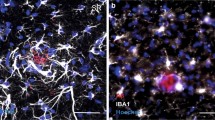
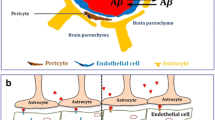
Abstract
Alzheimer disease (AD) is a major cause of dementia. Several mechanisms have been postulated to explain its pathogenesis, beta-amyloid (Aß toxicity, cholinergic, dysfunction, Tau hyperphosphorylation, oxidative damage, synaptic dysfunction and inflammation secondary to senile plaques, among others. Glial cells are the major producers of inflammatory mediators, and cytotoxic activation of glial cells is linked to several neurodegenerative diseases; however, whether inflammation is a consequence or the cause of neurodegeneration is still unclear. I propose that inflammation and cellular stress associated with aging are key events in the development of AD through the induction of glial dysfunction. Dysregulated inflammatory response can elicit glial cell activation by compounds which are normally poorly reactive. Inflammation can also be the major cause of defective handling of Aß and the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Here I review evidence that support the proposal that dysfunctional glia and the resulting neuroinflammation can explain many features of AD. Evidence supports the notion that damage caused by inflammation is not only a primary cause of neurodegeneration but also an inducer for the accumulation of Aß in AD. Dysfunctional glia can result in im paired neuronal function in AD, as well as in many progressive neurodegenerative disorders. We show that microglial cell activation is enhanced under pro-inflammatory conditions, indicating that glial cell responses to Aß related proteins can be critically dependent on the priming of glial cells by pro-inflammatory factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramov AY, L Canevari and MR Duchen (2003) Changes in intracellular calcium and glutathione in astrocytes as the primary mechanism of amyloid neurotoxicity.J. Neurosci. 23, 5088–5095.
Akama KT, C Albanese, RG Pestell and CJ Van Eldik, (1998) Amyloid ß-peptide stimulates nitric oxide production in astrocytes through an NFkB-dependent mechanism.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 95, 5795–5800.
Akiyama H, S Barger, S Barnmm, B Bradt, J Bauer, GM Cle, NR Cooper, P Eikelenboom, M Emmerling, BL Fiebich, CE Finch, S Frautschy, WST Griffin, H Hampel, M Hull, G Landreth, L Lue, R Mrak, IR Mackenzie P McGeer, MK O’Banion, J Pachter, G Pasinetti, C Plata-Salaman, J Rogers, R Rydel, Y Shen, W Streit, R Strohmeyer, I Tooyoma, F Van Muiswinkel, R Veerhuis, S Walker, B Wegrzyniak G Wenk and T Wyss-Coray (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 21, 383–421.
Alarcón R, C Fuenzalida, M Santibañez and R von Bernhardi (2005) Expression of Scavenger Receptors in glial cells: comparing the adhesion of astrocytes and microglia from neonatal rats to surface-bound ß-amyloid.J. Biol. Chem. 280, 30406–30415.
Apelt J and R Schliebs (2001) Beta-amyloid-induced glial expression of both pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines in cerebral cortex of aged transgenic Tg2576 mice with Alzheimer plaque pathology.Brain Res. 894, 21–30.
Arnett HA, J Masson, M Marino, K Suzuki, GK Matsushima and JPY Ting (2001) TNFα, promotes proliferation of oligoden drocyte progenitors and remyelinization.Nat. Neurosci. 4, 1116–1121.
Arnett HA, Y Wang, GK Matsushima, K Suzuki and JPY Ting (2003) Functional genomic analysis of remyelination reveals importance of inflammation in oligodendrocytes regeneration.J. Neurosci. 23, 9824–9832.
Avital A, I Goshen, A Kamsler, M Segal, K Iverfeldt, G Richter-Levin and R Yirmiya (2003) Impaired interleukin-1 signaling is associated with deficits in hippocampal memory processes and neural plasticity.Hippocampus 13, 826–834.
Bal-Price A and C Brown (2001) Inflammatory neuro degeneration mediated by nitric oxide from activated glia-inhibiting neuronal respiration, causing glutamate release and excitotoxicity.J. Neurosci. 17, 6480–6491.
Barger SW, D Hörster, K Furukawa, Y Goodman, J Krieglstein and MP Mattson (1995) Tumor necrosis factors α and β protect neurons against amyloid ß-peptide toxicity: evidence for involvement of a κB-binding factor and attenuation of peroxide and Ca2+ accumulation.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9328–9332.
Basu A, J Krady and S Levinson (2004) Interleukin-1: a master regulator of neuroinflammation.J. Neurosci. Res. 78, 151–156.
Bell MD, R Lopez-Gonzalez, L Lawson, D Hughes, I Fraser, S Gordon, and VH Perry (1994) Upregulation of the macrophage scavenger receptor in response to different forms of injury in the CNS.J. Neurocytol. 23, 605–613.
Benzing WC, JR Wujek, EK Ward, D Ward, D Shaffer, KH Ashe, SG Youkin and KR Brunden (1999) Evidence for glial-mediated inflammation in aged APP (SW) transgenic mice.Neurobiol. Aging 20, 581–589.
Blasko I, F Marx, E Steiner, T Hartmann and B Grubeck-Loebenstein (1999) TNFα plus IFNψ induce the production of Alzheimer ß-amyloid peptides and decrease the secretion of APPs.FASEB J. 13, 63–68.
Blondel O, C Collin, WJ McCarran, S Zhu, R Zamostiano, I Gozes, DE Brenneman and RD McKay (2000) A glia-derived signal regulating neuronal differentiation.,J. Neurosci. 20, 8012–8020.
