Abstract
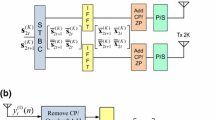
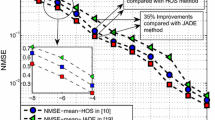
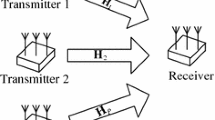
This paper deals with a blind channel estimation method for space-time coded block transmission system. By concatenating the real part and imaginary part of the received signal to form an elongated vector, we derive an equivalent input–output system model. Then channel state information (CSI) is blindly estimated using subspace method, utilizing only the redundancy inherent in space-time block coding (STBC) and cyclic prefix (CP). The estimation ambiguity, which is common to all blind methods, is analyzed in detail and we prove that there only exist four scalar indeterminacies. Three effective methods to eliminate the ambiguities are also proposed. Compared with other blind channel estimation methods for space time systems, this method needs neither redundant precoding nor oversampling, and thus has higher data rate. Besides, this method is robust to channel order overestimation, which is effectively demonstrated by numerical simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou S., Muquet B. and Giannakis G.B. (2002). Subspace-based (semi-) blind channel estimation for block precoded space-time OFDM. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50: 1215–1228
Scaglione A. and Giannakis G.B. (1999). Redundant filterbank precoders and equalizers Part I and Part II. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 47: 1988–2022
Bai W., He C., Jiang L. and Zhu H. (2002). Blind channel estimation in MIMO-OFDM systems. Proc. GLOBECOM 1: 317–321
Shin C. and Powers E.J. (2004). Blind channel estimation for MIMO-OFDM systems using virtual carriers. Proc. GLOBECOM 4: 2465–2469
Ding Z. and Ward D.B. (2005). Subspace approach to blind and semi-blind channel estimation for space-time block codes. IEEE Trans. Wireless Comm. 4: 357–362
Wang Z., Ma X. and Giannakis G.B. (2004). OFDM or single-carrier block transmissions?. IEEE Trans. Comm. 52(3): 380–394
Ohno S. (2006). Performance of single-carrier block transmissions vver multipath fading channels with linear equalization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(10): 3678–3687
ETRI proposal.http://www.ieee802.org/20/Contribs/C802.20-05-90.ppt.
Xu D. and Yang L. (2006). Subspace-based blind channel estimation for STBC-OFDM. Proc. IEEE ICASSP 4: 365–368
Alamouti S.M. (1998). A simple transmit diversity technique for wireless communications. IEEE J. Select. Areas Comm. 16: 1451–1458
Moulines E., Duhamel P., Cardoso J. and Mayrargue S. (1995). Subspace methods for the blind identification of multichannel FIR filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 43(2): 516–525
Roy S. and Li C. (2002). A subspace blind channel estimation method for OFDM systems without cyclic prefix. IEEE Trans. Wireless Comm. 1(40): 572–579
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by NSFC (60496310, 60672093), NSFJS(BK2005061) and BK2005061.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Yang, L. (Semi-)blind channel estimation for space time block coded system with transmit diversity. SIViP 1, 89–97 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-007-0008-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-007-0008-5