential ecological risk of cadmium, lead and arsenic in agricultural black soil in Jilin Province, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23:57–64
CCME (1995) Protocol for the derivation of Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life. Canadian Council of Ministers for the Environment, Report CCME EPC-98E
Chen C, Pickhardt P, Xu M, Folt C (2008) Mercury and arsenic bioaccumulation and eutrophication in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 190:115–127
Chen Y, Wang J, Shi G, Sun X, Chen Z, Xu S (2011) Human health risk assessment of lead pollution in atmospheric deposition in Baoshan District, Shanghai. Environ Geochem Health 33(6):515–523
Chi Q, Zhu G, Alan L (2007) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fishes from Taihu Lake, China. J Environ Sci China 19:1500–1504
China Environmental Monitoring Station (1990) Chinese soil background values of elements
Dai S (2001) Environmental chemistry. Beijing, Higher Education Press, Beijing
Frickel S, Elliott JR (2008) Tracking industrial land use conversions: a new approach for studying relict waste and urban development. Organ Environ 21:128–147
Garg N, Singla P (2011) Arsenic toxicity in crop plants: physiological effects and tolerance mechanisms. Environ Chem Lett 9(3):303–321
Gonzalez ZI, Krachler M, Cheburkin AK, Shotyk W (2006) Spatial distribution of natural enrichments of arsenic, selenium, and uranium in a minerotrophic peatland, Gola diLago, Canton Ticino, Switzerland. Environ Sci Technol 40:6568–6574
Guo W, Liu X, Liu Z, Li G (2010) Pollution and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the sediments around Dongjiang Harbor, Tianjin. Int Soc Environ Inf Sci 2:729–736
Håkanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Han Y, Du P, Cao J, Posmentier ES (2006) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi′an, Central China. Sci Total Environ 355:176–186
Horvat T, Vidakovic-Cifrek Z, Orescanin V, Tkalec M, Pevalek-Kozlina B (2007) Toxicity assessment of heavy metal mixtures by Lemna minor L. Sci Total Environ 384:229–238
Jefferies DJ, Freestone P (1984) Chemical analysis of some coarse fish from a Suffolk River carried out as part of the preparation for the first release of captive-bred otters. J Otter Trust 18:17–22
Kabir MI, Lee H, Kim G, Jun T (2011) Correlation assessment and monitoring of the potential pollutants in the surface sediments of Pyeongchang river, Korea. Int J Sediment Res 26(2):152–162
Kashem MA, Singh BR (2001) Metal availability in contaminated soils: II. Uptake of Cd, Ni and Zn in rice plants grown under flooded culture with organic matter addition. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 61:257–266
Kim D, Yu S, Lee E (2010) Effects of blood lead concentration on intelligence and personality in school children. Mol Cell Toxicol 6(1):19–23
Kumpiene J, Lagerkvist A, Maurice C (2008) Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using immobilization. Waste Manage 28:215–225
Laing GD, Meyer BD, Meers E, Lesage E, Moortel AVD, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2008) Metal accumulation in intertidal marshes: role of sulphide precipitation. Wetlands 28:735–746
Li A, Xin H (1996) Baiyangdian annals. Chinese Bookstore Press, China
Liu X, Xu M, Yang Z, Sun T, Cui B, Wang L, Wu D (2010) Sources and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Baiyangdian Lake, North China. J Environ Sci Health 45:413–420
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Marschner B, Kalbitz K (2003) Controls of bioavailability and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in soils. Geoderma 113:211–235
Mench M, Bussiere S, Boisson J, Castaing E, Vangronsveld J, Ruttents A, Koe TD, Bleeker P, Assuncao A, Manceau A (2003) Progress in remediation and revegetation of the barren Jales gold mine spoil after in situ treatments. Plant Soil 249:187–202
Mico C, Recatala L, Peris M, Sanchez J (2006) Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 65:863–872
NSMMC (National Standard Material Management Committee) (2010) Standard material directory of P.R.C. Chinese Measuring Press, Beijing
Opfer SE, Farver JR, Miner JG, Krieger K (2011) Heavy metals in sediments and uptake by burrowing mayflies in western Lake Erie basin. J Great Lakes Res 37(1):1–8
Öztürk M, Özözen G, Minareci O, Minareci E (2009) Determination of heavy metals in fish, water and sediments of Avsar dam lake in Turkey. Iran J Environ Health 6(2):73–80
Panda UCUY, Rath P, Bramha S, Sahu KC (2010) Application of factor analysis in geochemical speciation of heavy metals in the sediments of a Lake System-Chilika (India): a case study. J Coast Res 26:860–868
Paterson E, Sanka M, Clark L (1999) Urban soil as pollutant sinks—a case study from Aberdeen, Scotland. Appl Geochem 11:129–131
Pedersen F, Bjørnestad E, Andersen HV, Kjø HJ, Poll C (1998) Characterization of sediments from Copenhagen Harbour by use of biotests. Water Sci Technol 37:233–240
Pham NTT, Pulkownik A, Buckney RT (2007) Assessment of heavy metals in sediments and aquatic organisms in West Lake (Ho Tay), Hanoi, Vietnam. Lakes Reserv Res Manage 12(4):285–294
Qu W, Dickman M, Wang S (2001) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal and nutrient concentrations in sediments of Taihu Lake, China. Hydrobiologia 450:83–89
Ren H, Cui B, Bai J, Dong S, Hu B, Zhao H (2008) Distribution of heavy metal in paddy soil of Hani Terrace core zone and assessment on its potential ecological risk. Acta Ecol Sinica 28:1625–1634
