Abstract
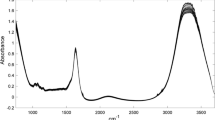
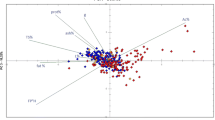
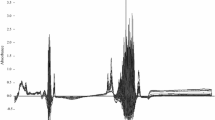
The dairy industry is continuously developing new strategies to obtain healthier dairy products preserving expected properties. However, when modifying a food process, the reassessment of each parameters and their interaction should be considered as highly influencing the final quality. Among others, rennet process features are fundamental for both sensory properties and typical characteristics of a cheese. In this contest, the research addresses the development of a FT-NIR spectroscopic method, coupled with chemometrics, for the study of the effect of process variables on milk renneting. The effects of temperature (30 °C, 35 °C, 40 °C), milk fat concentration (0.1, 2.55, 5 g/100 mL), and pH (6.3, 6.5, 6.7) were investigated by means of a Box-Behnken experimental design. FT-NIR data collected along the 17 trials were explored by interval-PCA (i-PCA) and ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis (ASCA). i-PCA revealed differences in the occurrence and trends of coagulation phases, related to the three considered factors. ASCA allowed the characterization of renneting evolution and the assessment of the factor role, demonstrating that main and interaction effects are significant for the process progress. The proposed approach demonstrated that i-PCA and ASCA on FT-NIR data, highlighting the effects of the operating factors, allow a rapid and accurate analysis of process modifications in cheese manufacturing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aernouts, B., Van Beers, R., Watté, R., Huybrechts, T., Lammertyn, J., & Saeys, W. (2015). Visible and near-infrared bulk optical properties of raw milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 98(10), 6727–6738.
Brandao, M. C. P., Carmo, A., Bell, M. J. V., & Anjos, V. C. (2010). Characterization of milk by infrared spectroscopy. Revista do Instituto de Laticicinos “Cândido Tostes”, 373(65), 30–33.
Bratchell, N. (1989). Multivariate response surface modelling by principal component analysis. Journal of Chemometrics, 3(4), 579–588.
Cabassi, G., Profaizer, M., Marinoni, L., Rizzi, N., & Cattaneo, T. M. (2013). Estimation of fat globule size distribution in milk using an inverse light scattering model in the near infrared region. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy, 21(5), 359–373.
Cama-Moncunill, R., Markiewicz-Keszycka, M., Dixit, Y., Cama-Moncunill, X., Casado-Gavalda, M. P., Cullen, P. J., & Sullivan, C. (2016). Multipoint NIR spectroscopy for gross composition analysis of powdered infant formula under various motion conditions. Talanta, 154, 423–430.
Cattaneo, T. M., Giardina, C., Sinelli, N., Riva, M., & Giangiacomo, R. (2005). Application of FT-NIR and FT-IR spectroscopy to study the shelf-life of Crescenza cheese. International Dairy Journal, 15(6-9), 693–700.
Cattaneo, T. M., Cabassi, G., Profaizer, M., & Giangiacomo, R. (2009). Contribution of light scattering to near infrared absorption in milk. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy, 17(6), 337–343.
Cipolat-Gotet, C., Cecchinato, A., De Marchi, M., Penasa, M., & Bittante, G. (2012). Comparison between mechanical and near-infrared methods for assessing coagulation properties of bovine milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 95(11), 6806–6819.
Čurda, L., & Kukačková, O. (2004). NIR spectroscopy: a useful tool for rapid monitoring of processed cheeses manufacture. Journal of Food Engineering, 61(4), 557–560.
De Luca, S., De Filippis, M., Bucci, R., Magrì, A. D., Magrì, A. L., & Marini, F. (2016). Characterization of the effects of different roasting conditions on coffee samples of different geographical origins by HPLC-DAD, NIR and chemometrics. Microchemical Journal, 129, 348–361.
Downey, G., Sheehan, E., Delahunty, C., O’Callaghan, D., Guinee, T., & Howard, V. (2005). Prediction of maturity and sensory attributes of Cheddar cheese using near-infrared spectroscopy. International Dairy Journal, 15(6-9), 701–709.
Engel, J., Blanchet, L., Bloemen, B., Van den Heuvel, L. P., Engelke, U. H. F., Wevers, R. A., & Buydens, L. M. C. (2015). Regularized MANOVA (rMANOVA) in untargeted metabolomics. Analytica Chimica Acta, 899, 1–12.
Grassi, S., Alamprese, C., Bono, V., Casiraghi, E., & Amigo, J. M. (2014). Modelling milk lactic acid fermentation using multivariate curve resolution-alternating least squares (MCR-ALS). Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(6), 1819–1829.
Grassi, S., Lyndgaard, C. B., Rasmussen, M. A., & Amigo, J. M. (2017). Interval ANOVA simultaneous component analysis (i-ASCA) applied to spectroscopic data to study the effect of fundamental fermentation variables in beer fermentation metabolites. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 163, 86–93.
Harrington, P. d. B., Vieira, N. E., Chen, P., Espinoza, J., Nien, J. K., Romero, R., & Yergey, A. L. (2005). Analysis of variance–principal component analysis: A soft tool for proteomic discovery. Analytica chimica acta, 544(1–2),118–127.
Henihan, L. E., O’Donnell, C. P., Esquerre, C., Murphy, E. G., & O’Callaghan, D. J. (2018). Quality assurance of model infant milk formula using a front-face fluorescence process analytical tool. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(7), 1402–1411.
