Abstract
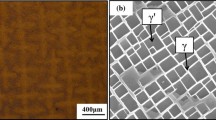
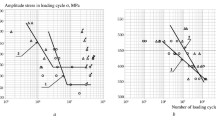
The effects of microstructure and stress ratio on high cycle fatigue of nickel superalloy Nimonic 80A were investigated. The stress ratios of 0.1, 0.5 and 0.8 were chosen to perform fatigue tests in a frequency of 110 Hz. Cleavage failure was observed, and three competing failure crack initiation modes were discovered by a scanning electron microscope, which were classified as surface without facets, surface with facets and subsurface with facets. With increasing the stress ratio from 0.1 to 0.8, the occurrence probability of surface and subsurface with facets also increased and reached the maximum value at R = 0.5, meanwhile the probability of surface initiation without facets decreased. The effect of microstructure on the fatigue fracture behavior at different stress ratios was also observed and discussed. Based on the Goodman diagram, it was concluded that the fatigue strength of 50% probability of failure at R = 0.1, 0.5 and 0.8 is lower than the modified Goodman line.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Miao, T.M. Pollock, and J. Wayne Jones, Microstructural Extremes and the Transition from Fatigue Crack Initiation to Small Crack Growth in a Polycrystalline Nickel-Base Superalloy, Acta Mater., 2012, 60(6), p 2840–2854
B. Larrouy, P. Villechaise, J. Cormier, and O. Berteaux, Grain Boundary–Slip Bands Interactions: Impact on the Fatigue Crack Initiation in a Polycrystalline Forged Ni-Based Superalloy, Acta Mater., 2015, 99, p 325–336
T. Nicholas and J.R. Zuiker, On the Use of the Goodman Diagram for High Cycle Fatigue Design, Int. J. Fract., 1996, 80(2–3), p 219–235
B.A. Cowles, High Cycle Fatigue in Aircraft Gas Turbines—An Industry Perspective, Int. J. Fract., 1996, 80(2), p 147–163
T. Nicholas, Critical Issues in High Cycle Fatigue, Int. J. Fatigue, 1999, 21(99), p S221–S231
H. Oguma and T. Nakamura, Fatigue Crack Propagation Properties of Ti-6Al-4 V in Vacuum Environments, Int. J. Fatigue, 2013, 50, p 89–93
Y. Gao, M. Kumar, R.K. Nalla, and R.O. Ritchie, High-Cycle Fatigue of Nickel-Based Superalloy ME3 at Ambient and Elevated Temperatures: Role of Grain-Boundary Engineering, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36A(12), p 3325–3333
M.J. Caton and S.K. Jha, Small Fatigue Crack Growth and Failure Mode Transitions in a Ni-Base Superalloy at Elevated Temperature, Int. J. Fatigue, 2010, 32(9), p 1461–1472
X. Huang, L. Wang, Y. Hu, G. Guo, D. Salmon, Y. Li, and W. Zhao, Fatigue Crack Propagation Behavior of Ni-Based Superalloys After Overloading at Elevated Temperatures, Progr. Nat. Sci. Mat. Int., 2016, 26(2), p 197–203
K.S. Chan, Roles of Microstructure in Fatigue Crack Initiation, Int. J. Fatigue, 2010, 32(9), p 1428–1447
S.R. Yeratapally, M.G. Glavicic, M. Hardy, and M.D. Sangid, Microstructure Based Fatigue Life Prediction Framework for Polycrystalline Nickel-Base Superalloys with Emphasis on the Role Played by Twin Boundaries in Crack Initiation, Acta Mater., 2016, 107, p 152–167
T. Alp and A. Wazzan, The Influence of Microstructure on the Tensile and Fatigue Behavior of SAE 6150 Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2002, 11(4), p 351–359
J. Liu, Q. Zhang, Z. Zuo, and Y. Xiong, Effect of Fatigue Behavior on Microstructural Features in a Cast Al-12Si-CuNiMg Alloy Under High Cycle Fatigue Loading, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22(12), p 3834–3839
K. Tamada, T. Kakiuchi, and Y. Uematsu, Crystallographic Analysis of Fatigue Crack Initiation Behavior in Coarse-Grained Magnesium Alloy Under Tension-Tension Loading Cycles, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26(7), p 3169–3179
B. Oberwinkler, Modeling the Fatigue Crack Growth Behavior of Ti-6Al-4 V by Considering Grain Size and Stress Ratio, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(18), p 5983–5992
X. Liu, C. Sun, and Y. Hong, Effects of Stress Ratio on High-Cycle and Very-High-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of a Ti–6Al–4 V Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 622, p 228–235
L. Bertini, L. Le Bone, C. Santus, F. Chiesi, and L. Tognarelli, High Load Ratio Fatigue Strength and Mean Stress Evolution of Quenched and Tempered 42CrMo4 Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26(8), p 3784–3793
O. Hatamleh, S. Forth, and A.P. Reynolds, Fatigue Crack Growth of Peened Friction Stir-Welded 7075 Aluminum Alloy under Different Load Ratios, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2010, 19(1), p 99–106
