Abstract
Purpose
Despite advances that have been made in systemic chemotherapy, the prognosis of advanced triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients is still poor. The identification of key factors governing TNBC development is considered imperative for the development of novel effective therapeutic approaches. Previously, it has been reported that microRNA (miR)-761 may act as either a tumor suppressor or as an oncogene in different types of cancer. Here, we aimed at assessing the biological role of this miRNA in TNBC.
Methods
First, we measured the expression of miR-761 in primary breast cancer tissues and breast cancer-derived cell lines using qRT-PCR. Subsequently, over-expression and silencing experiments were performed to determine the role of miR-761 in TNBC cell proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion in vitro. The in vivo role of miR-761 in TNBC growth and metastasis was determined in mouse models. Bioinformatics analyses, dual-luciferase reporter assays, Western blot analyses and rescue experiments were performed to identify miR-761 target gene(s).
Results
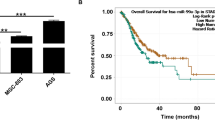
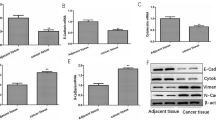
We found that miR-761 was up-regulated in primary breast cancer tissues and its derived cell lines and, particularly, in TNBC tissues and cell lines. We also found that exogenous miR-761 over-expression augmented in vitro TNBC cell proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion, whereas miR-761 down-regulation impaired these features. In vivo, we found that miR-761 over-expression facilitated TNBC growth and lung metastasis. Mechanistically, miR-761 was found to negatively regulate the expression of tripartite motif-containing 29 (TRIM29) in TNBC cells by binding to the 3′-untranslated region of its mRNA. In conformity with these results, a significant negative correlation between miR-761 expression and TRIM29 protein expression was noted in primary TNBC tissues (r = −0.452, p = 0.0126). We also found that exogenous TRIM29 over-expression reversed the proliferative and invasive capacities of TNBC cells.
Conclusions
Our data indicate that miR-761 acts as an oncogene in TNBC. This mode of action can, at least partially, be ascribed to the down-regulation of its target TRIM29. We suggest that miR-761 may serve as a promising therapeutic target for TNBC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.A. Torre, F. Bray, R.L. Siegel, J. Ferlay, J. Lortet-Tieulent, A. Jemal, Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 65, 87–108 (2015)
G. Palma, G. Frasci, A. Chirico, E. Esposito, C. Siani, C. Saturnino, C. Arra, G. Ciliberto, A. Giordano, M. D’Aiuto, Triple negative breast cancer: looking for the missing link between biology and treatments. Oncotarget 6, 26560–26574 (2015)
I. Fkih M’hamed, M. Privat, F. Ponelle, F. Penault-Llorca, A. Kenani, Y.J. Bignon, Identification of miR-10b, miR-26a, miR-146a and miR-153 as potential triple-negative breast cancer biomarkers. Cell. Oncol. 38, 433–442 (2015)
C.B. Moelans, E.J. Vlug, C. Ercan, P. Bult, H. Buerger, G. Cserni, P.J. van Diest, P.W. Derksen, Methylation biomarkers for pleomorphic lobular breast cancer - a short report. Cell. Oncol. 38, 397–405 (2015)
E. Robles-Escajeda, U. Das, N.M. Ortega, K. Parra, G. Francia, J.R. Dimmock, A. Varela-Ramirez, R.J. Aguilera, A novel curcumin-like dienone induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell. Oncol. 39, 265–277 (2016)
J. Hugh, J. Hanson, M.C. Cheang, T.O. Nielsen, C.M. Perou, C. Dumontet, J. Reed, M. Krajewska, I. Treilleux, M. Rupin, E. Magherini, J. Mackey, M. Martin, C. Vogel, Breast cancer subtypes and response to docetaxel in node-positive breast cancer: use of an immunohistochemical definition in the BCIRG 001 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 27, 1168–1176 (2009)
J. Collignon, L. Lousberg, H. Schroeder, G. Jerusalem, Triple-negative breast cancer: treatment challenges and solutions. Breast Cancer 8, 93–107 (2016)
Q. Huang, B. Xiao, X. Ma, M. Qu, Y. Li, P. Nagarkatti, M. Nagarkatti, J. Zhou, MicroRNAs associated with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 295-296, 148–161 (2016)
M. Tomasetti, M. Amati, L. Santarelli, J. Neuzil, microRNA in metabolic re-programming and their role in tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 754 (2016)
V. Taucher, H. Mangge, J. Haybaeck, Non-coding RNAs in pancreatic cancer: challenges and opportunities for clinical application. Cell. Oncol. 39, 295–318 (2016)
