Abstract
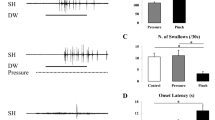
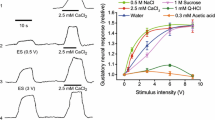
In anesthetized cats, swallowing elicited by electrical stimulation of the superior laryngeal nerves (SLNs) was inhibited by the GABA-mimetic muscimol and by diazepam, an action that was reversed by picrotoxin and bicuculline. This inhibition supports the involvement of GABA receptors, specifically those of the GABAA subtype which both antagonists have been shown to block in various areas of the central nervous system. The inhibition of reflex swallowing and its reversal were unaltered by a transection of the brainstem at a midcollicular level. Stimulation of the SLNs also caused a bradycardia that was inhibited by both muscimol and diazepam and was restored by both GABA antagonists. Data from these experiments provide suggestive evidence for a role of GABA-ergic transmission in the central control of the deglutitory reflex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnston GAR: Amino acid inhibitory transmitters in the central nervous system. In: Hockman CH, Bieger D (eds.) Chemical Transmission in the Mammalian Central Nervous System. Baltimore: University Park Press, 1976, pp 31–81
Costa E, Guidotti A: Molecular mechanisms in the receptor action of benzodiazepines. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 19:531–554, 1979
Haefely WE: Allosteric modulation of the GABAA receptor channel: a mechanism for interaction with a multitude of central nervous functions. In: Möhler H, DaPrada M (eds.) The Challenge of Neuropharmacology. Basel: Editiones Roche, 1994, pp 15–39
Matsumoto RR: GABA receptors: are cellular differences reflected in function? Brain Res Rev 14:203–225, 1989
Wang YT, Bieger D: Role of solitarial GABAergic mechanisms in control of swallowing. Am J Physiol 261:R639-R646, 1991
Sumi T: Role of the pontine reticular formation in the neural organization of deglutition. Jap J Physiol 22:295–314, 1972
Hockman CH, Bieger D: Inhibitory effect of diazepam on reflexly induced deglutition. Proc Can Fed Biol Soc 22:34, 1979
Bieger D, Hockman CH: Suprabulbar modulation of reflex swallowing. Exp Neurol 52:311–324, 1976
Berman AL: The Brain Stem of the Cat. A Cytoarchitectonic Atlas with Stereotaxic Coordinates. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1968
Miller, FR, Sherrington CS: Some observations on the buccopharyngeal stage of reflex deglutition in the cat. Quart J Exptl Physiol 9:147–186, 1915–1916
Weerasuriya A, Bieger D, Hockman CH: Interaction between primary afferents in the elicitation of reflex swallowing. Am J Physiol 239:R407-R414, 1980
Hockman CH, Livingston KE: Inhibition of reflex vagal bradycardia by diazepam. Neuropharmacol 10:307–314, 1971
Quest JA, Freer LS, Gillis RA: Chlordiazepoxide inhibition of reflex bradycardia in the cat. Life Sci 21:656–659, 1977
Ngai SH, Tseng DTC, Wand SC: Effect of dizepam and other central nervous system depressants on spinal reflexes in cats. A study of site of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 153:344–351, 1966
Theobald W, Buch O, Kunz HA, Krupp P, Stenger EG, Heimann H: Pharmacologische und experimental-psychologische Untersuchungen mit 2 Inhaltsstoffen des Fliegenpilzes (Amanita Muscaria). Arzneim Forsch 18:311–315, 1968
Bennett JA, McWilliam PN, Shepheard SL: A gamma-aminobutyric acid-mediated inhibition of neurones in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 392:417–426, 1987
Catelli JM, Giakas WJ, Sved AF: GABAergic mechanisms in nucleus tractus solitarius alter blood pressure and vasopressin release. Brain Res 403:279–289, 1987
Wang O, Li P: Inhibition of baroreflex following microinjection of GABA or morphine into the nucleus tractus solitarii in rabbits. J Auton Nerv Syst 25:165–172, 1988