Broe GA, DA Grayson, HM Creasey, LM Waite, BJ Casey, HP Bennett, WS Brooks and GM Halliday (2000) Antiinflammatory drugs protect against. Alzheimer’s disease at low doses.Arch. Neurol. 57, 1586–1591.
Brown DR (1999) Dependence of neurones on astrocytes in a co-culture system renders neurones sensitive to transforming growth factor ß1-induced glutamate toxicity.J. Neurochem. 72, 943–953.
Butterfield DA, A Castegna, CM Lauderback and J Drake (2002) Evidence that amyloid ß-peptide-induced lipid peroxidation and its sequelae in Alzheimer’s disease brain contribute to neuronal death.Neurobiol. Aging 23, 655–664.
Cagnin A, DJ Brooks, AM Kennedy, RN Gunn, R Myers, FE Rurkheimer, T Jones and RB Banati (2001)In vivo measurement of activated microglia in dementia.Lancet 358, 461–467.
Canevari L, AY Abramov and MR Duchen (2004) Toxicity of amyloid-ß peptide: tales of calcium, mitochondria, and oxidative stress.Neurochem. Res. 29, 637–650.
Chapman PF, GL White, MW Jones, D Cooper-Blacketer, VJ Marshall, M Irizarry, L Younkin, MA Good, TV Bliss BT Hyman, SG Younkin and KK Hsiao (1999) Impaired synaptic plasticity and learning in aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice.Nat. Neurosci. 2, 271–276.
Chen GJ, J Xu, SA Lahousse, NL Caggiano and SM de la Monte (2003) Transient hypoxia causes Alzheimer-type molecular biochemical abnormalities in cortical neurons: potential strategies for neuroprotection.J Alzhemer’s Dis. 5, 209–228.
Chen J, Y Zhou, S Mueller-Steiner, L-F Chen, H Kwon, S Yi, L Mucke and L Gan (2005) SIRT1 protects against microglia-dependent amyloid-ß toxicity through inhibiting NF-κB signaling.J. Biol. Chem. 280, 40364–40374.
Cheng B, S Christakos and MP Mattson (1994) Tumor necrosis factors protect neurons against metabolic-excitotoxic insults and promote maintenance of calcium homeostasis.Neuron 12, 130–153.
Choi J, CA Malakowsky, JM Talent, CC Conrad, CA Carroll, ST Weintraub and RW Gracy (2003) Anti-apoptotic proteins are oxidized by Aβ25–35 in Alzheimer’s fibroblastsBiochim. Biophys. Acta 1637, 135–141.
Christie, RH, M Freeman and BT Hyman (1996) Expression of the macrophage scavenger receptor, a multifunctional lipoprotein receptor, in microglia associated with senile plaques in Alzheimer’s disease.Am. J. Pathol. 148, 399–403.
Colangelo V, J Schurr, MJ Ball, RP Pelaez, NG Bazan and WJ Lukiw (2002) Gene expression profiling of 12633 genes in Alzheimer hippocampal CA1: transcription and neurotrophic factor down-regulation and up-regulation of apoptotic and pro-inflammatory signaling.J. Neurosci. Res. 70, 462–473.
Combs CK, JC Karlo, S-C Kao and GE Landreth (2001) ß-Amyloid stimulation of microglia and monocytes results in TNFα-dependent expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and neuronal apoptosis.J. Neurosci. 21, 1179–1188.
Coraci IS, J Husemann, JW Berman, C Hulette, JH Dufour, GK Campanella, AD Luster, SC Silverstein and JB El Khoury (2002) CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, is expressed on microglia in Alzheimer’s disease brains and can mediate production of reactive oxygen species in response to ß-amyloid fibrils.Am. J. Pathol. 160, 101–112.
D’Andrea MR, GM Cole and MD Ard (2004) The microglial phagocytic role with specific plaque types in the Alzheimer disease brain.Neurobiol. Aging 25, 675–683.
De Kosky ST, SD Styren, ME O’Malley, JR Gross, P Kochanek, D Marion, CH Evans and PD Robbins (1996), Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist suppresses neurotrophin response in injured rat brain.Ann. Neurol. 39, 123–127.
de la Torre JC (2002) Alzheimer’s disease as a vascular disorder: nosological evidence.Stroke 33, 1152–1162.
De Sampaio E, TC Spohr, R Martinez, EF da Silva, VM Neto and FC Gomez (2002) Neuro-glia interaction effects on GFAP gene: a novel role for TGBß1.Eur. J. Neurosci. 16, 2059–2069.
De Witt DA, G Perry, M Cohen, C Doller and J Silver (1998) Astrocytes regulate microglial phagocytosis of senile plaque cores of Alzheimer’s disease.Exp. Neurol 149, 329–340.
Dhandapani KM, M Hadman, L De Sevilla, MF Wade, VB Mahesh and DW Brann (2003) Astrocyte protection of neurons. Role of transforming growth factor-ß signaling via c-jun-Ap-1 protective pathway.J. Biol. Chem. 278, 43329–43339.
Dickson DW (1997) The pathogenesis of senile plaques.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 56, 321–339.
Duyckaerts C, MA Colle, F Dessi, Y Crignon, F Piette and JJ Hauw (1998) The progression of the lesions in Alzheimerdisease — insights from a prospective clinicopathological study.J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 53, 119–126.
Dziedzic T, I Wybranska, A Dembinska-Kiec, A Klimkowicz, A Slowik, J Pankiewicz, A Adzienicka and A Szczudlik (2003) Dexamethasone inhibits TNF-α synthesis more effectively in Alzheimer’s disease patients than in healthy individuals.Dement. Geriatr: Cogn. Disord. 16, 283–286.
