Abstract
Background
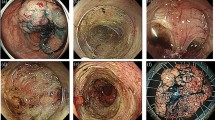
Colorectal laterally spreading tumours (LSTs) are classified into granular (LST-G) and non-granular (LST-NG) type; each type was sub-grouped into LST-G-H (homogenous) and LST-G-M (nodular mixed) type or LST-NG-F (flat elevated) and LST-NG-FD (pseudodepressed) type, respectively. We assessed the clinicopathological factors associated with clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for colorectal LSTs, and conducted follow-up after ESD.
Methods
ESD was performed in 196 patients with 204 LSTs that fulfilled the inclusion criteria for colorectal neoplasms. Clinical outcomes including resectability and curability of ESD and perforation were investigated, and factors related to the outcomes were analysed using logistic regression. One hundred thirty-eight patients received endoscopic follow-up for more than 12 months and metastatic surveys in 79 cases of cancerous LSTs.
Results
The incidence of submucosal cancer was lower in LST-G type. There were no significant differences in outcomes regarding LST macroscopic types. Overall en bloc, complete and curative resection, and perforation rates were 86.8%, 77.5%, 82.8% and 9.8%, respectively. Logistic regression analysis showed higher risk of non-curative resection in LST-G-M than in LST-G-H type. No other factors were associated with outcomes. During median follow-up of 35.5 months, no locally recurrent or metastatic tumours were observed, and overall survival was still 100%.
Conclusions
ESD provides acceptable resectability for colorectal LSTs by facilitating en bloc resection, irrespective of macroscopic types. The relatively long-term outcomes may be excellent, but further evaluation is needed for appropriate treatment strategy for each type of LST.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gotoda T, Kondo H, Ono H, Saito Y, Yamaguchi H, Saito D, Yokota T (1999) A new endoscopic mucosal resection procedure using an insulation-tipped electrosurgical knife for rectal flat lesions: report of two cases. Gastrointest Endosc 50:560–563
Ono H, Kondo H, Gotoda T, Shirao K, Yamaguchi H, Saito D, Hosokawa K, Shimoda T, Yoshida S (2001) Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer. Gut 48:225–229
Isomoto H, Shikuwa S, Yamaguchi N, Fukuda E, Ikeda K, Nishiyama H, Ohnita K, Mizuta Y, Shiozawa J, Kohno S (2009) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: a large-scale feasibility study. Gut 58:331–336
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Nakamura M, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Ono S, Kobayashi K, Hashimoto T, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Shimizu Y, Oka M, Ogura K, Kawabe T, Ichinose M, Omata M (2006) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for rectal epithelial neoplasia. Endoscopy 38:493–497
Tanaka S, Oka S, Kaneko I, Hirata M, Mouri R, Kanao H, Yoshida S, Chayama K (2007) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasia: possibility of standardization. Gastrointest Endosc 66:100–107
Tamegai Y, Saito Y, Masaki N, Hinohara C, Oshima T, Kogure E, Liu Y, Uemura N, Saito K (2007) Endoscopic submucosal dissection: a safe technique for colorectal tumors. Endoscopy 39:418–422
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, Kodashima S, Muraki Y, Ono S, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Oka M, Ogura K, Kawabe T, Ichinose M, Omata M (2007) Outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms in 200 consecutive cases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:678–683
Saito Y, Uraoka T, Matsuda T, Emura F, Ikehara H, Mashimo Y, Kikuchi T, Fu KI, Sano Y, Saito D (2007) Endoscopic treatment of large superficial colorectal tumors: a case series of 200 endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 66:966–973
Tanaka S, Oka S, Chayama K (2008) Colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection: present status and future perspective, including its differentiation from endoscopic mucosal resection. J Gastroenterol 43:641–651
Uraoka T, Saito Y, Matsuda T, Ikehara H, Gotoda T, Saito D, Fujii T (2006) Endoscopic indications for endoscopic mucosal resection of laterally spreading tumours in the colorectum. Gut 55:1592–1597
Kudo S, Kashida H, Tamura T, Kogure E, Imai Y, Yamano H, Hart AR (2000) Colonoscopic diagnosis and management of nonpolypoid early colorectal cancer. World J Surg 24:1081–1090
Kudo S, Shimoda R, Kashida H (2005) Laterally spreading tumor of colon: definition and history (in Japanese with English abstract). Stomach Intestine 40:1721–1725
Tanaka S, Haruma K, Oka S, Takahashi R, Kunihiro M, Kitadai Y, Yoshihara M, Shimamoto F, Chayama K (2001) Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm. Gastrointest Endosc 54:62–66
Hiraoka S, Kato J, Tatsukawa M, Harada K, Fujita H, Morikawa T, Shiraha H, Shiratori Y (2006) Laterally spreading type of colorectal adenoma exhibits a unique methylation phenotype and K-ras mutations. Gastroenterology 131:379–389
Oda I, Gotoda T, Hamanaka H (2005) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: technical feasibility, operation time and complications from a large consecutive series. Dig Endosc 17:54–58
Schlemper RJ, Riddell RH, Kato Y, Borchard F, Cooper HS, Dawsey SM, Dixon MF, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Fléjou JF, Geboes K, Hattori T, Hirota T, Itabashi M, Iwafuchi M, Iwashita A, Kim YI, Kirchner T, Klimpfinger M, Koike M, Lauwers GY, Lewin KJ, Oberhuber G, Offner F, Price AB, Rubio CA, Shimizu M, Shimoda T, Sipponen P, Solcia E, Stolte M, Watanabe H, Yamabe H (2000) The Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia. Gut 47:251–255
Hurlstone DP, Atkinson R, Sanders DS, Thomson M, Cross SS, Brown S (2007) Achieving R0 resection in the colorectum using endoscopic submucosal dissection. Br J Surg 94:1536–1542
Kudo SE, Kashida H (2005) Flat and depressed lesions of the colorectum. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3(Suppl 1):S33–S36
Hurlstone DP, Sanders DS, Cross SS, George R, Shorthouse AJ, Brown S (2005) A prospective analysis of extended endoscopic mucosal resection for large rectal villous adenomas: an alternative technique to transanal endoscopic microsurgery. Colorectal Dis 7:339–344
Disclosures
Authors Hitoshi Nishiyama, Hajime Isomoto, Naoyuki Yamaguchi, Hiroyuki Ishii, Eiichiro Fukuda, Haruhisa Machida, Takashi Nakamura, Ken Ohnita, Saburo Shikuwa, Shigeru Kohno and Kazuhiko Nakao have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Nishiyama, H. Isomoto, and N. Yamaguchi equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishiyama, H., Isomoto, H., Yamaguchi, N. et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for laterally spreading tumours of the colorectum in 200 consecutive cases. Surg Endosc 24, 2881–2887 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1071-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1071-5