Abstract
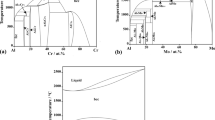
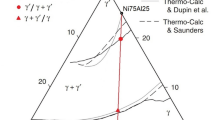
NiAl-based alloys are promising candidates for high-temperature structural applications but their use is restricted by the limited mechanical properties. However, an improved performance can be achieved by strengthening the NiAl matrix with embedded fibers of refractory metals, such as Cr and Mo. Such composites can be manufactured in-situ by directional solidification of alloys with eutectic composition. For these processes the location of the eutectic trough in the NiAl-Cr-Mo system has to be known. The determination of the respective compositions was achieved by combining experimental investigations with computational thermodynamics. Thus, a series of melts in the NiAl-Cr-Mo system were prepared and their microstructures were investigated after solidification. The information on the primary phases was used to model the liquidus surface of the system NiAl-Cr-Mo using the CALPHAD approach. For this purpose, the thermodynamic datasets of the respective sub-systems from the literature have been combined into a quaternary database. The database will be used in the development of NiAl-based alloys for directional solidification. The dataset allows the calculation of the eutectic temperatures, the phase fractions and further thermodynamic properties along the eutectic trough. The present dataset will provide a reliable description for the NiAl-Cr-Mo system, but other regions of the Al-Cr-Mo-Ni system have an inferior representation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.D. Noebe, R.R. Bowman, and M.V. Nathal, Physical and Mechanical Properties of the B2 Compound NiAl, Int. Mater. Rev., 1993, 38, p 193-232
D.B. Miracle, Overview No. 104 The Physical and Mechanical Properties of NiAl, Acta Metall. Mater., 1993, 41, p 649-684
E.P. George and C.T. Liu, Brittle Fracture and Grain Boundary Chemistry of Microalloyed NiAl, J. Mater. Res., 1990, 5, p 754-762
C.A. Barrett, Effect of 0.1 at.% Zirconium on the Cyclic Oxidation Resistance of β-NiAl, Oxid. Met., 1988, 30, p 361-390
F. Ebrahimi and S. Shrivastava, Brittle-to-ductile Transition in NiAl Single Crystal, Acta Mater., 1998, 46, p 1493-1502
J.L. Walter and H.E. Cline, The Effect of Solidification Rate on Structure and High-Temperature Strength of the Eutectic NiAl-Cr, Metall. Trans., 1970, 1, p 1221-1229
P. Ferrandini, W.W. Batista, and R. Caram, Influence of Growth Rate on the Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviour of a NiAl-Mo Eutectic Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2004, 381, p 91-98
H. Bei and E.P. George, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of a Directionally Solidified NiAl-Mo Eutectic Alloy, Acta Mater., 2005, 53, p 69-77
J.F. Zhang, J. Shen, Z. Shang, Z.R. Feng, L.S. Wang, and H.Z. Fu, Microstructure and Room Temperature Fracture Toughness of Directionally Solidified NiAl-Mo Eutectic in situ Composites, Intermetallics, 2012, 21, p 18-25
S. Bogner, L. Hu, S. Hollad, W. Hu, G. Gottstein, and A. Bührig-Polaczek, Microstructure of a Eutectic NiAl-Mo Alloy Directionally Solidified using an Industrial Scale and a Laboratory Scale Bridgman Furnace, Int. J. Mater. Res., 2012, 103, p 17-23
