Abstract
Objective
In this study, we evaluated the performance of a newly commercialized small-animal positron emission tomography (PET) scanner, ClairvivoPET, which provides significant advantages in spatial resolution, sensitivity, and quantitative accuracy.
Methods
This scanner consists of depth of interaction detector modules with a large axial extent of 151 mm and an external 137Cs source for attenuation correction. Physical performances, resolution, sensitivity, scatter fraction (SF), counting rate including noise equivalent count (NEC) rate, quantitative accuracy versus activity strength, and transmission accuracy, were measured and evaluated. Animal studies were also performed.
Results
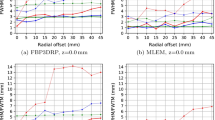
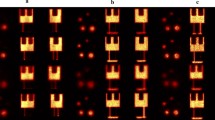
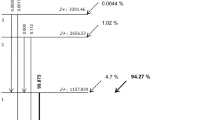
Transaxial spatial resolution, measured with a capillary tube, was 1.54 mm at the center and 2.93 mm at a radial offset of 40 mm. The absolute sensitivity was 8.2% at the center, and SFs for mouse-and rat-sized phantoms were 10.7% and 24.2%, respectively. Peak NEC rates for mouse-and rat-sized uniform cylindrical phantoms were 328 kcps at 173 kBq/ml and 119 kcps at 49 kBq/ml, respectively. The quantitative stability of emission counts against activity strength was within 2% over 5 half-lives, ranging from 0.6 MBq to 30 MBq. Transmission measurement based on segmented attenuation correction allowed 6-min and 10-min scans for mouse-and rat-sized cylindrical phantoms, respectively. Rat imaging injected with 18F-NaF resulted in visibility of fine bone structures, and mouse imaging injected with 18F-D-fluoromethyl tyrosine demonstrated the feasibility of using this system to obtain simultaneous time activity curves from separate regions, such as for the heart and tumors.
Conclusions
ClairvivoPET is well suited to quantitative imaging even with short scan times, and will provide a number of advantages in new drug development and for kinetic measurement in molecular imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weissleder R, Mahmood U. Molecular imaging. Radiology 2001;219:316–333.
Martin GP. Can small animal imaging accelerate drug development? J Cell Biochem Suppl 2002;39:211–220.
Knoess C, Siegel S, Smith A, Newport D, Richerzhagen N, Winkeler A, et al. Performance evaluation of the microPET R4 PET scanner for rodents. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:737–747.
Jin SK, Jae SL, Ki CI, Su JK, Seog-Young K, Dong SL, et al. Performance measurement of the microPET Focus 120 scanner. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1527–1535.
Yuchuan W, Jurgen S, Benjamin MW, Tsui BM, Juan JV, Martin GP. Performance evaluation of GE healthcare eXplore VISTA dual-ring small-animal PET scanner. J Nucl Med 2006;47:1891–1900.
Marc CH, Sybille R, Axel WW, Sibylle IZ, Markus S. Performance evaluation of the Philips MOSAIC small animal PET scanner. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:532–540.
Sempere Roldana P, Chereulc E, Dietzelb O, Magnierc L, Pautrota C, Rbahc L, et al. Raytest ClearPET™: a new generation small animal PET scanner. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A 2007;571:498–501.
Badawi RD, Marsden PK. Developments in component-based normalization for 3D PET. Phys Med Biol 1999;48:571–594.
Lehnert W, Meikle SR, Siegel S, Newport D, Banati RB, Rosenfeld AB. Evaluation of transmission methodology and attenuation correction for the microPET Focus 220 animal scanner. Phys Med Biol 2006;51:4003–4016.
Tanaka E, Kudo H. Subset-dependent relaxation in block-iterative algorithms for image reconstruction in emission tomography. Phys Med Biol 2003;48:1405–1422.
Defrise M, Kinahan PE, Townsend DW, Michel C, Sibomana M, Newport DF. Exact and approximate rebinning algorithms for 3-D PET data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1997;16:145–158.
National Electrical Manufacturers Association. NEMA standards publication NU 2-2001. Performance measurements of positron emission tomographs. Rosslyn: National Electrical Manufacturers Association; 2001.
Tsukada H, Sato K, Fukumoto D, Kakiuchi T. Evaluation of d-isomers of O-18F-fluoromethyl, O-18F-fluoroethyl and O-18F-fluoropropyl tyrosine as tumour imaging agents in mice. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006;33:1017–1024.
Func T, Sun M, Hasegawa BH. Radiation dose estimate in small animal SPECT and PET. Am Assoc Phys Med 2004;31:2680–2686.
Hume SP, Gunn NG, Jones T. Pharmacological constraints associated with positron emission tomographic scanning of small laboratory animals. Eur J Nucl Med 1998;25:173–176.
Goertzen AL, Young Suk J, Tompson CJ. Imaging of weaksource distributions in LSO-based small-animal PET scanners. J Nucl Med 2007;48:1692–1698.
Leeta AG, Sanjiv SG, Ashok S, Pranab KB, Carl KH, Simon RC, et al. Noninvasive methods for quantitating blood time activity curves from mouse PET images obtained with fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose. J Nucl Med 1998;39:729–734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizuta, T., Kitamura, K., Iwata, H. et al. Performance evaluation of a high-sensitivity large-aperture small-animal PET scanner: ClairvivoPET. Ann Nucl Med 22, 447–455 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-008-0127-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-008-0127-2