Abstract
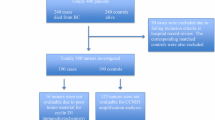
Cyclin E is an important regulator of cell cycle progression. Various studies examined the relationship between cyclin E overexpression with the clinical outcome in patients with breast cancer but yielded conflicting results. Electronic databases updated to May 2013 were searched to find relevant studies. A meta-analysis was conducted with eligible studies which quantitatively evaluated the relationship between cyclin E overexpression and survival of patients with breast cancer. Survival data were aggregated and quantitatively analyzed. We conducted a final analysis of 7,759 patients from 23 eligible studies and evaluated the correlation between cyclin E overexpression and survival in patients with breast cancer. Combined hazard ratios suggested that cyclin E overexpression had an unfavorable impact on overall survival (OS) (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.30, 95 % confidence interval (CI), 1.12–1.49) and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) (HR = 1.48, 95 % CI, 1.03–1.93), but not disease-free survival (HR = 1.11; 95 % CI, 0.96–1.27) in patients with breast cancer. Significantly, risks were found among stage I–II breast cancer for (HR = 1.75; 95 % CI, 1.30–2.19). Cyclin E overexpression is associated with poor OS and BCSS in breast cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Saurel CA, Patel TA, Perez EA. Changes to adjuvant systemic therapy in breast cancer: a decade in review. Clin Breast Cancer. 2010;10:196–208.
Colozza M, Azambuja E, Cardoso F, Sotiriou C, Larsimont D, Piccart MJ. Proliferative markers as prognostic and predictive tools in early breast cancer: where are we now? Ann Oncol. 2005;16:1723–39.
Hayes DF. Prognostic and predictive factors revisited. Breast. 2008;14:493–9.
Callagy GM, Webber MJ, Pharoah PD, Caldas C. Meta-analysis confirms BCL2 is an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:153.
Tandis SH, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 1998;48:6–29.
Qu Z, Weiss JN, MacLellan WR. Regulation of the mammalian cell cycle: a model of the G1-to-S transition. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;284:349–64.
Bortner DM, Rosenberg MP. Induction of mammary gland hyperplasia and carcinomas in transgenic mice expressing human cyclin E. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:453–9.
Ohtsubo M, Theodoras AM, Schumacher J, Roberts JM, Pagano M. Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein essential for the G1-to-S phase transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:2612–24.
Ekholm-Reed S, Mendez J, Tedesco D, Zetterberg A, Stillman B, Reed SI. Deregulation of cyclin E in human cells interferes with prereplication complex assembly. J Cell Biol. 2004;165:789–800.
Berglund P, Landberg G. Cyclin E overexpression reduces infiltrative growth in breast cancer. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(6):606–9.
Altman DG. Systematic reviews of evaluations of prognostic variables. BMJ. 2001;323(7306):224–8.
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med. 1998;17:2815–34.
Yusuf S, Peto R, Lewis J, et al. Blockade during and after myocardial infarction: an overview of the randomized trials. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1985;27:335–71.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–88.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–34.
Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994;50:1088–101.
Porter PL, Malone KE, Heagerty PJ, Alexander GM, Gatti LA, et al. Expression of cell cycle regulators p27Kip1 and cyclin E, alone and in combination, correlate with survival in young breast cancer patients. Nat Med. 1997;3(2):222–5.
Donnellan R, Kleinschmidt I, Chetty R. Cyclin E immunoexpression in breast ductal carcinoma: pathologic correlations and prognostic implications. Hum Pathol. 2001;32(1):89–94.
Kim HK, Park IA, Heo DS, Noh DY, Choe KJ, et al. Cyclin E overexpression as an independent risk factor of visceral relapse in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2001;27(5):464–71.
Bukholm IR, Bukholm G, Nesland JM. Overexpression of cyclin A is highly associated with early relapse and reduced survival in patients with primary breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 2001;93(2):283–7.
Keyomarsi K, Tucker SL, Buchholz TA, Callister M, Ding Y, et al. Cyclin E and survival in patients with breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(20):1566–75.
Span PN, Tjan-Heijnen V, Manders P, Beex LV, Sweep CG. Cyclin-E is a strong predictor of endocrine therapy failure in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 2003;22(31):4898–904.
Han S, Park K, Bae BN, Kim KH, Kim HJ, Kim YD, et al. Prognostic implication of cyclin E expression and its relationship with cyclin D1 and p27Kip1 expression on tissue microarrays of node negative breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2003;83(4):241–7.
Rudolph P, Kuhling H, Alm P, Ferno M, Baldetorp B, et al. Differential prognostic impact of the cyclins E and B in premenopausal and postmenopausal women with lymph node-negative breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2003;105(5):674–80.
Peters MG, Vidal Mdel C, Gimenez L, Mauro L, Armanasco E, et al. Prognostic value of cell cycle regulator molecules in surgically resected stage I and II breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2004;12(5):1143–50.
