Abstract
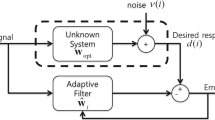
The white noise deconvolution or input white noise estimation problem has important applications in oil seismic exploration, communication and signal processing. By the modern time series analysis method, based on the autoregressive moving average (ARMA) innovation model, a new information fusion white noise deconvolution estimator is presented for the general multisensor systems with different local dynamic models and correlated noises. It can handle the input white noise fused filtering, prediction and smoothing problems, and it is applicable to systems with colored measurement noises. It is locally optimal, and is globally suboptimal. The accuracy of the fuser is higher than that of each local white noise estimator. In order to compute the optimal weights, the formula computing the local estimation error cross-covariances is given. A Monte Carlo simulation example for the system with Bernoulli-Gaussian input white noise shows the effectiveness and performances.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. M. Mendel. White-estimators for seismic data processing in oil exploration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1977, 22(5):694–706.
J. M. Mendel. Minimum variance deconvolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1981, 19(3): 161–171.
J. M. Mendel. Optimal Seismic Deconvolution and Estimation-Based Approach[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1983.
J. M. Mendel, J. Kormylo. New fast optimal white-noise estimators for deconvolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience Electronics, 1977, 15(1): 32–41.
J. Kormylo, J. M. Mendel. Maximum likelihood detection and estimation of Bernoulli-Gaussian processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1982, 28(3): 482–488.
J. M. Mendel. Lessons in Estimation Theory for Signal Processing, Communication, and Control[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1995.
Z. Deng, H. Zhang, S. Liu, et al. Optimal and self tuning white noise estimators with approach to deconvolution and filtering problem[J]. Automatica, 1996, 32(2): 199–216.
Z. Deng, Y. Gao, L. Mao, et al. New approach to information fusion steady-state Kalman filtering[J]. Automatica, 2005, 41(10): 1695–1707.
Z. Deng, Y. Li, X. Wang. Multisensor optimal information fusion white noise deconvolution filter[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2006, 23(3): 439–442 (in Chinese).
S. Sun. Multi-sensor infomration fusion white noise filter weighted by scalars based on Kalman predictor[J]. Automatica, 2005, 127(4):1447–1453.
S. Sun. Multisensor optimal information fusion input white noise deconvolution estimators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B: Cybernetics, 2004, 34(4): 1886–1893.
X. Sun, J. Wang, Z. Deng. Globally optimal weighted measurement fusion white noise deconvolution estimator for time-varying systems[C]//Proceedings of the 25th Chinese Control Conference. Beijing: Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press, 2006: 399–402.
X. Sun, Y. Gao, Z. Deng. Multisensor information fusion white noise deconvolution smoother[C]//2007 IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2007: 1741–1746.
X. Sun, Y. Gao, Z. Deng. Information fusion white noise deconvolution estimators for time-varying systems[J]. Signal Processing, 2008, 88(5): 1233–1247.
M. Gevers, W. R. E. Wouters. An innovation approach to the discretetime realization problem[J]. Quarterly Journal of Automatica, 1978, 28(2): 90–109.
Z. Deng. Unifying and universal optimal white noise estimators for time-varying systems[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2003, 21(1):143–146 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.60874063), Science and Technology Research Foudation of Heilongjiang Education Department (No.11523037) and Automatic Control Key Laboratory of Heilongjiang University.
Xiaojun SUN was born in Harbin, China in 1980. She received the B.S. degree and M.S. degree from the Department of Automation, Heilongjiang University in 2003 and 2006, respectively. She is now a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Automation, Heilongjiang University. From July 2003, she has been an assistant professor at the Applied Technology College, Heilongjiang University. She is now an instructor at the Applied Technology College, Heilongjiang University. Her main research interests are state estimation, optimal filtering and information fusion.
Shigang WANG was born in Harbin, China in 1979. He received the B.S. degree and M.S. degree from the Department of Automation, Heilongjiang University in 2003 and 2008, respectively. He is now an assistant professor at the Applied Technology College, Heilongjiang University. His main research interests are state estimation, optimal filtering and information fusion.
Zili DENG was born in Harbin, China in 1938. He graduated from the Department of Mathematics, Heilongjiang University, China, in 1962. From 1978, he was an instructor at the Department of Mathematics, Heilongjiang University. In 1982, he became an associate professor of Automatic Control at the Institute of Applied Mathematics, Heilongjiang University, where he has been a professor of Automatic Control since 1985. Currently, he is a professor at the Department of Automation, Heilongjiang University. He has published more than 400 papers and 7 books in the fields of optimal filtering, self-tuning filtering, time series analysis, and multisensor information fusion. He is the author of the books “Kalman Filtering and Wiener Filtering-Modern Time Series Analysis Method” (2001), “Self-tuning Filtering Theory with Applications-Modern Time Series Analysis Method” (2003), “Optimal Estimation Theory with Application-Modeling, Filtering, Information Fusion Estimation” (2005), and “Information Fusion Filtering Theory and Applications” (2007). His research interests include optimal and self-tuning filtering, deconvolution, state estimation, signal processing, estimation theory, identification, time-series analysis and multisensor information fusion.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Wang, S. & Deng, Z. A new information fusion white noise deconvolution estimator. J. Control Theory Appl. 7, 438–444 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-009-7154-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-009-7154-y