Abstract
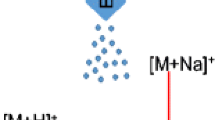
The paper presents the results of studying the system of a liquid chromatograph (LC) coupling with an ion-mobility spectrometer (IMS) with orthogonal electrostatic deflection of ions obtained by the electrospray method at high flow rates of the liquid under analysis (200 to 300 microL/min), which ensures stable operation of the LC/IMS analytical setup without separating the liquid flow leaving the liquid chromatograph column.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksandrov ML, Gall’ LN, Krasnov NV, Nikolaev VI, Pavlenko VA, Shkurov VA (1984) Ion extraction from solution at the atmospheric pressure as a new mass-spectroscopy technique. J Anal Chem (in Russian) 9:1596–1602
Clinton A, Christopher K, Osgood M, Wu J, Wu C (2009) High resolution electrospray ionization ion mobility spectrometry. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 12:33–37
Dahl DA (2000) SIMION 7 User’s Manual. Idaho National Engineering Lab
Eiceman GA, Karpas Z (2005) Ion mobility spectrometry, 2nd edn. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton
Gieniec J, Cox HL Jr, Dole M (1972) Enhanced Electrospray Ionization for mass spectrometry and ion mobility spectrometry. Conference on MS and Allied Topics, Dallas, 216
Hill HH Jr, Siems WF, Eatherton RL, St. Louis RH, Morrissey MA, Shumate CB, McMinn DG (1992) Gas, supercritical fluid, and liquid chromatographic detection of trace organics by ion mobility spectrometry. Instr. for Trace Organic Monitoring, Lewis: Chelsea, Mich, 49–64
Kebarle P, Ho Y (1997) In: Cole RB (ed) Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: fundamentals, instrumentation and applications. Wiley, New York
Krasnov NV, YaI P, Samokish AV, Samokish VA, Khasin YI (2007) The resolving power of the ion mobility spectrometer with double consecutive ion separation at corona discharge ionization. Nauchnoe Priborostroenie (Research Instrumentation in Russian) 1:40–48
Kurnin IV, Samokish VA, Krasnov NV (2010) Simulation of operation of the ion-mobility spectrometer with the Bradbury-Nielsen ion gate. Nauchnoe Priborostroenie (Research Instrumentation in Russian ) 3:14–21
McDaniel EW, Mason EA (1976) The mobility and diffusion of ions in gases. Willey, New York, 1973
Reese CS, Taraszewsky SJ, Limero TF (1999) Near-real-time analysis of toxicologically important compounds using the volatile organic analyzer for the international space station, in: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on IMS, Buxton, UK
Shumate CB, Hill HH Jr (1989) Coronaspray nebulization and ionization of liquid samples for ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Chem 61:601–606
Smith RD, Loo JA, Loo RRO, Bussmann M, Udseth HR (1991) Hydrogen/Deuterium exchange electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: a method for probing protein conformational changes in solution. Mass Spectrom Rev 10:359–451
Smith RD, Loo JA, Loo RRO, Udseth HR (1992) Combined ion mobility/time-of-flight mass spectrometry study of electrospray-generated ions. Mass Spectrom Rev 11:434–443
Tadjimukhamedov FK, Stone JA, Papanastasiou D, Rodriguez JE, Mueller W, Sukumar H, Eiceman GA (2008) Liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization/ion mobility spectrometry of chlorophenols with full flow from large bore LC columns. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 11:51–60
Wittmer D, Chen YH, Luckenbill WK, Hill HH Jr (1994) Electrospray ionization Ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Chem 66:2348–2355
Acknowledgments
The work was performed under the State Contract in the scope of Federal Program “National System of Chemical and Biological Safety of the Russian Federation (2009–2014)”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The paper presents the results of studying the system of a liquid chromatograph (LC) coupling with an ion-mobility spectrometer (IMS) with orthogonal electrostatic deflection of ions obtained by the electrospray method at high flow rates of the liquid under analysis (200 to 300 microL/min), which ensures stable operation of the LC/IMS analytical setup without separating the liquid flow leaving the liquid chromatograph column.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurnin, I.V., Kayumov, A.A., Muradymov, M.Z. et al. Coupling of liquid chromatograph with ion-mobility spectrometer. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spec. 16, 169–176 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-012-0110-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-012-0110-4