Abstract
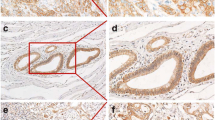
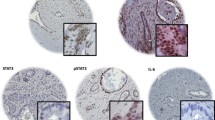
Ephrin (Eph) receptors have been reported to be frequently overexpressed in a wide variety of cancer types, being associated with tumor growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the clinical significance of Eph-A1, -A2, -A4, -A5 and -A7 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eph-A1, -A2, -A4, -A5 and -A7 expression and staining intensity were assessed immunohistochemically in tumoral samples of 67 pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients and were statistically analyzed in relation to clinicopathological characteristics, tumor proliferative capacity and patients’ survival. Eph receptors were abundantly expressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cases examined. Eph-A1 staining intensity was significantly associated with tumor size (pT, p = 0.008) and tumor histopathological stage (pStage, p = 0.012). Eph-A2 expression was significantly associated with patients’ age (p = 0.007), while Eph-A4 and Eph-A5 with tumor proliferative capacity (p = 0.019 and p = 0.011, respectively). Pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients with moderate/intense Eph-A5 or Eph-A7 staining presented significantly shorter survival times compared to those with negative/mild one (log-rank test, p = 0.024 and p = 0.009, respectively). Multivariate analysis identified Eph-A5 and Eph-A7 staining intensity as independent prognostic factors (p = 0.048 and p = 0.004, respectively). In conclusion, the present study revealed that Eph receptors were associated with pancreatic cancer characteristics, supporting evidence for their potential clinical application in management and prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Hughes SE (2006) Role of the ephrin and Ephrin receptor tyrosine kinase families in angiogenesis and development of the cardiovascular system. J Pathol 208:453–461
Pasquale EB (2008) Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell 133:38–52
Nakamoto M, Bergemann AD (2002) Diverse role for the Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases in carcinogenesis. Microscopy Res Technique 59:58–67
Surawska H, Ma PC, Salgia R (2004) The role of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15:419–433
Cheng N, Brantley DM, Chen J (2002) The ephrins and Eph receptors in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13:75–85
Brandley-Sieders DM, Chen J (2007) Eph receptor tyrosine kinase in angiogenesis: from development to disease. Angiogenesis 7:17–28
Castaño J, Davalos V, Schwartz S Jr, Arango D (2008) EPH receptors in cancer. Histol Histopathol 23:1011–1023
Ireton RC, Chen J (2005) EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising target for cancer therapeutics. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 5:149–157
Brantley-Sieders D, Schmidt S, Parker M, Chen J (2004) Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in tumor and tumor microenvironment. Curr Pharm Des 10:3431–342
Heroult M, Schaffner F, Augustin HG (2004) Eph receptor and ephrin ligand-mediated interactions during angiogenesis and tumor progression. Exp Cell Res 312:642–650
Jemal A, Siegel E, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ (2006) Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 56:106–130
Sener DB, Jessup JM, Colacchio T (1999) Pancreatic cancer: a report of treatment and survival trends for 100, 313 patients diagnosed from 1985–95, using national cancer database. J Am Coll Surg 189:1–7
Sarkar FH, Banerjee S, Li Y (2007) Pancreatic cancer: pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 224:326–336
Hamilton SR (2000) World health organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics tumours of the digestive system. IARC, Lyon
Sobin LH, Wittekind C (1997) TNM classification of malignant tumors, 5th edn. Wiley-Liss, New York
Theocharis S, Giaginis C, Chatzopoulou E, Tsourouflis G, Samiou F, Kouraklis G (2007) Clinical significance of ephrin receptor A1 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Virchows Archiv 451:374–374
Giaginis C, Vgenopoulou S, Tsourouflis G, Politi E, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S (2009) Expression and clinical significance of focal adhesion kinase in the two distinct histological types, intestinal and diffuse, of human gastric adenocarcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res 15:173–181
Giaginis C, Daskalopoulou S, Vgenopoulou S, Sfiniadakis I, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S (2009) Heat shock protein −27, −60 and −90 expression in gastric cancer: association with clinicopathological variables and patient survival. BMC Gastroenterol 9:14
Giaginis C, Davides D, Zarros A, Noussia O, Zizi-Serbetzoglou A, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S (2008) Clinical significance of tumor-associated antigen RCAS1 expression in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 53:1728–1734
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, Whang EE (2004) EphA2: a determinant of malignant cellular behavior and a potential therapeutic target in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 23:1448–1456
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, Whang EE (2004) Ligation of EphA2 by Ephrin A1-Fc inhibits pancreatic adenocarcinoma cellular invasiveness. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320:1096–1102
