Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the accuracy of MRI using pelvic-phased-array and endocavitary coils in detecting intestinal wall invasion by an endometriotic nodule.
Materials and methods
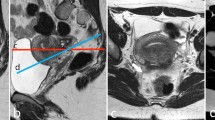
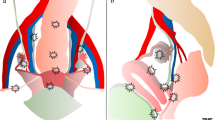
Forty-seven patients (32.1 ± 4.2 years) who were planned for a surgical cure of deep endometriosis underwent MRI with conventional sequences using both coils. A thin bright layer on T2-w with enhancement on post-Gd T1-w defined our MR pattern for muscular layer involvement. MR results were correlated with surgical and pathological findings of the removed nodule.
Results
MR results for Group 1 (both coils) achieved a sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy of 100–63%, 96–92%, 90–70%, 100–85%, and 97–83% for endovaginal coil and phased-array coil, respectively. Group 2 (phased-array coil) had a sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy of 73%, 93%, 84%, 88%, and 87% for this coil, respectively.
Conclusion
Combined pelvic-phased-array and endovaginal coils are better than phased array alone in the detection of intestinal wall invasion. Easy to perform, it has to be considered as a preoperative staging for deep posterior endometriosis to orientate the surgical management.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olive DL, Schwartz LB (1993) Endometriosis. N Engl J Med 328:1759–1769
Clement M (2002) Disease of the peritoneum (including endometriosis). In: Kurmann R, (ed). Blaustein’s pathology of the female genital tract. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp 729–789
Koninckx PR, Martin D (1994) Treatment of deeply infiltrating endometriosis. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 6:231–241
Kinkel K, Chapron C, Balleyguier C et al (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of deep endometriosis. Hum Reprod 14:1080–1086
Bazot M, Thomassin I, Hourani R et al (2004) Diagnostic accuracy of transvaginal sonography for deep pelvic endometriosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 24:180–185
Kataoka ML, Togashi K, Yamaoka T et al (2005) Posterior cul-de-sac obliteration associated with endometriosis: MR imaging evaluation. Radiology 234:815–823
Togashi K (2002) MR imaging in obstetrics and gynecology. Nippon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 62:7–16
Katayama M, Masui T, Kobayashi S et al (2001) Evaluation of pelvic adhesions using multiphase and multislice MR imaging with kinematic display. Am J Roentgenol 177:107–110
Hoeffel CC, Azizi L, Mourra N et al (2006) MRI of rectal disorders. Am J Roentgenol 187:W275–284
Vigano P, Parazzini F, Somigliana E et al (2004) Endometriosis: epidemiology and aetiological factors. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 18:177–200
Schindler AE (2004) Pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Minerva Ginecol 56:419–435
Cornillie FJ, Oosterlynck D, Lauweryns JM et al (1990) Deeply infiltrating pelvic endometriosis: histology and clinical significance. Fertil Steril 53:978–983
Del Frate C, Girometti R, Pittino M et al (2006) Deep retroperitoneal pelvic endometriosis: MR imaging appearance with laparoscopic correlation. Radiographics 26:1705–1718
Chapron C, Boucher E, Fauconnier A et al (2002) Anatomopathological lesions of bladder endometriosis are heterogeneous. Fertil Steril 78:740–742
Kinkel K, Frei KA, Balleyguier C et al (2006) Diagnosis of endometriosis with imaging: a review. Eur Radiol 16:285–298
Redwine DB (1987) The distribution of endometriosis in the pelvis by age groups and fertility. Fertil Steril 47:173–175
Chapron C, Dumontier I, Dousset B et al (1998) Results and role of rectal endoscopic ultrasonography for patients with deep pelvic endometriosis. Hum Reprod 13:2266–2270
Sampson J (1921) Perforating hemorrhagic (chocolate) cyst of the ovary: their importance and especially their relation to pelvic adenomas of endometrial type (“adenomyoma of the uterus, rectovaginal septum, sigmoid, etc”). Archiv Surg 3:245–323
Bazot M, Detchev R, Cortez A et al (2003) Transvaginal sonography and rectal endoscopic sonography for the assessment of pelvic endometriosis: a preliminary comparison. Hum Reprod 18:1686–1692
Chapron C, Fauconnier A, Vieira M et al (2003) Anatomical distribution of deeply infiltrating endometriosis: surgical implications and proposition for a classification. Hum Reprod 18:157–161
Cullen T (1914) Adenomyoma of the rectovaginal septum. JAMA 62:835–839
Hoogeveen M, Dorr PJ, Puylaert JB (2003) Endometriosis of the rectovaginal septum: endovaginal US and MRI findings in two cases. Abdom Imaging 28:897–901
Nisolle M, Donnez J (1997) Peritoneal endometriosis, ovarian endometriosis, and adenomyotic nodules of the rectovaginal septum are three different entities. Fertil Steril 68:585–596
Donnez J, Nisolle M, Gillerot S et al (1997) Rectovaginal septum adenomyotic nodules: a series of 500 cases. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 104:1014–1018
Eguchi S, Komuta K, Haraguchi M et al (2000) MRI facilitated a diagnosis of endometriosis of the rectum. J Gastroenterol 35:784–788
Bazot M, Nassar J, Darai E et al (2005) Value of sonography and MR imaging for the evaluation of deep pelvic endometriosis. J Radiol 86:461–467
Carbognin G, Guarise A, Minelli L et al (2004) Pelvic endometriosis: US AND MRI features. Abdom Imaging 29:609–618
Zanardi R, Del Frate C, Zuiani C et al (2003) Staging of pelvic endometriosis based on MRI findings versus laparoscopic classification according to the American Fertility Society. Abdom Imaging 28:733–742
Thomassin I, Bazot M, Detchev R et al (2004) Symptoms before and after surgical removal of colorectal endometriosis that are assessed by magnetic resonance imaging and rectal endoscopic sonography. Am J Obstet Gynecol 190:1264–1271
Puglielli E, Di Cesare E, Masciocchi C (2004) Rectal endometriosis: MRI study with rectal coil. Eur Radiol 14:2362–2363
Stollfuss JC, Becker K, Sendler A et al (2006) Rectal carcinoma: high-spatial-resolution MR imaging and T2 quantification in rectal cancer specimens. Radiology 241:132–141
Tran KT, Kuijpers HC, Willemsen WN et al (1996) Surgical treatment of symptomatic rectosigmoid endometriosis. Eur J Surg 162:139–141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, C., Balzan, C., Thoma, V. et al. Efficiency of MR imaging to orientate surgical treatment of posterior deep pelvic endometriosis. Abdom Imaging 34, 251–259 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-008-9367-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-008-9367-9