Eikelenboom P and WA van Gool (2004) Neuroinflammatory perspectives on the two faces of Alzheimer’s disease.,J. Neural Transm. 111, 281–294.
Eikelenboom P, C Bate, WA Van Gool, JJM Hoozemans, JM Rozemuller, R Veerhuis and A Williams (2002) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and Prion disease.Glia 40, 232–239.
El Khoury JB, KJ Moore, TK Means, J Leung, K Terada, M Toft, MW Freeman and AD Luster (2003) CD36 mediates the innate response to ß-amyloid.J. Exp. Med. 197, 1657–1666.
Eriksen JL, SA Sagi, TE Smith, S Weggen, P Das, DC McLendon, W Ozols, KW Jessing, KH Zavitz, EH Koo and TE Golde (2003) NSAIDs and enantiomers of flurbiprofen target ψ-secretase and lower Aß42 in vivo.J. Clin. Invest. 112, 440–449.
Etminan M, S Gill and A Samii (2003) Effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on risk of Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.BMJ 327, 128–131.
Eyüpoglu LY, L Bechmann and R Nitsch (2003) Modification of microglial function protects from lesion-induced neuronal alteration and promotes sprouting in the hippocampus.FASEB J. 17, 1110–1111.
Farkas E, GI De Jong, RA de Vos, EN Jansen Steur and PG Luiten (2000) Pathological features of cerebral cortical capillaries are doubled in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.Acta Neurophathol. (Berl.) 100, 395–402.
Farrer LA, LA Cupples, JL Haines, B Hyman, WA Kukull, R Mayeux, RH Myers, MA Pericak-Vance, N Risch and CM van Duijn (1997) Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer’s disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer’s disease Meta Analysis Consortium.JAMA 278, 1349–1356.
Flanders KC, RF Ren and CF Lippa (1998) Transforming growth factor-betas in neurodegenerative disease.Prog. Neurobiol. 54, 71–85.
Forloni G, F Mangiarotti, N Angeretti, E Lucca and MG De Simoni (1997) ß-Amyloid fragment potentiates IL-6 and TNF-α secretion by LPS in astrocytes but not in microglia,Cytokine 9, 759–762.
Fu C, DJ Chute, ES Farag, J Garakian, JL Cummings and HV Vinters (2004) Comorbidity in dementia: an autopsy study.Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 128, 32–38.
Geula C, CK Wu, D Saroff, A Lorenzo, M Yuan and BA Yankner (1998) Aging renders the brain vulnerable to amyloid ß-protein neurotoxicity.Nat. Med. 4, 827–831.
Giulian D and M Corpuz (1993) Microglial secretion products and their impact on the nervous system.Adv. Neurol. 59, 315–320.
Giulian D, K Vaca and M Corpuz (1993) Brain glia release factors with opposing actions upon neuronal survival.J. Neurosci. 13, 29–37.
Goldgaber D, HW Harris, T Hla, T Maciag, RJ Donnelly, JS Jacobsen, MP Vitek and DC Gajdusek (1989). Interleukin 1 regulates synthesis of amyloid ß-protein precursor mRNA in human endothelial cells.Proc. Natl., Acad. Sci. USA 86, 7606–7610.
Griffin WS and RE Mrak (2002) Interleukin-1 in the genesis and progression of and risk for development of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease.J. Leukoc. Biol. 72, 233–238.
Griffin WS, JG Sheng, SM Gentleman, DI Graham, RE Mrak and GW Roberts (1994) Microglial interleukin-1α expression in human head injury: correlations with neuronal and neuritic ß-amyloid precursor protein expression.Neurosci. Lett. 176, 133–136.
Griffin R, R Nally, Y Nolan, Y McCartney, J Linden and MA Lynch (2006) The age-related attenuation in long-term potentiation is associated with microglial activation.J. Neurochem. 99, 1263–1272.
Gylys KH, JA Fein, F Yang, DJ Willey, CA Miller and GM Cole (2004) Synaptic changes in Alzheimer’s disease: increased amyloid-ß and gliosis in suiviving terninals is accompanied by decreased PSD-95 fluorescence.Am. J. Pathol. 165, 1809–1817.
Haass C (2004) Take five-BACE and the γ-secretase quartet conducts Alzheimer’s amyloid β-peptide generation.EMBO J 23, 483–488.
Hanisch UK (2002) Microglia as a source and target of cytokines.Glia 40, 140–155.
Harkany T, I Abraham, C Konva, C Nyakas, M Zarandi, B Penke and PG Lutten (2000) Mechanism of β-amyloid neurotoxicity perspectives of pharmacotherapy.Rev. Neurosci. 11, 329–382.
Hashioka S, A Monji, T Ueda, S Kanba and H Nakanishi (2005) Amyloid-β fibril formation is not necessarily required for microglial activation by the peptidesNeurochem. Int. 47, 369–376.
Hauss-Wegrzyniak B, L Lukovic, M Bigaud and ME Stoeckel (1998) Brain inflammatory response induced by intiacerebroventricular infusion of lipopolysaccharide: an immunohistochemical study.Brain Res. 794, 211–224.
Herrera-Molina R and R von Bernhardi (2005) Transforming growth factor-β1 produced by hippocampal cells modulates glial reactivity in culture.Neurobiol. Dis. 19, 229–236.
Herx, LM, S Rivest and VW Yong (2000) Central nervous system-initiated inflammation and neurotrophism in trauma: IL-1β is required for the production of ciliary neurotrophic factor.J. Immunol. 165, 2232–1239.
