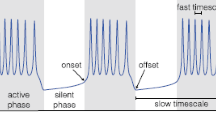
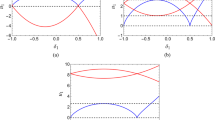
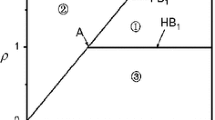
Abstract
We describe a classification scheme for bursting oscillations which encompasses many of those found in the literature on bursting in excitable media. This is an extension of the scheme of Rinzel (inMathematical Topics in Population Biology, Springer, Berlin, 1987), put in the context of a sequence of horizontal cuts through a two-parameter bifurcation diagram. We use this to describe the phenomenological character of different types of bursting, addressing the issue of how well the bursting can be characterized given the limited amount of information often available in experimental settings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alving, B. 1968. Spontaneous activity in isolated somata of Aplysia pacemaker neurons.J. Gen. Physiol. 51, 29–45.
Ashcroft, F. and P. Rorsman. 1989. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cell.Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol. 54, 87–143.
Av-Ron, E., H. Parnas and L. Segel. 1993. A basic biophysical model for bursting neurons.Biol. Cybern. 69, 87–95.
Baer, S. M., T. Erneux and J. Rinzel. 1989. The slow passage through a Hopf bifurcation: delay, memory effects, and resonance.SIAM J. Appl. Math. 49, 55–71.
Bertram, R. 1993. A computational study of the effects of serotonin on a molluscan burster neuron.Biol. Cybern. 69, 257–267.
Bertram, R. 1994. Reduced-system analysis of the effects of serotonin on a molluscan burster neuron.Biol. Cybern. 70, 359–368.
Canavier, C. C., J. W. Clark and J. H. Byrne. 1991. Simulation of the bursting activity of neuron R15 in Aplysia: role of ionic currents, calcium balance, and modulatory transmitters.J. Neurophysiol. 66, 2107–2124.
Canavier, C. C., D. A. Baxter, J. W. Clark and J. H. Byrne. 1993. Nonlinear dynamics in a model neuron provide a novel mechanism for transient synaptic inputs to produce long-term alterations of postsynaptic activity.J. Neurophysiol. 69, 2252–2257.
Chay, T. R. and D. L. Cook. 1988. Endogenous bursting patterns in excitable cells.Math. Biosci. 90, 139–153.
Crunelli, V., J. S. Kelly, N. Leresche and M. Pirchio. 1987. The ventral and dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the rat: intracellular recordings in vitro.J. Physiol. 384, 587–601.
Dean, P. M. and E. K. Matthews. 1970. Glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells.J. Physiol. 210, 255–264.
Deschênes, M., J. P. Roy and M. Steriade. 1982. Thalamic bursting mechanism: an inward slow current revealed by membrane hyperpolarization.Brain Res. 239, 289–293.
Doedel, E. 1981. Auto: A program for the automatic bifurcation analysis of autonomous systems.Cong. Num. 30, 265–284.
Dumortier, F., R. Roussarie and J. Sotomayor. 1991. Generic 3-parameter families of planar vector fields, unfoldings of saddle, focus and elliptic singularities with nilpotent linear parts. InBifurcations of Planar Vector Fields: Nilpotent Singularites and Abelian Integrals, F. Dumortier, R. Roussarie, J. Sotomayor and H. Żoŀadek (Eds), Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Vol. 1480, pp. 1–164. Berlin: Springer.
Ermentrout, G. B. and N. Kopell. 1986. Parabolic bursting in an excitable system coupled with a slow oscillation.SIAM J. Appl. Math. 46, 233–253.
FitzHugh, R. 1961. Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane.Biophys. J. 1, 445–466.
Gear, C. 1967. The numerical integration of ordinary differential equations.Math. Comp. 21, 146–156.
Guckenheimer, J. 1986. Multiple bifurcation problems for chemical reactions.Physica 20D, 1–20.
Guckenheimer, J. and P. Holmes. 1983.Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems and Bifurcations of Vector Fields, pp. 353–423. Berlin: Springer.
