Abstract
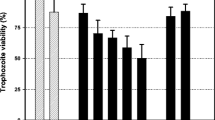
Trichomonas vaginalis is a flagellated protozoan that causes trichomonosis, the most prevalent non-viral STD worldwide. The pathogen has been associated with serious health consequences including predisposition to cervical cancer and adverse pregnancy outcomes and infertility. It also acts as a co-factor in HIV transmission and acquisition. The 5-nitroimidazole drugs are used in the treatment, however, treatment noncompliance is observed, and a growing number of T. vaginalis isolates resistant to the drugs have been related. Saponins are natural products possessing many biological activities such as antiprotozoan activity. The aim of this study was to evaluate the anti-T. vaginalis activity of saponins from Quillaja, Passiflora, and Ilex species. Saponins from Passiflora alata and Quillaja saponaria presented the best anti-T. vaginalis activity (MIC = 0.025%). In addition, all samples induced erythrocyte lysis and LDH release. As far as we know, this is the first report demonstrating the potential anti-T. vaginalis activity of these saponins.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebajo AC, Ayoola OF, Iwalewa EO, Akindahunsi AA, Omisore NOA, Adewunmi CO, Adenowo TK (2006) Anti-trichomonal, biochemical and toxicological activities of methanolic extract and some carbazole alkaloids isolated from the leaves of Murraya koenigii growing in Nigeria. Phytomedicine 13(4):246–254
Ali V, Nozaki T (2007) Current therapeutics, their problems, and sulfur-containing-amino-acid metabolism as a novel target against infections by “amitochondriate” protozoan parasites. Clin Microbiol Rev 20(1):164–187
Arthan D, Sithiprom S, Thima K, Limmatvatirat C, Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr P, Svasti J (2008) Inhibitory effects of Thai plants β-glycosides on Trichomonas vaginalis. Parasitol Res 103(2):443–448
Barbosa E, Calzada F, Campos R (2006) Antigiardial activity of methanolic extracts from Helianthemum glomeratum Lag. and Rubus coriifolius Focke in suckling mice CD-1. J Ethnopharmacol 108(3):395–397
Barbosa E, Calzada F, Campos R (2007) In vivo antigiardial activity of three flavonoids isolated of some medicinal plants used in Mexican traditional medicine for the treatment of diarrhea. J Ethnopharmacol 109(3):552–554
Basiglio CL, Sánchez Pozzi EJ, Mottino AD, Roma MG (2009) Differential effects of silymarin and its active component silibinin on plasma membrane stability and hepatocellular lysis. Chem-Biol Interact 179(2–3):297–303
Birk CD, Provensi G, Gosmann G (2005) TLC fingerprint of flavonoids and saponins from Passiflora species. J Liq Chrom Rel Technol 28:1–7
Borst P, Ouellette M (1995) New mechanisms of drug resistance in parasitic protozoa. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:427–460
Calzada F, Yépez-Mulia L, Aguilar A (2006) In vitro susceptibility of Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia lamblia to plants used in Mexican traditional medicine for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. J Ethnopharmacol 108(3):367–370
Coleman JJ, Okoli I, Tegos GP, Holson EB, Wagner FF, Hamblin MR, Mylonakis E (2010) Characterization of plant-derived saponin natural products against Candida albicans. ACS Chem Biol 5(3):321–332
Diamond LS (1957) The establishment of various Trichomonas of animals and man in axenic cultures. J Parasitol 43:488–490
Duarte M, Giordani RB, De Carli GA, Zuanazzi JA, Macedo AJ, Tasca T (2009) A quantitative resazurin assay to determinate the viability of Trichomonas vaginalis and the cytotoxicity of organic solvents and surfactant agents. Exp Parasitol 123(2):195–198
Fleck JD, Kauffmann C, Spilki F, Lencina CL, Roehe PM, Gosmann G (2006) Adjuvant activity of Quillaja brasiliensis saponins on the immune responses to bovine herpesvirus type 1 in mice. Vaccine 24:7129–7134
Gauthier C, Legault J, Girard-Lalancette K, Mshvildadze V, Pichette A (2009) Haemolytic activity, cytotoxicity and membrane cell permeabilization of semi-synthetic and natural lupane- and oleanane-type saponins. Bioorg Med Chem 17(5):2002–2008