Ho L, D Purohit, V Haroutinian, JD Luterman, F Willis, J Naslund, JD Buxbaum, RC Mohs, PS Aisen and GM Pasinetti (2001) Neuronal cyclooxigenase 2 expression in the hippocampal formation as a function of the clinical progression of Alzheimer disease.Arch. Neurol. 58, 487–492.
Hock C, K Heese, C Hulette, C Rosenberg and U Otten (2000) Region-specific neurotrophin imbalances in Alzheimer disease: decreased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and increased levels of nerve growth factor in hippocampus and cortical areas.Arch. Neurol. 57, 846–851.
Hofmann MA, S Drury, C Fu, W Qu, A Taguchi, YT Lu, C Avila, N Kambham, A Bierhaus, P Nawroth, MF Neurath, T Slattery, D Beach, J McClary, M Nagashima, J Morser, D Stern and AM Schmidt (1999) RAGE mediates a novel proinflammatory axis: a central cell surface receptor for S100/calgranulin polypeptides.Cell 97, 889–901.
Hsu H-Y, S-L Chiu, M-H Wen, K-Y Chen and K-F Hua (2001) Ligands of macrophage scavenger receptor induce cytokine expression via differential modulation of protein kinase signaling pathways.J. Biol. Chem. 276, 28719–28730.
Hu J and LJ Van Eldik (1999) Glial-derived proteins activate cultured astrocytes and enhance β-amyloid-induced glial activation.Brain Res. 842, 46–54.
Hu J, K Akama, G Krafft, B Chromy and L Van Eldik (1998) Amyloid-β peptide activates cultured astrocytes: morphological alterations, cytokine induction and nitric oxide release.Brain Res. 785, 195–206.
Husemann J and SC Silverstein (2001) Expression of scavenger receptor class B, type I, by astrocytes and vascular smooth muscle cells in normal adult mouse and human brain and in Alzheimer’s disease brain.Am. J. Pathol. 158, 825–832.
Husemann J, JD Loike, R Anankov, M Febbraio and SC Silverstein (2002) Scavenger receptors in neurobiology and neuropathology: their role on microglia and other cells of the nervous system.Glia 40, 195–205.
Ishii K, F Muelhauser, U Lieb, M Picard, S Kuhl, B Penke, T Bayer, M Weissler, M Hennerici, K Beyreuther, T Hartmann and K Fassbender (2000) Subacute NO generation induced by Alzheimer’s β-amyloid in the living brain: reversal by inhibition of the inducible NO synthase.FASEB J. 14, 1485–1489.
Itzhaki RF, MA Wozniak, DM Appelt and BJ Balin (2004) Infiltration of the brain by pathogens causes Alzheiner’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 25, 619–627.
Kalaria RN, SU Batí, WD Lust and G Perry (1993) The amyloid precursor protein in ischemic brain injury and chronic hypoperfusion.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 695, 190–193.
Kamenetz F, T Tomita, H Hsieh, G Seabrook, D Borchelt, T Iwatsubo, S Sisodia and R Malinow (2003) APP processing and synaptic function.Neuron 37, 925–937.
Katsel PL, KL Davis and V Haroutunian (2005) Large-scale microarray studies of gene expression in multiple regions of the brain in schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease.Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 63, 41–82.
Kayed R, E Head, JL Thompson, TM McIntire, SC Milton, CW Cotman and CG Glabe (2003) Common structure of soluble amyloid oligomers implies common mechanism of pathogenesis.Science 300, 486–489.
Kirchhoff F, R Dringen and C Giaume (2001) Pathways of neuron-astrocyte interactions and their possible role in neuroprotection.Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 251, 158–169.
Knopman DS, JE Parisi, A Salviati, M Floriach-Robert, BF Boeve, RJ Ivnik, GE Smith, DW Dickson, KA Johnson, LE Petersen, WC McDonald, H Braak and RC Petersen (2003) Neuropathology of cognitively normal elderly.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 62, 1087–1095.
Kolsch H, U Ptok, M Bagli, A Papassotiropoulos, S Schmitz, K Barkow, M Kockler, ML Rao, W Maier and R Heun (2001) Gene polymorphisms of interleukin-1α influence the course of Alzheimer’s disease.Ann. Neurol. 49, 818–819.
Krupinski J, P Kumar, S Kumar and J Kaluza (1996) Increased expression of TGF-β1 in brain tissue after ischemic stroke in humans.Stroke 27, 852–857.
Kukull WA and JD Bowen (2002) Dementia epidemiology.Med. Clin. North Am. 86, 573–590.
Lambert MP, AK Barlow, BA Chromy, C Edwards, R Freeds, M Liosatos, TE Morgan, L Rozovsky, B Trommer, KL Viola, P Wals, C Zhang, CE Finch, GA Krafft and WL Klein (1998) Diffusible, nonfibrillar ligands derived from Aβ1–42 are potent central nervous system neurotoxins.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6448–6453.
Lim GP, F Yang, T Chu, P Chen, W Beech, B Teter, T Tran, O Ubeda, K Hsiao Ashe, SA Frautschy and GM Cole (2000) Ibuprofen suppresses plaque pathology and inflammation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.J. Neurosci. 20, 5709–5714.
Liu Y, R Dargusch and D Schubert (1997) β-Amyloid toxicity does not require RAGE protein.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comman. 237, 37–40.
Lovell MA, SP Gabbita and WR Markesbery (1999) Increased DNA oxidation and decreased levels of repair products in Alzheimer’s disease ventricular CSF.J. Neurochem. 72, 771–776.
Lovell MA, C Xie and WR Markesbery (2001) Acrolein is increased in Alzheimer’s disease brain and is toxic to primary hippocampal cultures.Neurobiol. Aging 22, 187–194.