A. Ferraro, Altered primary chromatin structures and their implications in cancer development. Cell. Oncol. 39, 195–210 (2016)
E. Tsouko, J. Wang, D.E. Frigo, E. Aydoğdu, C. Williams, miR-200a inhibits migration of triple-negative breast cancer cells through direct repression of the EPHA2 oncogene. Carcinogenesis 36, 1051–1060 (2015)
X. Sui, X. Wang, W. Han, D. Li, Y. Xu, F. Lou, J. Zhou, X. Gu, J. Zhu, C. Zhang, H. Pan, MicroRNAs-mediated cell fate in triple negative breast cancers. Cancer Lett. 361, 8–12 (2015)
A. Yan, C. Yang, Z. Chen, C. Li, L. Cai, MiR-761 promotes progression and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting ING4 and TIMP2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 37, 55–66 (2015)
C. Shi, Z. Zhang, miR-761 inhibits tumor progression by targeting MSI1 in ovarian carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37, 5437–5443 (2016)
X. Zhou, L. Zhang, B. Zheng, Y. Yan, Y. Zhang, H. Xie, L. Zhou, S. Zheng, W. Wang, MicroRNA-761 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates tumorigenesis by targeting mitofusin-2. Cancer Sci. 107, 424–432 (2016)
K.J. Livak, T.D. Schmittgen, Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods 25, 402–408 (2001)
L. Ai, W.J. Kim, M. Alpay, M. Tang, C.E. Pardo, S. Hatakeyama, W.S. May, M.P. Kladde, C.D. Heldermon, E.M. Siegel, K.D. Brown, TRIM29 suppresses TWIST1 and invasive breast cancer behavior. Cancer Res. 74, 4875–4887 (2014)
J. Liu, B. Welm, K.M. Boucher, M.T. Ebbert, P.S. Bernard, TRIM29 functions as a tumor suppressor in nontumorigenic breast cells and invasive ER+ breast cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 180, 839–847 (2012)
P. Krishnan, S. Ghosh, B. Wang, D. Li, A. Narasimhan, R. Berendt, K. Graham, J.R. Mackey, O. Kovalchuk, S. Damaraju, Next generation sequencing profiling identifies miR-574-3p and miR-660-5p as potential novel prognostic markers for breast cancer. BMC Genomics 16, 735 (2015)
E. van Schooneveld, H. Wildiers, I. Vergote, P.B. Vermeulen, L.Y. Dirix, S.J. Van Laere, Dysregulation of microRNAs in breast cancer and their potential role as prognostic and predictive biomarkers in patient management. Breast Cancer Res. 17, 21 (2015)
R. Maqbool, R. Rashid, R. Ismail, S. Niaz, N.A. Chowdri, M.U. Hussain, The carboxy-terminal domain of connexin 43 (CT-Cx43) modulates the expression of p53 by altering miR-125b expression in low-grade human breast cancers. Cell. Oncol. 38, 443–451 (2015)
L. Ma, Y. Liu, C. Geng, X. Qi, J. Jiang, Estrogen receptor β inhibits estradiol-induced proliferation and migration of MCF-7 cells through regulation of mitofusin 2. Int. J. Oncol. 42, 1993–2000 (2013)
L. Wang, D.G. Heidt, C.J. Lee, H. Yang, C.D. Logsdon, L. Zhang, E.R. Fearon, M. Ljungman, D.M. Simeone, Oncogenic function of ATDC in pancreatic cancer through Wnt pathway activation and beta-catenin stabilization. Cancer Cell 15, 207–219 (2009)
X.M. Zhou, R. Sun, D.H. Luo, J. Sun, M.Y. Zhang, M.H. Wang, Y. Yang, H.Y. Wang, S.J. Mai, Upregulated TRIM29 promotes proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via PTEN/AKT/mTOR signal pathway. Oncotarget 7, 13634–13650 (2016)
F. Qiu, J.P. Xiong, J. Deng, X.J. Xiang, TRIM29 functions as an oncogene in gastric cancer and is regulated by miR-185. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8, 5053–5061 (2015)
P.L. Palmbos, L. Wang, H. Yang, Y. Wang, J. Leflein, M.L. Ahmet, J.E. Wilkinson, C. Kumar-Sinha, G.M. Ney, S.A. Tomlins, S. Daignault, L.P. Kunju, X.R. Wu, Y. Lotan, M.E. Liebert, M.E. Ljungman, D.M. Simeone, ATDC/TRIM29 drives invasive bladder cancer formation through miRNA-mediated and epigenetic mechanisms. Cancer Res. 75, 5155–5166 (2015)
M.R. Clarke, F.M. Imhoff, S.K. Baird, Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit breast cancer cell migration and invasion through secretion of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and -2. Mol. Carcinog. 54, 1214–1219 (2015)
Z. Li, Y. Xie, W. Sheng, J. Miao, J. Xiang, J. Yang, Tumor-suppressive effect of adenovirus-mediated inhibitor of growth 4 gene transfer in breast carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 25, 427–437 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, GC., Wang, JX., Han, ML. et al. microRNA-761 induces aggressive phenotypes in triple-negative breast cancer cells by repressing TRIM29 expression. Cell Oncol. 40, 157–166 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-016-0312-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-016-0312-6