Abstract
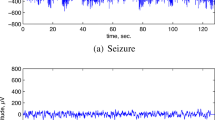
Since epileptic seizure is unpredictable and paroxysmal, an automatic system for seizure detecting could be of great significance and assistance to patients and medical staff. In this paper, a novel method is proposed for multichannel patient-specific seizure detection applying the earth mover’s distance (EMD) in scalp EEG. Firstly, the wavelet decomposition is executed to the original EEGs with five scales, the scale 3, 4 and 5 are selected and transformed into histograms and afterwards the distances between histograms in pairs are computed applying the earth mover’s distance as effective features. Then, the EMD features are sent to the classifier based on the Bayesian linear discriminant analysis (BLDA) for classification, and an efficient postprocessing procedure is applied to improve the detection system precision, finally. To evaluate the performance of the proposed method, the CHB-MIT scalp EEG database with 958 h EEG recordings from 23 epileptic patients is used and a relatively satisfactory detection rate is achieved with the average sensitivity of 95.65% and false detection rate of 0.68/h. The good performance of this algorithm indicates the potential application for seizure monitoring in clinical practice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunyadi B, Signoretto M, Van Paesschen W, Suykens JA, Van Huffel S, De Vos M. Incorporating structural information from the multichannel EEG improves patient-specific seizure detection. Clin Neurophysiol. 2012;123(12):2352–61.
Sharma P, Khan YU, Farooq O, Tripathi M, Adeli H. A wavelet-statistical features approach for nonconvulsive seizure detection. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2014;45(4):274–84.
Fu K, Qu J, Chai Y, Zou T. Hilbert marginal spectrum analysis for automatic seizure detection in EEG signals. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2015;18:179–85.
Shoeb A, Edwards H, Connolly J, Bourgeois B, Treves ST, Guttag J. Patient-specific seizure onset detection. Epilepsy Behav. 2004;5(4):483–98.
Jr CWH, Sarkar A. Mutual information in natural position order of electroencephalogram is significantly increased at seizure onset. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2011;49(2):133–41.
Faust O, Acharya UR, Adeli H. Adeli. A Wavelet-based EEG processing for computer-aided seizure detection and epilepsy diagnosis. Seizure. 2015;26:56–64.
Qu H, Gotman J. A patient-specific algorithm for the detection of seizure onset in long-term EEG monitoring: possible use as a warning device. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1997;44:115–22.
Gotman J. Automatic recognition of epileptic seizures in the EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1982;54(5):530–40.
Khan YU, Gotman J. Wavelet based automatic seizure detection in intracerebral electroencephalogram. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114(5):898–908.
Qu H, Gotman J. A seizure warning system for long-term epilepsy monitoring. Neurology. 1995;45:2250–4.
Meier R, Dittrich H, Schulze-Bonhage A, Aertsen A. Detecting epileptic seizures in long-term human EEG: a new approach to automatic online and real-time detection and classification of polymorphic seizure patterns. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2008;25:119–31.
Zhu JD, Lin CF, Chang SH, Wang JH, Peng TI, Chien YY. Analysis of spike waves in epilepsy using Hilbert–Huang transform. J Med Syst. 2015;39(1):170.
Kalbkhani H, Shayesteh MG. Stockwell transform for epileptic seizure detection from EEG signals. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2017;38:108–18.
Hsu KC, Yu SN. Detection of seizures in EEG using subband nonlinear parameters and genetic algorithm. Comput Biol Med. 2010;40(10):823–30.
Yuan Q, Zhou W, Yuan S, Li X, Wang J, Jia G. Epileptic EEG classification based on kernel sparse representation. Int J Neural Syst. 2014;24(04):1450015.
Liu Y, Zhou W, Yuan Q, Chen S. Automatic seizure detection using wavelet transform and SVM in long-term intracranial EEG. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2012;20(6):749–55.
Logesparan L, Casson AJ, Rodriguez-Villegas E. Optimal features for online seizure detection. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2012;50(7):659–69.
Guo L, Rivero D, Pazos A. Epileptic seizure detection using multiwavelet transform based approximate entropy and artificial neural networks. J Neurosci Methods. 2010;193(1):156–63.