Lue, LF, L Brachova, DG Walker, Y Shen and J Rogers (1996) Characterization of glial cultures from rapid autopsies of Alzheimer’s and control patients.Neurobiol. Aging 17, 421–429.
Lue LF, R Rydel, EF Brigham, LB Yang, H Hampel, GM Murphy Jr, L Brachova, SD Yan, DG Walker, Y Shen and J Rogers (2001a) Inflammatory repertoire of Alzheimer’s disease and nondemented elderly microgliain vitro.Glia 35, 72–79.
Lue LF, DG Walker, L Brachova, TG Beach, J Rogers, AM Schmidt, DM Stern and SD Yan (2001b) Involvement of microglial receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) in Alzheimer’s disease: identification of a cellular activation mechanism.Exp. Neurol. 171, 29–45.
Lukiw WJ and NG Bazan (2000) Neuroinflammatory signalling upregulation in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurochem. Res. 25, 1173–1184.
Luterman JD, V Haroutunian, S Yemul, L Ho, D Purohit, PS Aisen, R Mohs and GM Pasinetti (2000) Cytokine gene expression as a function of the clinical progression of Alzheimer disease dementia.Arch. Neurol. 57, 1153–1160.
Luth H, G Munch and T Arendt (2002) Aberant, expression of NOS isoforms in Alzheimer’s disease is structurally related to nitrotyrosine formation.Brain Res. 953, 135–143.
Malchiodi-Albedi F, MR Domenici, S Paradisi, A Bernardo, MA Ajmone-Cat and L Minghetti (2001) Astrocytes contribute to neuronal impairment in Aβ toxicity increasing apoptosis in rat hippocampal neurons.Glia 34, 68–72.
Matsuoka Y, M Picciano, B Malester, J LaFrancois, C Zehr, JM Daeschner, JA Olschowka, MI Fonseca, MK O’Banion, JA Tenner, CA Lemere and K Duff (2001) Inflammatory responses to amyloidosis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.Am. J. Pathol. 158, 1345–1354.
Mattson MP (2000) Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders.Mol. Cell Biol. Rev. 1, 120–129.
McCann SM (1997) The nitric oxide hypothesis of brain aging.Exp. Geront. 32, 431–440.
McCartney-Francis NL and SM Wahl (2002) Dysregulation of IFN-γ signaling pathways in the absence of TGF-β1.J. Immunol. 169, 5941–5947.
McDonalds DR, ME Bamberger, CK Combs and GE Landreth (1998) β-Amyloid fibrils activate parallel mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in microglia and THP1 monocytes.J. Neurosci. 18, 4451–4460.
McGeer PL and EG McGeer (2001) Inflammation, autotoxicity and Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 22, 799–809.
Meda L, MA Cassatella, GI Szendrei, LJ Otvos, P Baron, M Villalba, P Ferrari and F Rossi (1995) Activation of microglial cells by β-amyloid protein and interferon-γ.Nature 374, 647–650.
Meda L, P Baron, E Prat, E Scarpini, G Scarlato, MA Cassatella and F Rossi (1999) Proinflammatory profile of cytokine production by human monocytes and murine microglia stimulated with β-amyloid [25–35].J. Neuroimmunol. 93, 45–52.
Meda L, P Baron and G Scarlato (2001) Glial activation in Alzheimer’s disease: the role of Aβ and its associated proteins.Neurobiol. Aging 22, 885–893.
Mehlhorn G, M Hollbron and R Schliebs (2000) Induction of cytokines in glial cells surrounding cortical β-amyloid plaques in transgenic Tg2576 mice with Alzheimer pathology.Int. Dev. Neurosci. 18, 423–431.
Melton LM, AB Keith, S Davis, AE Oakley, JA Edwardson and CM Morris (2003) Chronic glial activation, neurodegeneration, and APP immunoreactive deposits following acute administration of double-stranded RNA.Glia 44, 1–12.
Mrak R and S Griffin (2001) The role of activated astrocytes and of the neurotrophic cytokine S100B in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 22, 915–922.
Mrak R, J Sheng and S Griffin (1995) Glial cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease.Hum. Pathol. 26, 816–823.
Murray CA and M Lynch (1998) Evidence that increased hippocampal expression of the cytokine interleukin-1β is a common trigger for age- and stress-induced impairments in long-term potentiation.J. Neurosci. 18, 2974–2981.
Murray CA, B McGahon, S McBennet and M Lynch (1997) Interleukin-1β inhibits glutamate release in hippocampus of young, but not aged, rats.Neurobiol. Aging 18, 343–348.
Nagele RG, J Wegiel, V Venkatamaran, H Imaki, KC Wang and J Wegiel (2004) Contribution of glial cells to the development of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 25, 663–674.
Nedergaard M (1994) Direct signaling from astrocytes to neurons in cultures of mammalian brain cells.Science 263, 1768–1771.
Neumann H and H Wekerle (1998) Neuronal control of the immune response in the central nervous system: linking brain immunity to neurodegeneration.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 57, 1–9.
Neuroinflammation Working group (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 21, 383–421.
Nguyen MD, J-P Julien and S Rivest (2002) Innate immunity: the missing link in neuroprotection and neurodegeneration?Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 216–227.
Nichols NR (1999) Glial responses to steroids as markers of brain aging.J. Neurobiol. 40, 585–601.
Obermayr RP, L Mayerhofer, M Knechtelsdorfer, N Merisch, ER Huber, G Geyer and K-H Tragl (2005) The age-related down-regulation of the growth horm one/insulin-like growth factor-1 axis in the elderly male is reversed considerably by donepezil, a drug for Alzheimer’s disease.Exp. Gerontol. 40, 157–163.
