Abstract.
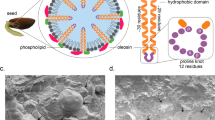
The oleosins are a group of hydrophobic proteins present on the surface of oil bodies in seeds, where they are thought to prevent coalescence. They contain a central hydrophobic domain of 68–74 residues that is thought to form a loop into the triacylglycerol matrix of the oil body, but the conformation adopted by this sequence is uncertain. We have therefore expressed an oleosin cDNA from sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) in Escherichia coli as a fusion with maltose-binding protein (MBP) and isolated a peptide corresponding to the hydrophobic domain by sequential digestion with factor Xa (to remove the MBP) followed by trypsin and Staphylococcus V8 protease to remove the N- and C-terminal domains of the oleosin. Circular dichroism spectroscopy of the peptide in two solvent systems chosen to mimic the environment within the oil body (trifluoroethanol and SDS) demonstrated high proportions of α-helical structure, with no β-sheet. A model was therefore developed in which the domain forms an α-helical hairpin structure, the two helices being separated by a turn region. We consider that this model is consistent with our current knowledge of oleosin structure and properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexander, L.G., Sessions, R.B., Clarke, A.R. et al. Characterization and modelling of the hydrophobic domain of a sunflower oleosin. Planta 214, 546–551 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250100655
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250100655