Abstract
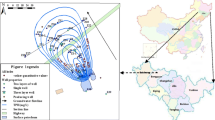
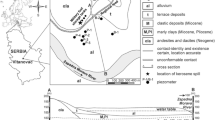
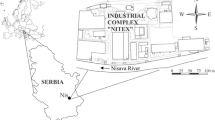
The objective of this paper was to investigate a petroleum-contaminated groundwater site in northeast China. Based on the monitoring and analysis of environmental characteristics of groundwater slightly contaminated with petroleum, microbes were added into the petroleum-contaminated groundwater via single-well and multiple-well models to enhance bioremediation. The effect of enhanced bioremediation was monitored and analyzed, and variations in the environmental characteristics of groundwater containing total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) were identified to provide a scientific basis for controlling and remediating petroleum-contaminated groundwater. Findings confirmed that this site was slightly contaminated and TPH levels exhibited a slight decreasing trend. After enhanced remediation, the microbial degradation effect was large, and the TPH concentration significantly reduced. In particular, near the wells treated by bioremediation, the amounts of electron acceptors, such as NO3 −, Fe3+, and SO4 2−, markedly decreased. The product of the microbial degradation process, HCO3 −, gradually increased in the treated wells. Activities of the enzyme catechol 1, 2-dioxygenase decreased, while those of catalase increased. Reductions in pH, from 7.4 to 6.1, were recorded, and the groundwater environment became further deoxidized.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boopathy L (2003) Use of anaerobic soil slurry reactors for the removal of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 52:162–166
Chen KF, Kao CM, Chen CW (2010) Control of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater by intrinsic and enhanced bioremediation. J Environ Sci 22:864–871
Cui ZS, Lai QL, Dong CM, Shao ZZ (2008) Biodiversity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria. Environ Microbiol 10:2138–2149
Da Silva MLB, Ruiz-Aguilar GML, Alvarez PJJ (2005) Enhanced anaerobic biodegradation of BTEX-ethanol mixtures in aquifer columns amended with sulfate, chelated ferric iron or nitrate. Biodegradation 16(2):105–114
Fan W, Yang YS, Du XQ, Lu Y, Yang MX (2011) Finger-printing biodegradation of petroleum contamination in shallow groundwater and soil system using hydro-bio-geochemical markers and modelling support. Water Air Soil Pollut 220:253–263
Fang J, Barcelona MJ, Krishnamurthy RV, Atekwana EA (2000) Stable carbon isotope biogeochemistry of a shallow sand aquifer contaminated with fuel hydrocarbons. Appl Geochem 15:157–169
Itoa H, Hosokawa R, Morikawaa M (2008) A turbine oil-degrading bacterial consortium from soils of oil fields and its characteristics. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 61:223–232
Janey V, Mark D, Eugene J (2010) Inland waterway resource and spill management needs in Southeastern USA. Diseaster Prev Manag 19(4):483–497
Jang WY, Aral MM (2009) Multiphase flow field in in situ air sparging and its effect on remediation. Transp Porous Media 76:99–119
Kumar M, Ramanathan A, Rao MS, Kumar B (2006) Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India. Environ Geol 50:1025–1039
Liang SH, Kao CM, Kuo YC (2011) In situ oxidation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater by using passive ISCO system. Water Res 45:2496–2506
Lu M, Zhang ZZ, Qiao W, Wei XF, Guan YM, Maa QX, Guan YC (2010) Remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil after composting by sequential treatment with Fenton-like oxidation and biodegradation. Bioresour Technol 101:2106–2113
Lv H, Liu MY, Su XS, Lin GY (2013) Determination of biogeochemical processes in oil-contaminated aquifer using principal component analysis. J Cent South Uni (Sci Technol) 44(8):3552–3560
Maths SE, Rasmussen TC (2006) Combining multivariate statistical analysis with geographic information systems mapping: a tool for delineating groundwater contamination. Hydrogeol J 14:1493–1507
Matteo D, Valeria T, Andrea F, Gandolfi I, Papacchini M, Careghini A, Sezenna E, Saponaro S, Bestetti G (2015) Hydrocarbon degrading microbial communities in bench scale aerobic biobarriers for gasoline contaminated groundwater treatment. Chemosphere 130:34–39
Munz G, Mannucci A, Arreola-Vargas J, Alatriste-Mondragon F, Giaccherini F, Mori G (2015) Nitrite and nitrate as electron acceptors for biological sulphide oxidation. Water Sci Technol 72(4):593–599
Naidu R, Nandy S, Megharaj M, Kumar RP, Chadalavada S, Chen ZL, Chen ZL (2012) Monitored natural attenuation of a long-term petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated sites: a case study. Biodegradation 23(6):881–895
Rowe BL, Toccalino PL, Moran MJ, Zogorski JS, Price CV (2007) Occurrence and potential human-health relevance of volatile organic compounds in drinking water from domestic wells in the United States. Environ Health Perspect 115(11):1539–1546
Ryan MP, Pembroke JT, Adley CC (2007) Ralstonia pickettii in environmental biotechnology: potential and applications. J Appl Microbiol 103(4):754–764
Su XS, Lv H, Zhang WJ, Zhang YL (2013) Evaluation of petroleum hydrocarbon biodegradation in shallow groundwater by hydrogeochemical indicators and C S-isotopes. Environ Earth Sci 69:2091–2101
Tfincsics A, Szabo I, Bake E, Szoboszlay S, Kukolya J, Kriszt B, Marialigeti K (2010) Investigation of catechol 2, 3-dioxygenase and 16S rRNA gene diversity in hypoxic, petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated groundwater. Syst Appl Microbiol 33(7):398–406
Wang W, Su XS (2012) The Research of petroleum contaminated site media for adsorption of petroleum pollutant. Adv Mater Res 2:393–395
Yang XM, Dennis B, Stephanie F, Niedermeier C (2005) Field study of pulsed air sparging for remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil and groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 39:7279–7286
Zhang ZN, Zhou QX, Peng SW, Cai Z (2010) Remediation of petroleum contaminated soils by joint action of Pharbitis nil L. and its microbial community. Sci Total Environ 408:5600–5605
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41203050) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province of China (Grant No. 20130101019JC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Qian, H., Wang, J. et al. Variations in the environmental characteristics of groundwater slightly contaminated with petroleum: effects of enhanced bioremediation in northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 76, 90 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6412-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6412-4