Abstract
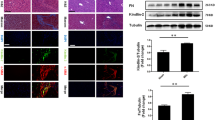
The relationship between Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) and the Notch pathway was determined to investigate the effect of KLF4 on the activation of hepatic stellate cells and underlying mechanisms. Fifty SPF BALB/c mice were randomly divided into two groups. A liver fibrosis model was established in 25 mice as the experimental group, and the remaining 25 mice served as controls. On the day 0, 7, 14, and 35, liver tissues were removed for immunofluorescent detection. The Notch pathway inhibitor DAPT was added to the primary original hepatic stellate cells, and KLF4 and Notch-associated factor expression was detected by qRT-PCR. Additionally, the hepatic stellate cell line LX-2 was used to establish control and experimental groups, and was cultured in vitro. LX-2 cells in the experimental groups were treated with DAPT and the Notch activator transforming growth factor-beta 1 separately, whereas those in the control group were given isotonic culture medium. After 48 h, KLF4 expression was examined by Western blotting. After transient transfection of LX-2 cells to increase KLF4, the expression of Notch factor was examined. Immunofluorescence analysis showed that, with the aggravation of liver fibrosis, the absorbance (A) values of KLF4 were decreased (day 0: 980.73±153.19; day 7: 1087.99±230.23; day 14: 390.95±93.56; day 35: 245.99±87.34). The expression of Notch pathway- related factors (Notch-1, Notch-2, and Jagged-1) in the hepatic stellate cell membrane was negatively correlated to KLF4 expression. With the increase of KLF4 expression, Notch-2 (0.73±0.13) and Jagged-1 (0.43±0.12) expression decreased, whereas Notch-1 level was not detectable. When the Notch pathway was inhibited, KLF4 levels generally increased (18.12±1.31). Our results indicate that KLF4 expression is negatively correlated to the Notch pathway in hepatic stellate cells, which may provide a reference for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei D, Wang L, Kanai M, et al. KLF4 alpha up-regulation promotes cell cycle progression and reduces survival time of patients with pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology, 2010,139(6):2135–2145
Shie JL, Chen ZY, O’Brien MJ, et al. Role of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor in colonic cell growth and differentiation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2000,279(4):G806–814
Dang DT, Chen X, Feng J, et al. Overexpression of Kruppel-like factor 4 in the human colon cancer cell line RKO leads to reduced tumorigenecity. Oncogene, 2003,22(22):3424–3430
Evans PM, Chen X, Zhang W, et al. KLF4 interacts with beta-catenin/TCF4 and blocks p300/CBP recruitment by beta-catenin. Mol Cell Biol, 2010,30(2):372–381
Wong CW, Hou PS, Tseng SF, et al. Kruppel-like transcription factor 4 contributes to maintenance of telomerase activity in stem cells. Stem Cells, 2010,28(9):1510–1517
Yoon HS, Yang VW. Requirement of Kruppel-like factor 4 in preventing entry into mitosis following DNA damage. J Biol Chem, 2004,279(6):5035–5041
Chen ZY, Wang X, Zhou Y, et al. Destabilization of Kruppel-like factor 4 protein in response to serum stimulation involves the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Cancer Res, 2005,65(22):10394–10400
Chen X, Whitney EM, Gao SY, et al. Transcriptional profiling of Kruppel-like factor 4 reveals a function in cell cycle regulation and epithelial differentiation. J Mol Biol, 2003,326(3):665–677
Butko E, Pouget C, Traver D. Complex regulation of HSC emergence by the Notch signaling pathway. Dev Biol, 2016,409(1):129–138
Zheng H, Pritchard DM, Yang X, et al. KLF4 gene expression is inhibited by the notch signaling pathway that controls goblet cell differentiation in mouse gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2009,296(3):G490–498
Fre S, Huyghe M, Mourikis P, et al. Notch signals control the fate of immature progenitor cells in the intestine. Nature, 2005,435(7044):964–968
Brandao DF, Ramalho LN, Ramalho FS, et al. Liver cirrhosis and hepatic stellate cells. Acta Cir Bras, 2006,21(Suppl 1):54–57
Sun XF, Sun XH, Cheng SF, et al. Interaction of the transforming growth factor-ß and Notch signaling pathways in the regulation of granulosa cell proliferation. Reprod Fertil Dev, 2015, doi: 10.1071/RD14398 [Epub ahead of print]
McCanless JD, Cole JA, Slack SM, et al. Modeling nucleus pulposus regeneration in vitro: mesenchymal stem cells, alginate beads, hypoxia, bone morphogenetic protein-2, and synthetic peptide B2A. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011,36(26):2275–2285
Blokzijl A, Dahlqvist C, Reissmann E, et al. Cross-talk between the Notch and TGF-beta signaling pathways mediated by interaction of the Notch intracellular domain with Smad3. J Cell Biol, 2003,163(4):723–728
Varela I, Karagiannidou A, Oikonomakis V, et al. Generation of human beta-thalassemia induced pluripotent cell lines by reprogramming of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells using modified mRNA. Cell Reprogram, 2014,16(6):447–455
Chitilian JM, Thillainadesan G, Manias JL, et al. Critical components of the pluripotency network are targets for the p300/CBP interacting protein (p/CIP) in embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells, 2014,32(1):204–215
Zhuang SJ, Li X, Li KQ, et al. Mechanism of JAK/STAT signal pathway and Notch signaling crosstalking in proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. J Int Pharm Res, 2013,40(6):743–746
Qin S, Zou Y, Zhang CL. Cross-talk between KLF4 and STAT3 regulates axon regeneration. Nat Commun, 2013,4:2633
Roshan S, Liu YY, Banafa A, et al. Fucoidan induces apoptosis of HepG2 cells by down-regulating p-Stat3. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol [Med Sci], 2014,34(3):330–336
Ema M, Mori D, Niwa H, et al. Kruppel-like factor 5 is essential for blastocyst development and the normal self-renewal of mouse ESCs. Cell Stem Cell, 2008,3(5):555–567
Ghaleb AM, Aggarwal G, Bialkowska AB, et al. Notch inhibits expression of the Kruppel-like factor 4 tumor suppressor in the intestinal epithelium. Mol Cancer Res, 2008,6(12):1920–1927
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81071541).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Yk., Tan, J., Dou, Dw. et al. Effect of Kruppel-like factor 4 on Notch pathway in hepatic stellate cells. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 36, 811–816 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-016-1667-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-016-1667-7