Sakan SM, Đorđević DS, Manojlović DD, Predrag PS (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J Environ Manage 90:3382–3390
Satarug S, Moore MR (2004) Adverse health effects of chronic exposure to low-level cadmium in foodstuffs and cigarette smoke. Environ Health Perspect 112(10):1099–1103
SEPAC (State Environmental Protection Administration of China) (2004) The technical specification for soil environmental monitoring. HJ/T 166–2004. Environmental Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Shao X, Wu M, Jiang K (2007) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal elements in soils of Xixi wetland. Wetl Sci 5:253–259
Smith SL, MacDonald DD, Keenleyside KA, Ingersoll CG, Field LJ (1996) A preliminary evaluation of sediment quality assessment values for freshwater ecosystems. J Great Lakes Res 22:624–638
Stoeva N, Bineva T (2003) Oxidative changes and photosynthesis in Oat plants grown in As-contaminated soil. Bulg J Plant Physiol 29(1–2):87–95
Su L, Liu J, Christensen P (2011) Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of metals in sediments of Baiyangdian wetland ecosystem. Ecotoxicology 20(5):1107–1116
Sun Y, Zhou Q, Xie X, Liu R (2010) Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. J Hazard Mater 174:455–462
Szymanowska A, Samecka-Cymerman A, Kempers AJ (1999) Heavy metals in three lakes in West Poland. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 43(1):21–29
Tam NFY, Wong YS (1996) Retention and distribution of heavy metals in mangrove soils receiving wastewater. Environ Pollut 94:283–291
Türkmen A, Türkmen M, Tepe Y, Akyurt I (2005) Heavy metals in three commercially valuable fish species from Iskenderun Bay, Northern East Mediterranean Sea. Turk Food Chem 91:167–172
Uluturhan E, Kucuksezgin F (2007) Heavy metal contaminants in Red Pandora (Pagellus erythrinus) tissues from the Eastern Aegean Sea, Turkey. Water Res 41:1185–1192
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method and a proposed modification of the chromic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Wang W, Wang D, Yin C (2002) A field study on the hydrochemistry of land/inland water ecotones with reed domination. Acta Hydroch Hydrob 30:117–127
Wang L, Yin C, Wang W (2010) Sedimentary enzyme kinetics of land/water ecotones with reed domination. Clean Soil Air Water 38:194–201
Wise S, JP, Payne R, Wise SS, LaCerte C, Wise J, Gianios Jr. C, Douglas Thompson W, Perkins C, Zheng T, Zhu C, Benedict L, Kerr I (2009) A global assessment of chromium pollution using sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) as an indicator species. Chemosphere 75(11):1461–1467
Wu G, Kang H, Zhang X, Shao H, Chu L, Ruan C (2010) A critical review on the bio-removal of hazardous heavy metals from contaminated soils: issues, progress, eco-environmental concerns and opportunities. J Hazard Mater 174(1–3):1–8
Xu Q, Shi G (2000) The toxic effects of single Cd and interaction of Cd with Zn on some physiological index of [Oenanthe javanica (Blume) DC]. J Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science) 23(4):97–100 (In Chinese with English abstract)
Xu M, Zhu J, Huang Y, Gao Y, Zhang S, Tang Y, Yin C, Wang Z (1998) The ecological degradation and restoration of Baiyangdian Lake, China. J Freshw Ecol 13:433–446
Yang Z, Li G, Wang D, Cui H, Shang T (2005) Pollution and the potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment of Baiyangdian Lake. J Agro Environ Sci 24:945–951
Yi Y, Yang Z, Zhang S (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159(10):2575–2585
Yin H, Gao Y, Fan C (2011) Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from Lake Taihu, China. Environ Res Lett 6(4). doi:10.1088/1748-9326/6/4/044012
Yu H, Zhang WB, Yu JP (2011) Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in surface sediments of Hongze Lake. Environ Sci 32:437–444
Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H, Ouyang Y, Qiu B, Wu F, Zhang G (2001) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ Pollut 159:84–91
Zhang X, Guo H, Li H, Li J (2008) Distinguishing origins of elements in environmental geochemistry of Baiyangdian billabong of Hebei province. Earth Sci Front 15:90–96
Zhang H, Cui B, Xiao R, Zhao H (2010) Heavy metals in water, soils and plants in riparian wetlands in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Int Soc Enivron Inf Sci 2:1344–1354
Zheng G (2008) The vertical distribution regularity of heavy metal elements in Guanzhong Tier soil profile. Acta Geosci Sinica 29:109–115
Zhuang C, Ouyang Z, Xu W, Bai Y, Zhou W, Zheng H, Wang X (2011) Impacts of human activities on the hydrology of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Environ Earth Sci 62:1343–1350
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Science and Technology Major Water Project (No. 2009ZX07209-008-03), National Nature Science Foundation (No. 51179006), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NECT-10-0235) and the Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation (132009). The authors also thank Dr. G. Christokas for critical reading and valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, H., Bai, J., Xiao, R. et al. Levels, sources and risk assessment of trace elements in wetland soils of a typical shallow freshwater lake, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 27, 275–284 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0587-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0587-8