Chua KC, Chandran V, Acharya UR, Lim CM. Application of higher order spectra to identify epileptic EEG. J Med Syst. 2011;35(6):1563–71.
Rubner Y, Tomasi C, Guibas LJ. The earth mover’s distance as a metric for image retrieval. Int J Comput Vis. 2000;40(2):99–121.
Grauman K, Darrell T. Fast contour matching using approximate earth mover’s distance. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit. 2004;1:220–7.
Indyk P, Thaper N. Fast color image retrieval via embeddings. In: International workshop on statistical & computational theories of vision 2003.
Tan H, Ngo CW. Common pattern discovery using earth movers distance and local flow maximization. IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis. 2005;2:1222–9.
Hoffmann U, Vesin JM, Ebrahimi T, Diserens K. An efficient P300-based brain–computer interface for disabled subjects. J Neurosci Methods. 2008;167(1):115–25.
Lei X, Yang P, Yao D. An empirical Bayesian framework for brain computer interfaces. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2009;17:521–9.
Shoeb AH, Guttag JV. Application of machine learning to epileptic seizure detection. In: International conference on machine learning 2010. pp. 975–982.
Saab ME, Gotman J. A system to detect the onset of epileptic seizures in scalp EEG. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;116:427–42.
Ling H, Okada K. An efficient earth mover’s distance algorithm for robust histogram comparison. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2006;29(5):840–53.
Fathima T, Khan YU, Bedeeuzzaman M, Farooq O. Discriminant analysis for epileptic seizure detection. In: international conference on devices and communications 2011. pp. 1–5.
MacKay DJC. Bayesian interpolation. Neural Comput. 1992;4(3):415–47.
Temko A, Thomas E, Marnane W, Lightbody G, Boylan G. EEG-based neonatal seizure detection with Support Vector Machines. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011;122:464–73.
Grewal S, Gotman J. An automatic warning system for epileptic seizures recorded on intracerebral EEGs. Clin Neurophysiol. 2005;116(10):2460–72.
Wang L, Xue W, Li Y, Luo M, Huang J, Cui W, Huang C. Automatic epileptic seizure detection in EEG signals using multi-domain feature extraction and nonlinear analysis. Entropy. 2017;19(6):222.
Li Y, Wang X, Luo L, Li K, Yang X, Guo Q. Epileptic seizure classification of EEGs using time–frequency analysis based multiscale radial basis functions. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2018;22(2):386–97.
Li Y, Cui W, Luo M, Li K, Wang L. Epileptic seizure detection based on time-frequency images of EEG signals using Gaussian mixture model and gray level co-occurrence matrix features. Int J Neural Syst. 2018;28(7):1850003.
Majumdar KK, Vardhan P. Automatic seizure detection in ECoG by differential operator and windowed variance. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2011;19(4):356–65.
Nasehi S, Pourghassem H. Epileptic seizure onset detection algorithm using dynamic cascade feed-forward neural networks. In: IEEE international conference on intelligent computation and bio-medical instrumentation 2011. pp. 193–195.
Khan YU, Rafiuddin N, Farooq OAutomated seizure detection in scalp EEG using multiple wavelet scales. In: IEEE international conference on signal processing, computing and control (ISPCC) 2012. pp. 1–5.
Orosco L, Correa AG, Diez P, Laciar E. Patient non-specific algorithm for seizures detection in scalp EEG. Comput Biol Med. 2016;71(C):128–34.
Samiee K, Kovács P, Gabbouj M. Epileptic seizure detection in long-term EEG records using sparse rational decomposition and local Gabor binary patterns feature extraction. Knowl Based Syst. 2017;118:228–40.
Tsiouris ΚΜ, Markoula S, Konitsiotis S, Koutsouris DD, Fotiadis DI. A robust unsupervised epileptic seizure detection methodology to accelerate large EEG database evaluation. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2018;40:275–85.
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61701279) and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2017PF006), and jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61572284, 61502272, 61702299 and 61501283), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2015M582129).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, S., Liu, J., Shang, J. et al. The earth mover’s distance and Bayesian linear discriminant analysis for epileptic seizure detection in scalp EEG. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 8, 373–382 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-018-0082-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-018-0082-3