Andrew BL: A laryngeal pathway for aortic baroreceptor impulses. J Physiol (Lond) 125:352–360, 1954
Doty R: Neural organization of deglutition. Handbook of Physiology. Alimentary Canal Motility. Washington DC: American Physiology Society, sect. 6, vol IV, 1968, pp 1861–1902
Geller HM, Taylor DA, Hoffer BJ: Benzodiazepines and central inhibitory mechanisms. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 304:81–88, 1978
Möhler H, Okada T: GABA receptor binding with 3H(+) bicuculline methiodide in rat CNS. Nature 267:65–67, 1977
Ticku MK, Ban M, Olson RW: Binding of 3H-dihydropicrotoxin, a gamma aminobutyric acid synaptic antagonist, to rat brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol 14:391–402, 1978
de Groat WC: The actions of g-aminobutyric acid and related amino acids on mammalian autonomic ganglia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 172:384–396, 1970
deGroat WC: GABA depolarization of a sensory ganglion: antagonism by pictotoxin and bicuculline. Brain Res 38:429–432, 1972
Barker YL, Nicol RA: The pharmacology and ionic dependency of amino acid responses in the frog spinal cord. J Physiol (Lond) 228:259–277, 1973
Haefely W, Kulcsar A, Möhler H, Pieri L, Polc P, Schaffner R: Possible involvement of GABA in the central actions of benzodiazepines. In: Costa E, Greengard P (eds.): Mechanism of Action of Benzodiazepines. New York: Raven Press, 1975
Nistri A, Constanti A: Pharmacological characterization of different types of GABA and glutamate receptors in vertebrates and invertebrates. Progr Neurobiol 13(2):117–235, 1979
Bieger D: Neuropharmacologic correlates of deglutition: lessons from fictive swallowing. Dysphagia 6:147–164, 1991
Sessle BJ, Henry JL: Neural mechanisms of swallowing: neurophysiological and neurochemical studies on brain stem neurons in the solitary tract region. Dysphagia 4:61–75, 1989
Cherkaoui N, Jean A, Kessler JP: Activation of excitatory amino acid receptors within the nucleus tractus solitarius elicits the swallowing motor pattern in the anesthetized rat. J Physiol (Lond) 406: 16P, 1988
Bieger D, Weerasuriya A, Hockman CH: The emetic action of L-DOPA and its effect on the swallowing reflex in the cat. J Neural Trasm 42: 87–98, 1978
Weerasuriya A, Bieger D, Hockman CH: Basal forebrain facilitation of reflex swallowing in the cat. Brain Res 174:119–133, 1979
Bartholini G, Keller H, Pieri I, Pletscher A: The effect of diazepam on the turnover of cerebral dopamine. In: Garattini S, Mussini E, Randall LO (eds.): The Benzodiazepines. New York: Raven Press, 1973, pp 235–240
Lidbrink P, Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Olson L: The effects of benzodiazepines, meprobamate, and barbiturates on central monoamine neurons. In: Garattini S, Mussini E, Randall LO (eds.): The Benzodiazepines. New York: Raven Press, 1973, pp 203–228
Nakamura M, Fukushima H: Effect of benzodiazepines on central serotonergic neuron systems. Psychopharmacology 53:121–126, 1977
Doty RW: Influence of stimulus pattern on reflex deglutition. Am J Physiol 166:142–158, 1951
Doty R, Bosma JF: An electromyographic analysis of reflex deglutition. J Neurophysiol 19:44–60, 1956
Wyllie E, Wyllie R, Cruse RP, Rothner AD, Erenberg G: The mechanism of nitrazepam-induced drooling and aspiration, N Engl J Med 314:35–38, 1986
Buchholz D, Jones B, Neumann S, Ravich W: Benzodiazepine-induced pharyngeal dysphagia: report of two probable cases. Third Annual Meeting of the Dysphagia Research Society Oct 14–16, 1994, McLean, VA, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hockman, C.H., Weerasuriya, A. & Bieger, D. GABA receptor-mediated inhibition of reflex deglutition in the cat. Dysphagia 11, 209–215 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00366388
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00366388