Mudali SV, Fu B, Lakkur SS, Luo M, Embuscado EE, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA (2006) Patterns of EphA2 protein expression in primary and metastatic pancreatic carcinoma and correlation with genetic status. Clin Exp Metastasis 23:357–365
Abraham S, Knapp DW, Cheng L, Snyder PW, Mittal SK, Bangari DS, Kinch M, Wu L, Dhariwal J, Mohammed SI (2006) Expression of EphA2 and Ephrin A-1 in carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Clin Cancer Res 12:353–360
Dong Y, Wang J, Sheng Z, Li G, Ma H, Wang X, Zhang R, Lu G, Hu Q, Sugimura H, Zhou X (2009) Downregulation of EphA1 in colorectal carcinomas correlates with invasion and metastasis. Mod Pathol 22:151–160
Saito T, Masuda N, Miyazaki T, Kanoh K, Suzuki H, Shimura T, Asao T, Kuwano H (2004) Expression of EphA2 and E-cadherin in colorectal cancer: correlation with cancer metastasis. Oncol Rep 11:605–611
Holm R, Knopp S, Suo Z, Tropè C, Nesland JM (2007) Expression of EphA2 and EphrinA-1 in vulvar carcinomas and its relation to prognosis. J Clin Pathol 60:1086–1091
Hafner C, Becker B, Landthaler M, Vogt T (2006) Expression profile of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in human skin and downregulation of EphA1 in nonmelanoma skin cancer. Mod Pathol 19:1369–1377
Li X, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhen H, Yang H, Fei Z, Zhang J, Liu W, Wang Y, Zhang X (2007) Expression of EphA2 in human astrocytic tumors: correlation with pathologic grade, proliferation and apoptosis. Tumour Biol 28:165–172
Xu F, Zhong W, Li J, Shanshen Z, Cui J, Nesland JM, Suo Z (2005) Predictive value of EphA2 and EphrinA-1 expression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 25:2943–2950
Han L, Dong Z, Qiao Y, Kristensen GB, Holm R, Nesland JM, Suo Z (2005) The clinical significance of EphA2 and Ephrin A-1 in epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Gynecol Oncol 99:278–286
Thaker PH, Deavers M, Celestino J, Thornton A, Fletcher MS, Landen CN, Kinch MS, Kiener PA, Sood AK (2004) EphA2 expression is associated with aggressive features in ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:5145–5150
Lin YG, Han LY, Kamat AA, Merritt WM, Landen CN, Deavers MT, Fletcher MS, Urbauer DL, Kinch MS, Sood AK (2007) EphA2 overexpression is associated with angiogenesis in ovarian cancer. Cancer 109:332–340
Herrem CJ, Tatsumi T, Olson KS, Shirai K, Finke JH, Bukowski RM, Zhou M, Richmond AL, Derweesh I, Kinch MS, Storkus WJ (2005) Expression of EphA2 is prognostic of disease-free interval and overall survival in surgically treated patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:226–231
Yuan W, Chen Z, Wu S, Ge J, Chang S, Wang X, Chen J, Chen Z (2009) Expression of EphA2 and E-cadherin in Gastric Cancer: Correlated with Tumor Progression and Lymphogenous Metastasis. Pathol Oncol Res (in press)
Zeng G, Hu Z, Kinch MS, Pan CX, Flockhart DA, Kao C, Gardner TA, Zhang S, Li L, Baldridge LA, Koch MO, Ulbright TM, Eble JN, Cheng L (2003) High-level expression of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Am J Pathol 163:2271–2276
Kinch MS, Moore MB, Harpole DH Jr (2003) Predictive value of the EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase in lung cancer recurrence and survival. Clin Cancer Res 9:613–618
Shao Z, Zhang WF, Chen XM (2008) Shang ZJ (2008) Expression of EphA2 and VEGF in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: correlation with the angiogenesis and clinical outcome. Oral Oncol 44:1110–1117
Kamat AA, Coffey D, Merritt WM, Nugent E, Urbauer D, Lin YG, Edwards C, Broaddus R, Coleman RL, Sood AK (2009) EphA2 overexpression is associated with lack of hormone receptor expression and poor outcome in endometrial cancer. Cancer (in press)
Miyazaki T, Kato H, Fukuchi M, Nakajima M, Kuwano H (2003) EphA2 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 103:657–663
Wang LF, Fokas E, Bieker M, Rose F, Rexin P, Zhu Y, Pagenstecher A, Engenhart-Cabillic R, An HX (2008) Increased expression of EphA2 correlates with adverse outcome in primary and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme patients. Oncol Rep 19:151–156
Wu D, Suo Z, Kristensen GB, Li S, Troen G, Holm R, Nesland JM (2004) Prognostic value of EphA2 and EphrinA-1 in squamous cell cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 94:312–319
Wang LF, Fokas E, Juricko J, You A, Rose F, Pagenstecher A, Engenhart-Cabillic R, An HX (2008) Increased expression of EphA7 correlates with adverse outcome in primary and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme patients. BMC Cancer 8:79
Iiizumi M, Hosokawa M, Takehara A, Chung S, Nakamura T, Katagiri T, Eguchi H, Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O, Nakamura Y, Nakagawa H (2006) EphA4 receptor, overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, promotes cancer cell growth. Cancer Sci 97:1211–1216
Oki M, Yamamoto H, Taniguchi H, Adachi Y, Imai K, Shinomura Y (2008) Overexpression of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA4 in human gastric cancers. World J Gastroenterol 14:5650–5656
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giaginis, C., Tsourouflis, G., Zizi-Serbetzoglou, A. et al. Clinical Significance of Ephrin (Eph)-A1, -A2, -A4, -A5 and -A7 Receptors in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 16, 267–276 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9221-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9221-6