Palop JJ, B Jones, L Kekonius, J Chin, GQ Yu, J Raber, E Masliah and L Mucke (2003) Neuronal depletion of calcium-dependent proteins in the dentate gyrus is tightly linked to Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 9572–9577.
Papassotiropoulos A, M Bagli, F Jessen, TA Bayer, W Maier, ML Rao and R Heun (1999) A genetic variation of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 delays the initial onset and reduces the risk for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease.Ann. Neurol. 45, 666–668.
Paresce DM, RN Ghosh and FR Maxfield (1996) Microglial cells internalize aggregates of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid β-protein via a scavenger receptor.Neuron 17, 553–565
Paresce DM, H Chung and FR Maxfield (1997) Slow degradation of aggregates of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid β-protein by microglial cells.J. Biol. Chem. 272, 29390–29397.
Pasinetti GL (1998) Cyclooxigenase and inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Experimental approaches and clinical interventions.J. Neurosci. Res. 54, 1–6.
Pawate S, Q Shen, F Fan and NR Bhat (2004) Redox regulation of glial inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide and interferon γ.J. Neurosci. Res. 77, 540–551.
Pike CJ, AJ Walencewicz, CG Glabe and CW Cotan (1991)In vitro aging of β-amyloid protein causes peptide aggregation and neurotoxicity.Brain Res. 563, 311–314.
Prehn JHM, WP Bindokas, J Jordán, MF Galindo, GD Ghadge, RP Roos, LH Boise, CB Thompson, S Krajewski, JC Reed and RJ Miller (1996) Protective effect of transforming growth factor-β1 on β-amyloid neurotoxicity in rat hippocampal neurons.Mol. Pharmacol. 49, 319–328.
Prinz M, O Kann, HJ Draheim, RR Schumann, H Kettenmann, JR Webwer and UK Hanisch (1999) Microglial activation by components of gram-positive and-negative bacteria: distinct and common routes to the induction of ion channels and cytokines.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 58, 1078–1089.
Ramirez G, R Toro, H Döbeli, R von Bernhardi (2005) Protection of rat primary hippocampal cultures from Aβ cytotoxicity by pro-inflammatory molecules is mediated by astrocytes.Neurobiol. Dis. 19, 243–254.
Rogers JT, LM Leiter, J McPhee, CM Cahill, SS Zhan, H Potter and LN Nilsson (1999) Translation of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein mRNA is up-regulated by interleukin-1 through 5′-untranslated region sequences.J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6421–6431.
Rogers J, R Strohmeyer, CJ Kovelowski and R Li (2002) Microglia and inflammatory mechanisms in the clearance of amyloid-β peptide.Glia 40, 260–269.
Roses AD (1996) Apolipoprotein E in neurology.Curr. Opin. Neurol. 4, 265–270.
Ross FM, SM Allan, NJ Rothwell, A Verkhratsky (2003) A dual role for interleukin-1 in LTP in mouse hippocampal slices.J. Neuroimmunol. 144, 61–67.
Rota E, G Bellone, P Rocca, P Bergamasco, G Emanuelli and P Ferrero (2006) Increased intrathecal TGF-β1, but not IL-12, IFN-γ and IL-10 levels in Alzheimer’s disease patients.Neurol. Sci. 27, 33–39
Roth AD, G Ramirez, R Alarcón and R von Bernhardi (2005) Oligodendrocytes damage in Alzheimer’s disease: β-amyloid toxicity and inflammation.Biol. Res. 38, 381–387.
Rothwell N and G Luheshi (2000) Interleukin 1 in the brain: biology, pathology and therapeutic target.Trends Neurosci. 23, 618–625.
Sala G, G Galimberti, C Canevari, ME Raggi, V Isella, M Facheris, I Appollonio and C Ferrarese (2003) Peripheral cytokine release in Alzheimer patients: correlation with disease severity.Neurobiol. Aging 24, 909–914.
Sastre M, I Dewachter, GE Landreth, TM Wilson, T Klockgether, F Van Leuven and MT Heneka (2003) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonists modulate immunostimulated processing of amyloid precursor protein through regulation of β-secretase.J. Neurosci. 23, 9796–9804.
Sastre M, I Dewachter, S Rossner, N Bogdanovic, E Rosen, P Borghgraef, BO Evert, L Dumitrescu-Ozimek, DR Thal, G Landreth, J Walter, T Kloockgether, F van Leuven and MT Heneka (2006) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs repress β-secretase gene promoter activity by the activation of PPARγ.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 443–448.
Saud K, R Herrera-Molina and R von Bernhardi (2005) Proand anti-inflammatory cytokines regulate the ERK pathway: implication of the timing for the activation of microglial cells.Neurotox. Res. 8, 277–287.
Schenk D, R Barbour, W Dunn, G Gordon, H Grajeda, T Guido, K Hu, J Huang, K Johnson-Wood, K Khan, D Kholodenko, M Lee, Z Liao, I Lieberburg, R Motter, L Mutter, F Soriano, G Shopp, N Vasquez, C Vandevert, S Walker, M Wogulis, T Yednock, D Games and P Seubert (1999) Immunization with amyloid-β attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse.Nature 400, 173–177.
Selkoe DJ (1996) Amyloid β-protein and the genetics of Alzheimer’s disease.J. Biol. Chem. 271, 18295–18298.
Selkoe DJ (2000) The origins of Alzheimer’s disease: A is for amyloid.JAMA 283, 1615–1617.
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins and therapy.Physiol. Rev. 81, 741–766.
Selkoe DJ (2002) Alzheimer’s disease: is a synaptic failure.Science 298, 789–791.
