Abstract
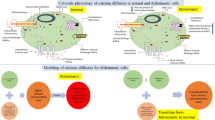
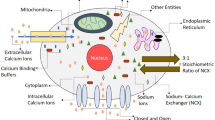
The present paper focuses on the solution of the three-dimensional calcium advection–diffusion equation in the presence of calcium-binding buffers. As buffers play an important role in maintaining cytosolic calcium concentration level, decrease in buffers leads to increase in cytoplasmic calcium which may further lead to toxicity of Alzheimer’s disease. The governing three-dimensional differential equation has been further converted into one-dimensional equation using similarity transforms. The solution is obtained analytically using Laplace transforms and suitable boundary conditions. The obtained solution is simulated in MATLAB. The graphs clearly show the impact of buffers on calcium concentration level for normal and Alzheimeric cells.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augustine GJ, Santamaria F, Tanaka K (2003) Local calcium signaling in neurons. Neuron 40:331–346
Bezprozvanny I (2011) Calcium signaling and neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Mol Med 15:89–100
Brzyska M, Elbaum D (2003) Dysregulation of calcium in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurobiol Exp 63:171–183
Carafoli E, Brini M (eds) (2007) Calcium signalling and disease. Springer, New York
Clapham DE (2007) Calcium signaling. Cell 131:1047–1058
Coe H, Michalak M (2009) Calcium binding chaperones of the endoplasmic reticulum. Gen Physiol Biophys 28:96–103
Crank J (1975) The mathematics of diffusion, Second edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Dave DD, Jha BK (2018a) Analytically depicting the calcium diffusion for Alzheimer’s affected cell. Int J Biomath 11(6):1850088–1850101
Dave DD, Jha BK (2018b) Delineation of calcium diffusion in alzheimeric brain. J Mech Med Biol 18(2):1–15
Demuro A, Parker I, Stutzmann GE (2010) Calcium signaling and amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 6:1–1
Fall C et al (2002) Computational cell biology. Springer, New York
Jha A, Adlakha N (2015) Two-dimensional finite element model to study unsteady state \(Ca^{2+}\) diffusion in neuron involving ER. LEAK and SERCA. Int J Biomath 8(1):1–14
Jha BK, Adlakha N, Mehta MN (2012) Analytic solution of two dimensional advection diffusion equation arising in cytosolic calcium concentration distribution. Int Math Forum 7(3):135–144
Jha BK, Adlakha N, Mehta MN (2014) Two-dimensional finite element model to study calcium distribution in astrocytes in presence of excess buffer. Int J Biomath 7(3):1–11
Jha A, Adlakha N, Jha BK (2015) Finite element model to study effect of \(Na^{+}-Ca^{2+}\) exchangers and source geometry on calcium dynamics in a neuron cell. J Mech Med Biol 16(2):1–22
Keener J, Sneyd J (2009) Mathematical physiology second. Springer, New York
Khachaturian ZS (1993) Calcium hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease and brain aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1–11
Kotwani M, Adlakha N, Mehta MN (2014) Finite element model to study the effect of buffers. Source amplitude and source geometry on spatio-temporal calcium distribution in fibroblast cell. J Med Imaging Health Inf 4(6):840–847
Laferla FM (2002) Calcium dyshomeostasis and intracellular signalling in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:862–872
Magi S et al (2016) Intracellular calcium dysregulation: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Res Int 2016:1–14
Makrariya A, Adlakha N (2013) Two-dimensional finite element model of temperature distribution in dermal tissues of extended spherical organs of a human body. Int J Biomath 6(1):1250065-01–1250065-15
Makrariya A, Adlakha N (2015) Two-dimensional finite element model to study temperature distribution in peripheral regions of extended spherical human organs involving uniformly perfused tumors. Int J Biomath 8(6):1550074-01–1550074-30
Mattson MP et al (2000) Calcium signaling in the ER: its role in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci 23(5):222–229
Morris G et al (2018) Could Alzheimer’s disease originate in the periphery and if so how so? Mol Neurobiol
Naik PA, Pardasani KR (2018a) Three-dimensional finite element model to study effect of RyR calcium channel. ER leak and SERCA pump on calcium distribution in oocyte cell. Int J Comput Methods 15(3):1–19
Naik PA, Pardasani KR (2018b) 2D finite-element analysis of calcium distribution in oocytes. Netw Model Anal Health Inf Bioinf. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-018-0172-2
Pathak K, Adlakha N (2015a) Finite element model to study calcium signalling in cardiac myocytes involving pump. Leak and excess buffer. J Med Imaging Health Inf 5:1–6
Pathak K, Adlakha N (2015b) Finite element model to study two dimensional unsteady state calcium distribution in cardiac myocytes. Alexandria J Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2015.09.007
Pchitskaya E, Popugaeva E, Bezprozvanny I (2017) Calcium signaling and molecular mechanisms underlying neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Calcium. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2017.06.008
Rajagopal S, Ponnusamy M (2017) Calcium signaling: from physiology to diseases. Springer, Singapore
Schmidt H (2012) Three functional facets of calbindin D-28k. Front Mol Neurosci 5:1–7
Schwaller B (2010) Cytosolic \(Ca^{2+}\) Buffers. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol 1–20
Singh N, Adlakha N (2019) A mathematical model for interdependent calcium and inositol 1,4,5trisphosphate in cardiac myocyte. Netw Model Anal Health Inf Bioinf. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-019-0198-0
Small DH (2009) Dysregulation of calcium homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 34:1824–1829
Smith GD (1996) Analytical steady-state solution to the rapid buffering approximation near an open \(Ca^{2+}\) channel. Biophys J 71:3064–3072
Squire L et al (2008) Fundamental neuroscience, Third edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Supnet C, Bezprozvanny I (2010) Neuronal calcium signaling, mitochondrial dysfunction and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 20(2):S487–S498
Tewari SG, Pardasani KR (2011) Finite element model to study two dimensional unsteady state cytosolic calcium diffusion. J Appl Math Inf 29:427–442
Turkington C, Mitchell D (2010) The encyclopedia of Alzheimer’s disease second. Facts on file: an imprint. Infobase Publishing, New York
Verkhratsky A et al (2010) Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherap J Am Soc Exp Neurotherap 7:399–412
Wang Y, Shi Y, Wei H (2017) Calcium dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease: a target for new drug development. J Alzheimer’s Dis Parkinsinism 7(5):
Yadav RR et al (2012) Three-dimensional temporally dependent dispersion through porous media: analytical solution. Environ Earth Sci 65:849–859
Yagami T, Kohma H, Yamamoto Y (2012) L-type voltage-dependent calcium channels as therapeutic targets for neuro- degenerative diseases. Curr Med Chem 1:4816–4827
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dave, D.D., Jha, B.K. 3D mathematical modeling of calcium signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinforma 9, 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-019-0207-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-019-0207-3