Gluçu-Ustundag O, Mazza G (2007) Saponins: properties, applications and processing. Crit Rev Food Sci 47(3):231–258
González-Coloma A, Reina M, Sáenz C, Lacret R, Ruiz-Mesia L, Arán VJ, Sanz J, Martínez-Díaz RA (2011) Antileishmanial, antitrypanosomal, and cytotoxic screening of ethnopharmacologically selected Peruvian plants. Parasitol Res. doi:10.1007/s00436-011-2638-3
Gosmann G, Guillaume D, Taketa ATC, Schenkel EP (1995) Triterpenoid saponins from Ilex paraguariensis. J Nat Prod 58(3):438–441
Hostettmann K, Marston A (1995) Saponins. Cambridge University Press, New York
Kauffmann C, Machado AM, Fleck JD, Provensi G, Pires VS, Guillaume D, Sonnet P, Reginatto FH, Schenkel EP, Gosmann G (2004) Constituents from leaves of Quillaja brasiliensis. Nat Prod Res 18(2):153–157
Lumsden WHR, Robertson DHH, Heyworth R, Harrison C (1988) Treatment failure in Trichomonas vaginalis vaginitis. Genitourin Med 64:217–218
Mendes-Silva W, Assafim M, Ruta B, Monteiro RQ, Guimarães JA, Zingali RB (2003) Antithrombotic effect of glycyrrhizin, a plant-derived thrombin inhibitor. Thromb Res 112(1–2):93–98
Oda K, Matsuda H, Murakami T, Katayama S, Ohgitani T, Yoshikawa M (2000) Adjuvant and haemolytic activities of 47 saponins derived from medicinal and food plants. Biol Chem 381(1):67–74
Petrin D, Delgaty K, Bhatt R, Garber G (1998) Clinical and microbiological aspects of Trichomonas vaginalis. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:300–317
Reginatto FH, Kauffmann C, Schripsema J, Guillaume D, Gosmann G, Schenkel EP (2001) Steroidal and triterpenoidal glucosides from Passiflora alata. J Brazil Chem Soc 12:32–36
Ródio C, da Rocha VD, Kowalski K, Panatieri L, von Poser G, Rott M (2008) In vitro evaluation of the amebicidal activity of Pterocaulon polystachyum (Asteraceae) against trophozoites of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Parasitol Res 104(1):191–194
Schenkel EP, Gosmann G, Montanha JA, Heizmann BM, Athayde ML, Taketa ATC, Pires VS, Guillaume D (1997) Saponins from maté (Ilex paraguariensis) and other South American Ilex species: ten years research on Ilex saponins. Cienc Cult 49:359–363
Sun Y, Tong H, Li M, Li Y, Guan S, Liu J (2008) Immunological adjuvant effect of Japanese ginseng saponins (JGS) on specific antibody and cellular response to ovalbumin and its haemolytic activities. Vaccine 26(47):5911–5917
Tiwari P, Singh D, Singh MM (2008) Anti-Trichomonas activity of Sapindus saponins, a candidate for development as microbicidal contraceptive. J Antimicrob Chemoth 62(3):526–534
Van Der Pol B, Kwok C, Pierre-Louis B, Rinaldi A, Salata Robert A, Chen P-L, van de Wijgert J, Mmiro F, Mugerwa R, Chipato T, Morrison CS (2008) Trichomonas vaginalis infection and human immunodeficiency virus acquisition in African women. J Infect Dis 197(4):548–554
Vermeersch M, Foubert K, Luz RLd, Puyvelde LV, Pieters L, Cos P, Maes L (2009) Selective antileishmania activity of 13,28-epoxy-oleanane and related triterpene saponins from the plant families Myrsinaceae, Primulaceae, Aceraceae and Icacinaceae. Phytother Res 23(10):1404–1410
World Health Organization (2010) Towards universal access. Progress Report 2010. www.who.int/hiv/pub/2010progressreport/full_report_en.pdf. Accessed 05 Jul 2011
Xiao X, Bai P, Bui Nguyen TM, Xiao J, Liu S, Yang G, Hu L, Chen X, Zhang X, Liu J, Wang H (2009) The antitumoral effect of Paris Saponin I associated with the induction of apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. Mol Cancer Ther 8(5):1179–1188
Acknowledgements
The authors thank CNPq and CAPES (Brazil) for fellowships and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tábitha Dahmer Rocha and Patrícia de Brum Vieira contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocha, T.D., de Brum Vieira, P., Gnoatto, S.C.B. et al. Anti-Trichomonas vaginalis activity of saponins from Quillaja, Passiflora, and Ilex species. Parasitol Res 110, 2551–2556 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2798-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2798-1