Sheng JG, FA Boop, RE Mrak and WS Griffin (1994) Increased neuronal β-amyloid precursor protein expression in human temporal lobe epilepsy: association with interleukin-1α immunoreactivity.J. Neurochem. 63, 1872–1879.
Sheng JG, RE Mrak and WS Griffin (1995) Microglial interleukin-1α expression in brain regions in Alzheimer’s disease: correlation with neuritic plaque distribution.Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 21, 290–301.
Sheng JG, RE Mrak and WS Griffin (1997) Neuritic plaque evolution in Alzheimer’s disease is accompanied by transition of activated microglia from primed to enlarged to phagocytic forms.Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 94, 1–5.
Sheng JG, SH Bora, G Xu, DR Borchelt, DL Price and VL Koliatos (2003) Lipopolysaccharide-induced-neuroinflammation increases intracellular accumulation of amyloid precursor protein and amyloid β-peptide in APPswe transgenic mice.Neurobiol. Dis. 14, 133–145.
Sierra A, AC Gottfried-Blackmore, BS McEwen and K Bulloch (2007) Microglia derived from aging mice exhibit an altered inflammatory profile.Glia 55, 412–424.
Simard AR, D Soulet, G Gowing, JP Julien and S Rivest (2006) Bone marrow-derived microglia play a critical role in restricting senile plaque formation in Alzheimer’s disease.Neuron 49, 489–502.
Smith MA, K Hirai, K Hsiao, MA Pappolla, PL Harris, SL Siedlak, M Tabaton and G Perry (1998) Amyloid-β deposition in Alzheimer transgenic mice is associated with oxidative stress.J. Neurochem. 70, 2212–2215.
Smits HA, LA Boven, CF Pereira, J Verhoef and HS Nottet (2000) Role of macrophage activation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated dementia.Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 30, 526–535.
Smits HA, AJ van Beelen, NM de Vos, A Rijmus, T van der Bruggen, J Verhoef, FL van Muiswinkel and HS Nottet (2001) Activation of human macrophages by amyloid-β is attenuated by astrocytes.J. Immunol. 166, 6869–6876.
Smits HA, A Rijsmus, JH van Loon, JW Wat, J Verhoef, LA Boven and HS Nottet (2002) Amyloid-β-induced chemokine production in primary human macrophages and astrocytes,J. Neuroimmunol. 127, 160–168.
Sortino MA, M Chisari, S Merlo, C Vancheri, M Caruso, F Nicoletti, PL Canonico and A Copan (2004) Glia mediates the neuroprotective action of estradiol on β-amyloid-induced neuronal death.Endocrinology 145, 5080–5086.
Stewart WF, C Kawas, M Corrada and EJ Metter (1997) Risk of Alzheimer’s disease and duration of NSAID use.Neurology 48, 626–632.
Streit WJ (2002) Microglia as neuroprotective, immunocompetent cells of the CNS.Glia 40, 133–139.
Streit WJ, NW Sammons, AJ Kuhns and DL Sparks (2004) Dystrophic microglia in the aging human brain.Glia 45, 208–212.
Sudo S, J Tanaka, K Toku, J Desaki, S Matsuda, T Arai, M Sakanaka and N Maeda (1998) Neurons induce the activation of microglial cellsin vitro.Exp. Neurol. 154, 499–510.
Takahashi RH, CG Almeida, PF Kearney, F Yu, MT Lin, TA Milner and GK Gouras (2004) Oligomerization of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid within processes and synapses of cultured neurons and brain.J. Neurosci. 24, 3592–3599.
Tegeder I, J Pfeilschifter and G Geisslinger (2001) Cyclooxygenase-independent actions of cyclooxygenase inhibitors.FASEB J. 15, 2057–2072.
Trejo JL, E Carro, E Garcia-Galloway and I Torres-Aleman (2004) Role of insulin-like growth factor-I signaling in neurodegenerative disease.J. Mol. Med. 82, 156–162.
Ueberham U, E Ueberham, H Gruschka and T Arendt (2006) Altered subcellular location of phosphorylated Smads in Alzheimer’s disease.Eur. J. Neurosci. 24, 2327–2334.
Uylings HB and JM de Brabander (2002) Neuronal changes in normal human aging and Alzheimer’s disease.Brain Cogn. 49, 268–276.
Vermeer SE, ND Prins, T den Heijer, A Hofman, PJ Koudstaat and MM Breteler (2003) Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline.N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1215–1222.
Vincent VA, FJ Tielders and AM Van Dam (1997) Inhibition of endotoxin-induced nitric oxide synthase production in microglial cells by the presence of astroglial cells: a role for transforming growth factor β.Glia 19, 190–198.
Vitkovic L, J Bockaert and C Jacque (2000) “Inflammatory” Cytokines: neuromodulators in normal Brain?J. Neurochem. 74, 457–471.
von Bernhardi R (2005) Aging: biochemistry and functional changes of the central nervous system.Rev. Chil Neuro-Psiquiat. 43, 297–304.
von Bernhardi R and J Eugenin (2004) Microglia — astrocyte interaction in Alzheimer’s disease: modulation of cell reactivity to Aβ.Brain Res. 1025, 186–193.
von Bernhardi R and G Ramirez (2001) Microglia-astrocyte interaction in Alzheimer’s disease: friends or foes for the nervous system?Biol. Res. 34, 123–128
von Bernhardi, R, G Ramirez, H Matile and H Döbeli (2001) Immobilized APP constructs: a tool for thein vitro screening of glial cell reactivity.Eur. J. Neurosci. 14, 946–956.
von Bernhardi R, G Ramirez, R Toro and J Eugenin (2007) Pro-inflammatory conditions promote neuronal damage mediated by amyloid precursor protein-and degradation by microglial cells in culture.Neurobiol. Dis. 26, 153–164.
