Abstract
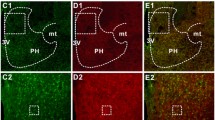
Relaxin-3 (RLN3) is a neuropeptide belonging to the insulin–relaxin superfamily. RLN3-expressing neurons are predominantly located in the dorsal pons known as the nucleus incertus, and project their axons to the forebrain including the hypothalamus. RLN3 has been suggested to be involved in the stress response. In the present study, we investigated the hypothalamic action of RLN3 in the stress-response system by intracerebroventricular (icv) administration of RLN3. Compared with saline icv injection, 1 nmol icv RLN3 injection induced c-Fos expression in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) at 1 h after administration. Some RLN3-induced c-Fos-positive cells in the PVN were also corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-expressing neurons. CRF and c-fos mRNA levels in the PVN were increased at 2 h after RLN3 administration. Plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) levels were also increased after RLN3 administration. These results suggest that RLN3 is able to stimulate the hypothalamopituitary CRF–ACTH system during the acute response.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaya F, Tanaka M, Hayashi S et al (2001) Hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis sensitization after chronic salt loading. Neuroendocrinology 73:185–193
Banerjee A, Shen PJ, Ma S et al (2010) Swim stress excitation of nucleus incertus and rapid induction of relaxin-3 expression via CRF1 activation. Neuropharmacology 58:145–155
Bathgate RA, Samuel CS, Burazin TC et al (2002) Human relaxin gene 3 (H3) and the equivalent mouse relaxin (M3) gene. Novel members of the relaxin peptide family. J Biol Chem 277:1148–1157
Bathgate RA, Ivell R, Sanborn BM et al (2005) Receptors for relaxin family peptides. Ann NY Acad Sci 1041:61–76
Blume A, Torner L, Liu Y et al (2009) Prolactin activates mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and corticotropin releasing hormone transcription in rat hypothalamic neurons. Endocrinology 150:1841–1849
Boels K, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Schaller HC (2004) Identification of a mouse orthologue of the G-protein-coupled receptor SALPR and its expression in adult mouse brain and during development. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 152:265–268
Burazin TC, Bathgate RA, Macris M et al (2002) Restricted, but abundant, expression of the novel rat gene-3 (R3) relaxin in the dorsal tegmental region of brain. J Neurochem 82:1553–1557
Chen J, Kuei C, Sutton SW et al (2005) Pharmacological characterization of relaxin-3/INSL7 receptors GPCR135 and GPCR142 from different mammalian species. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:83–95
Emanuel RL, Girard DM, Thull DL et al (1990) Second messengers involved in the regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA and peptide in cultured rat fetal hypothalamic primary cultures. Endocrinology 126:3016–3021
Hida T, Takahashi E, Shikata K et al (2006) Chronic intracerebroventricular administration of relaxin-3 increases body weight in rats. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 26:147–158
Kizawa H, Nishi K, Ishibashi Y et al (2003) Production of recombinant human relaxin 3 in AtT20 cells. Regul Pept 113:79–84
Liu C, Eriste E, Sutton S et al (2003) Identification of relaxin-3/INSL7 as an endogenous ligand for the orphan G-protein-coupled receptor GPCR135. J Biol Chem 278:50754–50764
Liu C, Chen J, Kuei C et al (2005) Relaxin-3/insulin-like peptide 5 chimeric peptide, a selective ligand for G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)135 and GPCR142 over leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 7. Mol Pharmacol 67:231–240
Ma S, Shen PJ, Burazin TC et al (2006) Comparative localization of leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor-7 (RXFP1) mRNA and [33P]-relaxin binding sites in rat brain: restricted somatic co-expression a clue to relaxin action? Neuroscience 141:329–344
Ma S, Bonaventure P, Ferraro T et al (2007) Relaxin-3 in GABA projection neurons of nucleus incertus suggests widespread influence on forebrain circuits via G-protein-coupled receptor-135 in the rat. Neuroscience 144:165–190
Ma S, Olucha-Bordonau FE, Hossain MA et al (2009) Modulation of hippocampal theta oscillations and spatial memory by relaxin-3 neurons of the nucleus incertus. Learn Mem 16:730–742
Maruyama M, Matsumoto H, Fujiwara K et al (2001) Prolactin-releasing peptide as a novel stress mediator in the central nervous system. Endocrinology 142:2032–2038
Matsumoto M, Kamohara M, Sugimoto T et al (2000) The novel G-protein coupled receptor SALPR shares sequence similarity with somatostatin and angiotensin receptors. Gene 248:183–189
McGowan BM, Stanley SA, Smith KL et al (2005) Central relaxin-3 administration causes hyperphagia in male Wistar rats. Endocrinology 146:3295–3300
McGowan BM, Stanley SA, White NE et al (2007) Hypothalamic mapping of orexigenic action and Fos-like immunoreactivity following relaxin-3 administration in male Wistar rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E913–E919
Otsubo H, Onaka T, Suzuki H et al (2010) Centrally administered relaxin-3 induces Fos expression in the osmosensitive areas in rat brain and facilitates water intake. Peptides 31:1124–1130
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in sterotaxic coordinates, Fourthth edn. Academic, San Diego
Sutton SW, Bonaventure P, Kuei C et al (2004) Distribution of G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)135 binding sites and receptor mRNA in the rat brain suggests a role for relaxin-3 in neuroendocrine and sensory processing. Neuroendocrinology 80:298–307
Tanaka M, Iijima N, Amaya F et al (1999) NGFI-A gene expression induced in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus by photic stimulation: spread into hypothalamic periventricular somatostatin neurons and GABA receptor involvement. Eur J Neurosci 11:3178–3184
Tanaka M, Iijima N, Miyamoto Y et al (2005) Neurons expressing relaxin 3/INSL 7 in the nucleus incertus respond to stress. Eur J Neurosci 21:1659–1670
Tanaka M, Watanabe Y, Yoshimoto K (2009) Regulation of relaxin 3 gene expression via cAMP-PKA in a neuroblastoma cell line. J Neurosci Res 87:820–829
van der Westhuizen ET, Werry TD, Sexton PM et al (2007) The relaxin family peptide receptor 3 activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 through a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism. Mol Pharmacol 71:1618–1629
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Nishi for providing us human RLN3. This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan for M.T. (No. 21500329), and the Research Project in Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine Research Institute for Neurological Diseases and Geriatrics to M.T.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This manuscript is prepared for the special issue of GPCR2010
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, Y., Miyamoto, Y., Matsuda, T. et al. Relaxin-3/INSL7 Regulates the Stress-response System in the Rat Hypothalamus. J Mol Neurosci 43, 169–174 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9468-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9468-0