Guckenheimer, J., S. Gueron and R. M. Harris-Warrick. 1993. Mapping the dynamics of a bursting neuron.Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. 341, 345–359.
Harris-Warrick, R. M. and R. E. Flamm. 1987. Multiple mechanisms of bursting in a conditional bursting neuron.J. Neurosci. 7, 2113–2128.
Hindmarsh, A. 1974. An ordinary differential equation solver. Technical report UCID-30001, Lawrence Livermore Laboratory.
Hindmarsh, J. L. and R. M. Rose. 1984. A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 221, 87–102.
Hudson, J. L., M. Hart and D. Marinko. 1979. An experimental study of multiple peak periodic and nonperiodic oscillations in the Belousov-Zhabotinskii reaction.J. Chem. Phys. 71, 1601–1606.
Johnson, S. W., V. Seutin and R. A. North. 1992. Burst firing in dopamine neurons induced by N-Methyl-D-Aspartate: role of electrogenic sodium pump.Science 258, 665–667.
Pernarowski, M. 1994. Fast subsystem bifurcations in a slowly varying Liénard system exhibiting bursting.SIAM J. Appl. Math. 54, 814–832.
Plant, R. E. and M. Kim. 1976. Mathematical description of a bursting pacemaker neuron by a modification of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations.Biophys. J. 16, 227–244.
Rinzel, J. 1985. Bursting oscillation in an excitable membrane model. InOrdinary and Partial Differential Equations, B. D. Sleeman and R. J. Jarvis (Eds), Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Vol. 1151, pp. 304–316. Berlin: Springer.
Rinzel, J. 1987. A formal classification of bursting mechanisms in excitable systems. InMathematical Topics in Population Biology, Morphogenesis and Neurosciences, E. Teramoto and M. Yamaguti (Eds), Lecture Notes in Biomathematics, Vol. 71, pp. 267–281. Berlin: Springer.
Rinzel, J. and Y. S. Lee. 1987. Dissection of a model for neuronal parabolic bursting.J. Math. Biol. 25, 653–675.
Rinzel, J. and W. C. Troy. 1982. Bursting phenomena in a simplified Oregonator flow system model.J. Chem. Phys. 76, 1775–1789.
Rush, M. E. and J. Rinzel. 1994. Analysis of bursting in a thalamic neuron model.Biol. Cybern. 71, 281–291.
Schecter, S. 1987. The saddle node separatrix loop.SIAM J. Math. Anal. 18, 1142–1156.
Sherman, A. and J. Rinzel. 1992. Rhythmogenic effects of weak electrotonic coupling in neuronal models.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 2471–2474.
Smolen, P. and J. Keizer. 1992. Slow voltage inactivation of Ca2+ currents and bursting mechanisms for the mouse pancreatic beta-cell.J. Membrane. Biol. 127, 9–19.
Smolen, P. and A. Sherman. 1994. Phase-independent resetting in relaxation and bursting oscillators.J. Theor. Biol. 169, 339–348.
Strumwasser, F. 1967. Types of information stored in single neurons. InInvertebrate Nervous Systems: Their Significance for Mammalian Neurophysiology, C. A. G. Wiersma (Ed.), pp. 290–319. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press.
Traub, R. D., R. K. S. Wong, R. Miles and H. Michelson. 1991. A model of a CA3 hippocampal pyramidal neuron incorporating voltage-clamp data on intrinsic conductances.J. Neurophysiol. 66, 635–650.
Wang, X.-J. and J. Rinzel. 1994. Oscillatory and bursting properties of neurons. InThe Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks, M. A. Arbib (Ed.). Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Wang, X.-J., J. Rinzel and M. A. Rogawski. 1991. A model of the T-type calcium current and the low-threshold spikes in the thalamic neurons.J. Neurophysiol. 66, 839–850.
Wong, R. K. S. and D. A. Prince. 1981. Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells.J. Neurophysiol. 45, 86–97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertram, R., Butte, M.J., Kiemel, T. et al. Topological and phenomenological classification of bursting oscillations. Bltn Mathcal Biology 57, 413–439 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460633
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460633