Abstract
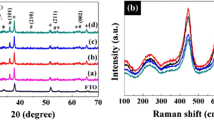
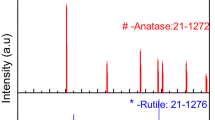
A nano-structured TiO2 with rutile phase was synthesized by using the hydrothermal method from a titanium carbide (TiC) nano-powder precursor at low temperature to produce a stable visible light responsive photocatalyst. The rutile phase was formed at temperature as low as 100°C, and both synthesis time and temperature affected its formation. The rutile particles showed a faceted nano-rod structure, and were tested for absorption and photo-degradation ability under visible light. Particles with shorter synthesis times showed higher visible light absorption and corresponding photo-degradation ability, while those synthesized at lower temperatures had lower, but still evident, degradation ability under visible light.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kudo A, Miseki Y. Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting. Chemical Society Reviews, 2008, 38(1): 253–278
Sunada K, Watanabe T, Hashimoto K. Studies on photokilling of bacteria on TiO2 thin film. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A Chemistry, 2003, 156(1–3): 227–233
Kim B, Kim D, Cho D, Cho S. Bactericidal effect of TiO2 photocatalyst on selected food-borne pathogenic bacteria. Chemosphere, 2003, 52(1): 277–281
Seo J W, Chung H W, Kim M Y, Lee J G, Choi I H, Cheon J W. Development of water-soluble single-crystalline TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic cancer-cell treatment. Small, 2007, 3(5): 850–853
Chen X B, Mao S S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chemical Reviews, 2007, 107(7): 2891–2959
Zhao J C, Chen C C, Ma WH. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants under visible light irradiation. Topics in Catalysis, 2005, 35(3–4): 269–278
Langford J I, Wilson A J C. Scherrer after sixty years: a survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1978, 11(2): 102–113
Czanderna A W, Rao C N R, Honig J M. The anatase-rutile transition. Part 1. Kinetics of the transformation of pure anatase. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 1958, 54: 1069–1073
Mattioli G, Filippone F, Alippi P, Amore Bonapasta A. Ab initio study of the electronic states induced by oxygen vacancies in rutile and anatase TiO2. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2008, 78(24): 241201
Zuo F, Wang L, Wu T, Zhang Z Y, Borchardt D, Feng P Y. Selfdoped Ti3+ enhanced photocatalyst for hydrogen production under visible light. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(34): 11856–11857
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tellam, J., Zong, X. & Wang, L. Low temperature synthesis of visible light responsive rutile TiO2 nanorods from TiC precursor. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 6, 53–57 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-011-1165-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-011-1165-1