L. Hu, W. Hu, G. Gottstein, S. Bogner, S. Hollad, and A. Bührig-Polaczek, Investigation into Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of NiAl-Mo Composites Produced by Directional Solidification, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 539, p 211-222
X.F. Chen, D.R. Johnson, R.D. Noebe, and B.F. Oliver, Deformation and Fracture of a Directionally Solidified NiAl-28Cr-6Mo Eutectic Alloy, J. Mater. Res., 1995, 10, p 1159-1170
D.R. Johnson, X.F. Chen, B.F. Oliver, R.D. Noebe, and J.D. Whittenberger, Directional Solidification and Mechanical Properties of NiAl Single Bond NiAlTa Alloys, Intermetallics, 1995, 3, p 141-152
J.M. Yang, The Mechanical Behavior of In-situ NiAl-Refractory Metal Composites, JOM, 1997, 49, p 40-43
J.D. Whittenberger, S.V. Raj, I.E. Locci, and J.A. Salem, Effect of Growth Rate on Elevated Temperature Plastic Flow and Room Temperature Fracture Toughness of Directionally Solidified NiAl-31Cr-3Mo, Intermetallics, 1999, 7, p 1159-1168
S.V. Raj and I.E. Locci, Microstructural Characterization of a Directionally-Solidified Ni-33 (at.%) Al-31Cr-3Mo Eutectic Alloy as a Function of Withdrawal Rate, Intermetallics, 2001, 9, p 217-227
S.V. Raj, I.E. Locci, J.A. Salem, and R.J. Pawlik, Effect of Directionally Solidified Microstructures on the Room-Temperature Fracture-toughness Properties of Ni-33(at.%)Al-33Cr-1Mo and Ni-33(at.%)Al-31Cr-3Mo Eutectic Alloys Grown at Different Solidification Rates, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, 33, p 597-612
J.D. Whittenberger, S.V. Raj, I.E. Locci, and J.A. Salem, Elevated Temperature Strength and Room-Temperature Toughness of Directionally Solidified Ni-33Al-33Cr-1Mo, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, 33, p 1385-1397
Z. Shang, J. Shen, L. Wang, Y. Du, Y. Xiong, and H. Fu, Investigations on the Microstructure and Room Temperature Fracture Toughness of Directionally Solidified NiAl-Cr(Mo) Eutectic Alloy, Intermetallics, 2015, 57, p 25-33
P.L. Ferrandini, F.L.G.U. Araujo, W.W. Batista, and R. Caram, Growth and Characterization of the NiAl-NiAlNb Eutectic Structure, J. Cryst. Growth, 2005, 275, p e147-e152
S. Milenkovic, A. Schneider, and G. Frommeyer, Constitutional and Microstructural Investigation of the Pseudobinary NiAl-W System, Intermetallics, 2011, 19, p 342-349
Z. Zhang, X. Liu, S. Gong, and H. Xu, Microstructure and Properties of β-NiAl and its Eutectic Alloy with Cr and Mo Additions, Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2006, 16, p s2046-s2049
I.I. Kornilov and R.S. Mints, Phase Diagram of the Cr-Ni-Al System, Izv. Sekt. Fiz.-Khim. Anal., Inst. Obschch. Neorg. Khim., Akad. Nauk. SSSR, 1953, 22, p 111-116, in Russian
N. Dupin, I. Ansara, and B. Sundman, Thermodynamic Re-Assessment of the Ternary System Al-Cr-Ni, Calphad, 2001, 25, p 279-298
W.J. Boettinger, U.R. Kattner, K.-W. Moon, and J.H. Perepezko, DTA and Heat-Flux DSC Measurements of Alloy Melting and Freezing, Methods for Phase Diagram Determination, J.C. Zhao, Ed., Elsevier, Ames, 2007, p 151-222
A.T. Dinsdale, SGTE Data for Pure Elements, Calphad, 1991, 15, p 317-425
N. Saunders, Al-Cr, COST 507, Thermodynamic Database for Light Metal Alloys, Vol. 2, EUR 18499, Ansara I, Dinsdale AT, Rand MH, Eds., European Commission, Luxembourg, 1998, p 23-27.
