Abstract
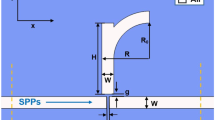
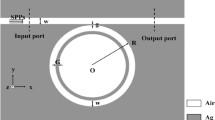
A surface plasmon polariton refractive index sensor which is composed of a metal–insulator–metal (MIM) waveguide, coupled with two stubs and one ring resonator, is proposed. The transmission characteristics of this plasmonic structure are numerically studied based on the finite element method. The simulation results display that a typical Fano profile is exhibited in the transmission spectra, and that the Fano resonance results from the coupling between broadband spectrum resonance (bright mode) in two stubs and the narrowband spectrum resonance (dark mode) in the ring resonator. Furthermore, the effect of various geometric parameters of this proposed structure and the refractive index sensitivity of the system based on Fano resonance is investigated. The investigations demonstrate that the spectral positions of the Fano resonances are highly sensitive to the radius of the ring resonator and the refractive index of the filling medium. The maximum sensitivity and the figure-of-merit of this structurer are 1268 nm/RIU and 280, respectively. These results provide a reference for achieving high-sensitivity sensors in MIM waveguide coupled systems based on the Fano resonance effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.L. Barnes, A. Dereux, and T.W. Ebbesen, Nature 424, 824 (2003).
A.V. Zayats, I.I. Smolyaninov, and A.A. Maradudin, Phys. Rep. 408, 131 (2005).
D.K. Gramotnev and S.I. Bozhevolnyi, Nat. Photonics 4, 83 (2010).
R. Zafar and M. Salim, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 51, 7200306 (2015).
O.S. Ahmed, M.A. Swillam, M.H. Bakr, and X. Li, Opt. Express 18, 21784 (2010).
Z.D. Zhang, H.Y. Wang, and Z.Y. Zhang, Plasmonics 8, 797 (2012).
Y.L. Jiang, J.C. Wang, and Y.K. Wang, Acta Photonica Sinica 43, 0923002 (2014).
V.A. Fedotov, M. Rose, S.L. Prosvirnin, N. Papasimakis, and N.I. Zheludev, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 147401 (2007).
A. Artar, A.A. Yanik, and H. Altug, Nano Lett. 11, 1685 (2011).
A. Artar, A.A. Yanik, and H. Altug, Nano Lett. 11, 3694 (2011).
D. Wang, X. Yu, and Q. Yu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 824 (2013).
J. Qi, Z. Chen, J. Chen, Y. Li, W. Qiang, and J. Xu, Opt. Express 22, 14688 (2014).
X. Yan, T. Wang, X. Han, S. Xiao, Y. Zhu, and Y. Wang, Plasmonics 12, 1449 (2017).
X. Piao, S. Yu, and N. Park, Opt. Express 20, 18994 (2012).
X. Piao, S. Yu, S. Koo, K. Lee, and N. Park, Opt. Express 19, 10907 (2011).
S. Yu, X. Piao, J. Hong, and N. Park, Phys. Rev. A 92, 011802 (2015).
X. Zhao, Z. Zhang, and S. Yan, Sensors 17, 1494 (2017).
S. Yan, M. Zhang, X. Zhao, Y. Zhang, J. Wang, and W. Jin, Sensors 17, 2879 (2017).
Z. Zhang, L. Luo, C. Xue, W. Zhang, and S. Yan, Sensors 16, 642 (2016).
Q. Liu, L. Bibbó, S. Albin, Q. Wang, M. Lin, H.H. Lu, and Z.B. Ouyang, Sci. Rep. 8, 88 (2018).
R.D. Kekatpure, A.C. Hryciw, E.S. Barnard, and M.L. Brongersma, Opt. Express 17, 4112 (2009).
H. Gai, J. Wang, and Q. Tian, Appl. Opt. 46, 2229 (2007).
R.D. Kekatpure, A.C. Hryciw, E.S. Barnard, and M.L. Brongersma, Opt. Express 17, 24112 (2009).
F. Hu, H. Yi, and Z. Zhou, Opt. Lett. 36, 1500 (2011).
J.H. Zhu, Q.J. Wang, P. Shum, and X.G. Huang, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 10, 1371 (2011).
H. Haus and W.P. Huang, Proc. IEEE 79, 1505 (2002).
K. Lee, N. Park, S. Koo, S. Yu, and X. Piao, Opt. Express 19, 10907 (2011).
Z.D. Zhang, R.B. Wang, Z.Y. Zhang, J. Tang, W.D. Zhang, and C.Y. Xue, Plasmonics 12, 1007 (2017).
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Natural Science Research Fund of North University of China (ZBQNJJ2017007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yifei Zhang analyzed the data and wrote the paper; Min Cui conceived and designed the simulations; Yifei Zhang performed the simulations.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Cui, M. Refractive Index Sensor Based on the Symmetric MIM Waveguide Structure. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 1005–1010 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6823-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6823-3