Foulkes WD, Brunet JS, Stefansson IM, Straume O, Chappuis PO, et al. The prognostic implication of the basal-like (cyclin E high/p27low/p53+/glomeruloid-microvascular-proliferation+) phenotype of BRCA1-related breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64(3):830–5.
Lindahl T, Landberg G, Ahlgren J, Nordgren H, Norberg T, et al. Overexpression of cyclin E protein is associated with specific mutation types in the p53 gene and poor survival in human breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25(3):375–80.
Chappuis PO, Donato E, Goffin JR, Wong N, Bégin LR, Kapusta LR, et al. Cyclin E expression in breast cancer: predicting germline BRCA1 mutations, prognosis and response to treatment. Ann Oncol. 2005;16(5):735–42.
Arnes JB, Brunet JS, Stefansson I, Bégin LR, Wong N, Chappuis PO, et al. Placental cadherin and the basal epithelial phenotype of BRCA1-related breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(11):4003–11.
Brennan DJ, Jirstrom K, Kronblad A, Millikan RC, Landberg G, Duffy MJ, et al. CA IX is an independent prognostic marker in premenopausal breast cancer patients with one to three positive lymph nodes and a putative marker of radiation resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(21):6421–31.
Callagy GM, Pharoah PD, Pinder SE, Hsu FD, Nielsen TO, Ragaz J, et al. Bcl-2 is a prognostic marker in breast cancer independently of the Nottingham Prognostic Index. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(8):2468–75.
Desmedt C, Ouriaghli FE, Durbecq V, Soree A, Colozza MA, Azambuja E, et al. Impact of cyclins E, neutrophil elastase and proteinase 3 expression levels on clinical outcome in primary breast cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2006;119(11):2539–45.
Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder ME, Timmermans M, Trapman AM, Garcia RR, et al. Which cyclin E prevails as prognostic marker for breast cancer? Results from a retrospective study involving 635 lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(11 Pt 1):3319–28.
Porter PL, Barlow WE, Yeh IT, Lin MG, Yuan XP, Donato E, et al. p27(Kip1) and cyclin E expression and breast cancer survival after treatment with adjuvant chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(23):1723–31.
Potemski P, Pluciennik E, Bednarek AK, Kusinska R, Jesionek-Kupnicka D, Pasz-Walczak G, et al. Cyclin E expression in operable breast cancer quantified using real-time RT-PCR: a comparative study with immunostaining. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2006;36(3):142–9.
Somlo G, Chu P, Frankel P, Ye W, Groshen S, Doroshow JH, et al. Molecular profiling including epidermal growth factor receptor and p21 expression in high-risk breast cancer patients as indicators of outcome. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(11):1853–9.
Potemski P, Kusińska R, Pasz-Walczak G, Piekarski JH, Watała C, Płuciennik E, et al. Prognostic relevance of cyclin E expression in operable breast cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15(2):MT34–40.
Sgambato A, Camerini A, Collecchi P, Graziani C, Bevilacqua G, Capodanno A, et al. Cyclin E correlates with manganese superoxide dismutase expression and predicts survival in early breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant epirubicin-based chemotherapy. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(6):1026–33.
Lemée F, Bergoglio V, Fernandez-Vidal A, Machado-Silva A, Pillaire MJ, Bieth A, et al. DNA polymerase theta up-regulation is associated with poor survival in breast cancer, perturbs DNA replication, and promotes genetic instability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(30):13390–5.
Koff A, Giordano A, Desai D, Yamashita K, Harper JW, et al. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992;257:1689–94.
Sauer K, Lehner CF. The role of cyclin E in the regulation of entry into S phase. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1995;1:125–39.
Malumbres M, Barbacid M. To cycle or not cycle: a critical decision in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1:222–31.
Clurman BE, Sheaff RJ, Thress K, Groudine M, Roberts JM. Turnover of cyclin E by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is regulated by cdk2 binding and cyclin phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1979–90.
Moberg KH, Bell DW, Wahrer DC, Haber DA, Hariharan IK. Archipelago regulates Cyclin E levels in Drosophila and is mutated in human cancer cell lines. Nature. 2001;413:311–6.
Wingate H, Puskas A, Duong M, Bui T, Richardson D, et al. Low molecular weight cyclin E is specific in breast cancer and is associated with mechanisms of tumor progression. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:1062–8.
Wang L, Shao ZM. Cyclin E expression and prognosis in breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis of published studies. Cancer Invest. 2006;24:581–7.
Begg CB, Berlin JA. Publication bias: a problem in interpreting medical data. J R Stat Soc A. 1988;151:419–63.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81172501).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sheng Gao and Jing-Jing Ma contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, S., Ma, JJ. & Lu, C. Prognostic value of cyclin E expression in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 34, 3423–3430 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0915-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0915-8