Holroyd, S. E. (2013). The use of near infrared spectroscopy on milk and milk products. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy, 21(5), 311–322.
Imram, N. (1999). Visual texture perception in formulated chilled dairy desserts. British Food Journal, 101(1), 22–31.
Jackson, J. (1980). Principal components and factor analysis: part I—principal components. Journal of Quality Technology, 12(4), 201–213.
Jansen, J. J., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., van der Greef, J., Timmerman, M. E., Westerhuis, J. A., & Smilde, A. K. (2005). ASCA: analysis of multivariate data obtained from an experimental design. Journal of Chemometrics, 19(9), 469–481.
Johnson, M. E., Chen, C. M., & Jaeggi, J. J. (2001). Effect of rennet coagulation time on composition, yield, and quality of reduced-fat cheddar cheese. Journal of Dairy Science, 84(5), 1027–1033.
Kasemsumran, S., Thanapase, W., & Kiatsoonthon, A. (2007). Feasibility of near-infrared spectroscopy to detect and to quantify adulterants in cow milk. Analytical Sciences, 23(7), 907–910.
Kirk, R. E. (1982). Experimental design. Hoboken: Wiley.
Kondakci, T., & Zhou, W. (2017). Recent applications of advanced control techniques in food industry. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10(3), 522–542.
Laporte, M. F., Martel, R., & Paquin, P. (1998). The near-infrared optic probe for monitoring rennet coagulation in cow’s milk. International Dairy Journal, 8(7), 659–666.
Logan, A., Day, L., Pin, A., Auldist, M., Leis, A., Puvanenthiran, A., & Augustin, M. A. (2014). Interactive effects of milk fat globule and casein micelle size on the renneting properties of milk. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 7(11), 3175–3185.
Marini, F., de Beer, D., Joubert, E., & Walczak, B. (2015). Analysis of variance of designed chromatographic data sets: The analysis of variance-target projection approach. Journal of Chromatography A, 1405, 94–102.
Martin, B., Chamba, J. F., Coulon, J. B., & Perreard, E. (1997). Effect of milk chemical composition and clotting characteristics on chemical and sensory properties of Reblochon de Savoie cheese. Journal of Dairy Research, 64(1), 157–162.
Nelson, D. L. (2018). Introduction to spectroscopy. In A. S. Franca & L. Nollet (Eds.), Spectroscopic methods in food analysis (pp. 3–33). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Núñez-Sánchez, N., Martínez-Marín, A. L., Polvillo, O., Fernández-Cabanás, V. M., Carrizosa, J., Urrutia, B., & Serradilla, J. M. (2016). Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for the determination of the milk fat fatty acid profile of goats. Food Chemistry, 190, 244–252.
Sbodio, O. A., Tercero, E. J., Coutaz, R., & Martinez, E. (2002). Optimizing processing conditions for milk coagulation using the hot wire method and response surface methodology. Journal of Food Science, 67(3), 1097–1102.
Shao, Y., & He, Y. (2009). Measurement of soluble solids content and pH of yogurt using visible/near infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2(2), 229–233.
Smilde, A. K., Jansen, J. J., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Lamers, R. J. A. N., van der Greef, J., & Timmerman, M. E. (2005). ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis (ASCA): A new tool for analyzing designed metabolomics data. Bioinformatics, 21(13), 3043–3048.
Ståhle, L., & Wold, S. (1990). Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA). Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 9(2), 127–141.
Subramanian, A., Prabhakar, V., & Rodriguez-Saona, L. (2011). Analytical methods: Infrared spectroscopy in dairy analysis. In Encyclopedia of dairy sciences (2nd ed., pp. 115–124). Cambridge: Academic Press.
Tsenkova, R., Atanassova, S., Itoh, K., Ozaki, Y., & Toyoda, K. (2000). Near infrared spectroscopy for biomonitoring: cow milk composition measurement in a spectral region from 1,100 to 2,400 nanometers. Journal of Animal Science, 78(3), 515–522.
Ullah, I., & Jones, B. (2015). Regularised manova for high-dimensional data. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Statistics, 57(3), 377–389.
Visentin, G., McDermott, A., McParland, S., Berry, D. P., Kenny, O. A., Brodkorb, A., Fenelon, M. A., & De Marchi, M. (2015). Prediction of bovine milk technological traits from mid-infrared spectroscopy analysis in dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science, 98(9), 6620–6629.
Wang, Y., Ding, W., Kou, L., Li, L., Wang, C., & Jurick, W. M. (2015). A non-destructive method to assess freshness of raw bovine milk using FT-NIR spectroscopy. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(8), 5305–5310.
Wittrup, C., & Nørgaard, L. (1998). Rapid near infrared spectroscopic screening of chemical parameters in semi-hard cheese using chemometrics. Journal of Dairy Science, 81(7), 1803–1809.
Woodcock, T., Fagan, C. C., O’Donnell, C. P., & Downey, G. (2008). Application of near and mid-infrared spectroscopy to determine cheese quality and authenticity. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1(2), 117–129.
Workman, J., & Weyer, L. (2007). Practical guide to interpretive near-infrared spectroscopy. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Zoon, P., van Vliet, T., & Walstra, P. (1988). Rheological properties of rennet-induced skim milk gels. 2. The effect of temperature. Netherlands Milk and Dairy Journal, 42, 271–294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strani, L., Grassi, S., Casiraghi, E. et al. Milk Renneting: Study of Process Factor Influences by FT-NIR Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Food Bioprocess Technol 12, 954–963 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02266-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02266-2