S.D. Antolovich, Microstructural Aspects of Fatigue in Ni-Base Superalloys, Philos. Trans., 2015, 373, p 2038
J. Miao, T.M. Pollock, and J. Wayne Jones, Crystallographic Fatigue Crack Initiation in Nickel-Based Superalloy René 88DT at Elevated Temperature, Acta Mater., 2009, 57(20), p 5964–5974
G.L. Miao, X.G. Yang, and D.Q. Shi, Competing Fatigue Failure Behaviors of Ni-Based Superalloy FGH96 at Elevated Temperature, Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct., 2016, 668, p 66–72
K.O. Findley and A. Saxena, Low Cycle Fatigue in Rene 88DT at 650 °C: Crack Nucleation Mechanisms and Modeling, Metall. Mat. Trans. A, 2006, 37(5), p 1469–1475
S.K. Jha, J.M. Larsen, and A.H. Rosenberger, Towards a Physics-Based Description of Fatigue Variability Behavior in Probabilistic Life-Prediction, Eng. Fract. Mech., 2009, 76(5), p 681–694
S.K. Jha, M.J. Caton, and J.M. Larsen, A New Paradigm of Fatigue Variability Behavior and Implications for Life Prediction, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 468–470, p 23–32
Metallic Materials—Fatigue Testing—Axial Force-Controlled Method, ISO 1099:2006, International Organization for Standardization 2006
X. Liu, C. Sun, and Y. Hong, Faceted Crack Initiation Characteristics for High-Cycle and Very-High-Cycle Fatigue of a Titanium Alloy Under Different Stress Ratios, Int. J. Fatigue, 2016, 92, p 434–441
K. Manigandan, T.S. Srivatsan, T. Quick, S. Sastry, and M.L. Schmidt, Influence of Microstructure and Load Ratio on Cyclic Fatigue and Final Fracture Behavior of Two High Strength Steels, Mater. Des., 2014, 55, p 727–739
A. Pineau, A.A. Benzerga, and T. Pardoen, Failure of Metals I: Brittle and Ductile Fracture, Acta Mater., 2016, 107, p 424–483
S.K. Jha, J.M. Larsen, A.H. Rosenberger, and G.A. Hartman, Dual Fatigue Failure Modes in Ti–6Al–2Sn–4Zr–6Mo and Consequences on Probabilistic Life Prediction, Scripta Mater., 2003, 48(12), p 1637–1642
S.K. Jha, J.M. Larsen, and A.H. Rosenberger, The Role of Competing Mechanisms in the Fatigue Life Variability of a Nearly Fully-Lamellar γ-TiAl Based Alloy, Acta Mater., 2005, 53(5), p 1293–1304
A.H. Fischer, A. Abel, M. Lepper, A.E. Zitzelsberger, and A. von Glasow, Modeling Bimodal Electromigration Failure Distributions, Microelectron. Reliab., 2001, 41(3), p 445–453
S. Tanaka, M. Ichikawa, and S. Akita, A Probabilistic Investigation of Fatigue Life and Cumulative Cycle Ratio, Eng. Fract. Mech., 1984, 20(3), p 501–513
P.J. Laz, B.A. Craig, and B.M. Hillberry, A Probabilistic Total Fatigue Life Model Incorporating Material Inhomogeneities, Stress Level and Fracture Mechanics, Int. J. Fatigue, 2001, 23(1), p 119–127
S. Stanzl-Tschegg and B. Schönbauer, Near-Threshold Fatigue Crack Propagation and Internal Cracks in Steel, Procedia Eng., 2010, 2(1), p 1547–1555
R.H.V. Stone, T.B. Cox, J.R. Low, and J.A. Psioda, Microstructural Aspects of Fracture by Dimpled Rupture, Int. Metals Rev., 2013, 30(1), p 157–180
A. Kolyshkin, M. Zimmermann, E. Kaufmann, and H.-J. Christ, Experimental Investigation and Analytical Description of the Damage Evolution in a Ni-Based Superalloy Beyond 106 Loading Cycles, Int. J. Fatigue, 2016, 93, p 272–280
C. Stocker, M. Zimmermann, and H.J. Christ, Localized Cyclic Deformation and Corresponding Dislocation Arrangements of Polycrystalline Ni-Base Superalloys and Pure Nickel in the VHCF Regime, Int. J. Fatigue, 2011, 33(1), p 2–9
C. Blochwitz, R. Richter, W. Tirschler, and K. Obrtlik, The Effect of Local Textures on Microcrack Propagation in Fatigued F.C.C. Metals, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, 234, p 563–566
S.E. Stanzl-Tschegg, O. Plasser, E.K. Tschegg, and A.K. Vasudevan, Influence of Microstructure and Load Ratio on Fatigue Threshold Behavior in 7075 Aluminum Alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 1999, 21, p S255–S262
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Research Foundation of China (Nos. 11327801, 11502151, 11572057), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team (No. IRT14R37), and Key Science and Technology Support Program of Sichuan Province (No. 2015JPT0001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Guan, Z.W., Wang, Q.Y. et al. Effects of Stress Ratio and Microstructure on Fatigue Failure Behavior of Polycrystalline Nickel Superalloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 2534–2544 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3331-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3331-9