I. Ansara, N. Dupin, H.L. Lukas, and B. Sundman, Thermodynamic assessment of the Al-Ni system, J. Alloys Comp., 1997, 247, p 20-30
B.-J. Lee, On the Stability of Cr Carbides, Calphad, 1992, 16, p 121-149
J. Peng, P. Franke, D. Manara, T. Watkins, R.J.M. Konings, and H.J. Seifert, Experimental Investigation and Thermodynamic Re-assessment of the Al-Mo-Ni System, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 674, p 305-314
S.H. Zhou, Y. Wang, C. Liang, J.Z. Zhu, L.-Q. Chen, and Z.-K. Liu, First-Principles Calculations and Thermodynamic Modeling of the Ni-Mo System, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, A397, p 288-296
K. Frisk and P. Gustafson, An Assessment of the Cr-Mo-W System, Calphad, 1988, 12, p 247-254
V.T. Witusiewicz, A.A. Bondar, U. Hecht, and T. Ya, Velikanova, Thermodynamic Re-Modelling of the Ternary Al-Cr-Ti System with Refined Al-Cr Description, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 644, p 939-958
N. Dupin, Contribution a l’eveluation thermodynamique des alliages polyconstitutes a base de nickel, Ph. D. Thesis, l’Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble, France, 1995 (in French).
W. Huang and A. Chang, Thermodynamic Properties of the Ni-Al-Cr System, Intermetallics, 1999, 7, p 863-874
L. Kaufman and H. Nesor, Calculation of Superalloy Phase Diagrams: Part II, Metall. Trans., 1974, 5, p 1623-1629
X. Lu, Y. Cui, and Z. Jin, Experimental and Thermodynamic Investigation of the Ni-Al-Mo System, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, 30, p 1785-1795
S.H. Zhou, Y. Wang, L.Q. Chen, Z.-K. Liu, and R.E. Napolitano, Solution-Based Thermodynamic Modeling of the Ni-Al-Mo System Using First-Principles Calculations, Calphad, 2014, 46, p 124-133
L. Kaufman and H. Nesor, Calculation of Superalloy Phase Diagrams: Part I, Metall. Trans., 1974, 5, p 1617-1621
K. Frisk, Report TRITA-MAC 429, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, 1990
S.S.O.L. Database, Thermo-Calc Version N, Foundation of Computational Thermodynamics, Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, 1998
O. Redlich and A.T. Kister, Algebraic Representation of Thermodynamic Properties and the Classification of Solutions, Ind. Eng. Chem., 1948, 40, p 345-348
M. Hillert, The Compound Energy Formalism, J. Alloys Compd., 2001, 320, p 161-176
J. Wang, G. Zhang, and S. Li, Investigation of Microstructure and Corrosive Behavior of NiAl-3 1Cr-3 Mo Alloy at High Temperature, Min. Metall. Eng., 2010, 30, p 93-96, in Chinese
B. Sundman, B. Janson, and J.O. Andersson, The Thermo-calc Databank System, Calphad, 1985, 9, p 153-190
J.O. Andersson, T. Helander, L. Höglund, P. Shi, and B. Sundman, Thermo-Calc & DICTRA, Computational Tools for Materials Science, Calphad, 2002, 26, p 273-312
P. Franke, Modeling of Thermal Vacancies in Metals within the Framework of the Compound Energy Formalism, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus., 2014, 35, p 780-787
P. Saltykov, V.T. Witusiewicz, I. Arpshofen, O. Fabrichnaya, H.J. Seifert, and F. Aldinger, Thermodynamics of Liquid and Undercooled Liquid Al-Cr-Ni Alloys, Scand. J. Metall., 2001, 30, p 297-301
P. Saltykov, V.T. Witusiewicz, I. Arpshofen, H.J. Seifert, and F. Aldinger, Enthalpy of Mixing of Liquid Al-Cr and Cr-Ni Alloys, J. Mater. Sci. Technol, 2002, 18, p 167-170
D.S. Bloom and N.J. Grant, An Investigation of the Systems Formed by Chromium, Molybdenum and Nickel, J. Metals, 1954, 2, p 261-268
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the Initiative and Networking Fund of the Helmholtz Association (VH-KO-610). The authors thank Alexandra Reif, Damian M. Cupid and Thomas Bergfeldt of IAM-AWP, KIT for the help in experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, J., Franke, P. & Seifert, H.J. Experimental Investigation and CALPHAD Assessment of the Eutectic Trough in the System NiAl-Cr-Mo. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 37, 592–600 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-016-0490-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-016-0490-y