Abstract
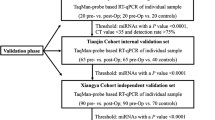
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common mesenchymal tumor of the intestinal tract. Imatinib is used as first-line therapy for GIST patients; however, secondary imatinib resistance poses a significant clinical challenge. Here, we analyzed serum miRNA expression profiles to identify specific serum miRNAs that could be used as early diagnostic markers. Candidate miRNAs were validated using Taqman quantitative PCR with serum samples from secondary imatinib-resistant GIST patients (n = 39), imatinib-sensitive GIST patients (n = 37), and healthy controls (n = 28). Serum miR-518e-5p and miR-548e levels were higher in secondary imatinib-resistant GIST than imatinib-sensitive GIST patients or healthy controls (P < 0.0001). However, ROC analysis indicated that only miR-518e-5p could distinguish imatinib-resistant GIST. To discriminate imatinib-resistant from imatinib-sensitive GIST patients, the AUC for serum miR-518e-5p was 0.9938, with 99.8% sensitivity and 82.1% specificity. Serum miR-518e-5p could also discriminate imatinib-resistant GIST patients from healthy controls with 99.9% sensitivity and 97.4% specificity. These data indicate that serum miR-518e-5p is a potentially promising non-invasive biomarker for early detection and diagnosis of secondary imatinib-resistant GIST.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcakaya P, Caramuta S, Åhlen J, Ghaderi M, Berglund E, Östman A, Branstron R, et al. 2014 microRNA expression signatures of gastrointestinal stromal tumours: associations with imatinib resistance and patient outcome. Br. J. Cancer 111 2091–2102
Antonescu CR 2011 The GIST paradigm: lessons for other kinase-driven cancers. J. Pathol. 223 251–261
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, et al. 2002 Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 15524–15529
Choi H 2008 Response evaluation of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncologist 13 Suppl 2: 4–7
Chun-Zhi Z, Lei H, An-Ling Z, Yan-Chao F, Xiao Y, Guang-Xiu W, Zhi-Fan J, et al. 2010 MicroRNA-221 and microRNA-222 regulate gastric carcinoma cell proliferation and radioresistance by targeting PTEN. BMC Cancer 10 367
Corless CL, Barnett CM and Heinrich MC 2011 Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: Origin and molecular oncology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 11 865–878
Debiec-Rychter M, Dumez H, Judson I, Wasag B, Verweij J, Brown M, Dimitrijevic S, et al. 2004 Use of c-KIT/PDGFRA mutational analysis to predict the clinical response to imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours entered on phase I and II studies of the EORTC Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group. Eur. J. Cancer 40 689–695
Dematteo RP, Heinrich MC, El-Rifai WM and Demetri G 2002 Clinical management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Before and after STI-571. Hum. Pathol. 33 466–477
Erinn DK and Brian PR 2011 Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Molecular mechanisms and targeted therapies. Patholog. Res. Int. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/708596
Fan R, Zhong J, Zheng S, Wang Z, Xu Y, Li S, Zhou J, et al. 2014 microRNA-218 increase the sensitivity of gastrointestinal stromal tumor to imatinib through PI3K/AKT pathway. Clin. Exp. Med. 15 137–144
Gao X, Shen K, Wang C, Ling J, Wang H, Fang Y, Shi Y, et al. 2014 MiR-320a downregulation is associated with imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 46 72–75
Haller F, von Heydebreck A, Zhang JD, Gunawan B, Langer C, Ramadori G, Wiemann S, et al. 2010 Localization- and mutation-dependent microRNA (miRNA) expression signatures in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs), with a cluster of co-expressed miRNAs located at 14q32.31. J. Pathol. 220 71–86
Heinrich MC, Griffith DJ, Druker BJ, Wait CL, Ott KA and Zigler AJ 2000 Inhibition of c-kit receptor tyrosine kinase activity by STI 571, a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Blood 96 925–932
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Demetri GD, Blanke CD, von Mehren M, Joensuu H, McGreevey LS, et al. 2003 Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 21 4342–4349
Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, Hashimoto K, Nishida T, Ishiguro S, Kawano K, et al. 1998 Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 279 577–580
Homick JL and Fletcher CD 2007 The role of KIT in the management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Hum. Pathol. 38 679–687
Jackson RJ and Standart N 2007 How do microRNAs regulate gene expression? Sci. STKE 2007 re1
Kang HJ, Nam SW, Kim H, Rhee H, Kim NG, Hyung WJ, Noh SH, et al. 2005 Correlation of KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha mutations with gene activation and expression profiles in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncogene 24 1066–1074
Kim WK, Park M, Kim YK, Tae YK, Yang HK, Lee JM and Kim H 2011 MicroRNA-494 downregulates KIT and inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell proliferation. Clin. Cancer Res. 17 7584–7594
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V 1993 The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75 843–854
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, et al. 2005 MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435 834–838
Michael MZ, O’Connor SM, van Holst Pellekaan NG, Young GP and Lames RJ 2003 Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol. Cancer Res. 1 882–891
Mol CD, Dougan DR, Schneider TR, Skene RJ, Kraus ML, Scheibe DN, Snell GP, et al. 2004 Structural basis for the autoinhibition and STI-571 inhibition of c-Kit tyrosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 279 31655–31663
Panarelli NC and Yantiss RK 2011 MicroRNA expression in selected carcinomas of the gastrointestinal tract. Patholog. Res. Int. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/124608.
Saleem TB and Ahmed I 2009 Gastrointestinal stromal tumor-evolving concepts. Surgeon 7 36–41
Shi Y, Gao X, Hu Q, Li X, Xu J, Lu S, Liu Y, et al. 2016 PIK3C2A is a gene-specific target of microRNA-518a-5p in imatinib mesylate-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Lab Invest. 96 652–660
Song B and Ju J 2011 Impact of miRNAs in gastrointestinal cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Exp. Rev. Mol. Med. 12 e33
Tuveson DA, Willis NA, Jacks T, Griffin JD, Singer S, Fletcher CD, Fletcher JA, et al. 2001 STI571 inactivation of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor c-KIT oncoprotein: Biological and clinical implications. Oncogene 20 5054–5058
Valladares-Ayerbes M, Blanco M, Haz M, Medina V, Iglesias-Diaz P, Lorenzo-Patino MJ, Reboredo M, et al. 2011 Prognostic impact of disseminated tumor cells and microRNA-17-92 cluster deregulation in gastrointestinal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 39 1253–1264
Xie L, Qian X and Liu B 2010 MicroRNAs: novel biomarkers for gastrointestinal carcinomas. Mol. Cell Biochem. 341 291–299
Yan X, Cen Y and Wang Q 2016 Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental rheumatoid arthritis through microRNA-regulated IkB expression. Sci. Rep. 29 28915
Yao Y, Suo AL, Li ZF, Liu LY, Tian T, Ni L, Zhang WG, et al. 2009 MicroRNA profiling of human gastric cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2 963–970
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Weiwei Li from Beijing Microread Genetics Co., Ltd., for providing technical support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Sorab Dalal.
Corresponding editor: Sorab Dalal
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kou, Y., Yang, R. & Wang, Q. Serum miR-518e-5p is a potential biomarker for secondary imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Biosci 43, 1015–1023 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-018-9805-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-018-9805-y