Walsh DM, DM Hartley, Y Kusumoto, Y Fezoui, MM Condrom, A Lomakin, GB Benedeck and DJ Selkoe (1999) Amyloid β-protein fibrillogenesis. Structure and biological activity of protofibrillar intermediates.J. Biol. Chem. 274, 25945–25952.
Walsh DM, I Klyubin, JV Fadeeva, WK Cullen, R Anwyl, MS Wolfe, MJ Rowan and DJ Selkoe (2002) Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid β-proteins potently inhibit hippocampal long term potentiationin vivo.Nature 416, 535–539.
Weggen S, JL Eriksen, P Das, SA Sagi, R Wang, CU Pietrzik, KA Findlay, TE Smith, MP Murphy, T Bulter, DE Kang, N Marquez-Sterling, TE Golde and EH Koo (2001) A subset of NSAIDs lower amyloidogenic Aβ42 independently of cyclooxygenase activity.Nature 414, 212–216.
Wegiel J, KC Wang, M Tarnawski and B Lach (2000) Microglial cells are the driving force in fibrillar plaque formation, whereas astrocytes are a leading factor in plaque degradation.Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 100, 356–364
Wegiel J, KC Wang, H Imaki, R Rubenstein, A Wronska, M Osuchowski, WJ Lipinski, LC Walker and H LeVine (2001) The role of microglial cells and astrocytes in fibrillar plaque evolution in transgenic APP(SW) mice.Neurobiol. Aging 22, 49–61.
Wen Y, O Onyewuchi, S Yang, R Liu and JW Simpinks (2004) Increased β-secretase activity and expression in rats following transient cerebral ischemia.Brain Res. 1009, 1–8.
Westphalen RI, HL Scott and PR Dodd (2003) Synaptic vesicle transport and synaptic membrane transporter sites in excitatory amino acid nerve terminals in Alzheimer disease.J. Neural Transm. 110, 1013–1027.
Witting A, P Muller, A Hermann, H Kettenmann and C Nolte (2000) Phagocytic clearance of apoptotic neurons by microglia/brain macrophagesin vitro: involvement of lectin-, integrin-, and phosphatidyl-serine-mediated recognition.J. Neurochem. 75, 1060–1070.
Wyss-Coray T (2006) Inflammation in Alzheimer disease: driving force, bystander or beneficial response?Nat. Med. 12, 1005–1015.
Wyss-Coray T and L Mucke (2002) Inflammation in neurodegenerative disease — a double-edged sword.Neuron 35, 419–432.
Wyss-Coray T, C Lin, F Yan, GQ Yu, M Rohde, L McConlogue, F Masliah and L Mucke (2001) TGF-β1 promotes microglial amyloid-β clearance and reduces plaque burden in transgenic mice.Nat. Med. 6, 612–618.
Wyss-Coray T, F Yan, AH Lin, JD Lambris, JJ Alexander, RJ Quigg and E Masliah (2002) Prominent neurodegeneration and increased plaque formation in complement-inhibited Alzheimer’s mice.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 10837–10842.
Wyss-Coray T, JD Loike, TC Brionne, E Lu, R Anankov, F Yan, SC Silverstein and J Husemann (2003) Adult mouse astrocytes degrade amyloid-βin vitro andin situ.Nat. Med. 9, 453–457.
Xiao B, X Bai, G Zhang, B Höjeberg and H Link (1996) Shift from anti- to pro-inflammatory cytokine profiles in microglia through LPS- or IFN-γ-mediated pathways.Neuro Report 7, 1893–1898.
Yasojima K, C Schwab, EG McGeer and PL McGeer (2000) Human neurons generate C-reactive protein and amyloid: upregulation in Alzheimer’s disease.Brain Res. 887, 80–89.
Yokota M, TC Saido, E Tani, I Yamaura and N Minami (1996) Cytotoxic fragment of amyloid precursor protein accumulates in hippocampus after global forebrain ischemia.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 16, 1219–1223.
Younkin SG (2001) Amyloid-β vaccination: reduced plaques and improved cognition.Nat. Med. 7, 18–19.
Zhang Z, M Chopp and C Powers (1997a) Temporal profile of microglial response following transient (2h) middle cerebral artery occlusion.Brain Res. 744, 189–198.
Zhang F, C Eckman, S Younkin, KK Hsiao and C Iadecola (1997b) Increased susceptibility to ischemic brain damage in transgenic mice overexpressing the amyloid precursor protein.J. Neurosci. 17, 7655–7661.
Zhu Y, S Roth-Eichhorn, N Braun, C Culmsee, A Rami and J Krieglstein (2000) The expression of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) in hippocampal neurons: a temporary upregulated protein level after transient forebrain ischemia in the rat.Brain Res. 866, 286–298.
Zhu Y, GY Yang, B Ahlemeyer, L Pang, XM Che and C Culmsee (2002) Transforming growth factor-β1 increasesbad phosphorylation and protects neurons against damage.J. Neurosci. 22, 3898–3909.
Zhu Y, C Culmsee, S Klumpp and J Krieglstein (2004a) Neuroprotection by transforming growth factor-β1 involves activation of nuclear factor-κB through phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase-extracellular-signal regulated kinase 1, 2 signaling pathways.Neuroscience 123, 897–906.
Zhu X, AK Raina, G Perry and MA Smith (2004b) Alzheimer’s disease: the two-hit hypothesis.Lancet Neurol. 3, 219–226.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Von Bernhardi, R. Glial cell dysregulation: a new perspective on Alzheimer disease. neurotox res 12, 215–232 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033906
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033906