Summary
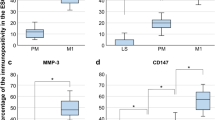
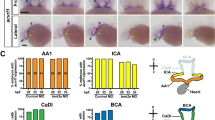
In this study, real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry were used to detect coxsakie and adenovirus receptor (CAR) expression. Both localization and quantity were evaluated in the uteri obtained at days post coitus (dpc) 2.5, 4.5, 6.5, 8.5. Outcome of PCR was assessed by 2−ΔΔCt method. Image Pro-Plus 6.0 software was used for quantifying mean density of CAR expression in immunohistochemical sections. We found relatively weak CAR expression in the mouse uteri during implantation window. PCR and immunohistochemistry revealed highest CAR expression was detected on dpc 2.5 followed by down-regulation of CAR at dpc 4.5 and 6.5 (with significant difference). At dpc 8.5, CAR expression was increased slightly again. It is concluded that during implantation, the expression of CAR mRNA and protein is declined, resulting in the impairment of tight junction between cavity epithelium cells. After implantation window closure, CAR appears again to maintain epithelium stability. CAR might play an important role during embryo implantation procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
James C, Cross ZW, Fisher SJ. Implantation and the plancenta: Key pieces of the development puzzle. Science, 1994,266(5190):1508–1518
Merviel P, Challier JC, Carbillon L, et al. The role of integrins in human embryo implantation. Fetal Diagn Ther, 2001,16(6):364–371
Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G, et al. Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science, 1997,275(5304):1320–1323
Bergelson JM, Krithivas A, Celi L, et al. The murine CAR homolog is a receptor for coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses. J Virol, 1998,72(1):415–419
Raschperger E, Thyberg J, Pettersson S, et al. The coxsackie- and adenovirus receptor (CAR) is an in vivo marker for epithelial tight junctions, with a potential role in regulating permeability and tissue homeostasis. Exp Cell Res, 2006,312(9):1566–1580
Dorner AA, Wegmann F, Butz S, et al. Coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor (CAR) is essential for early embryonic cardiac development. J Cell Sci, 2005,118(15): 3509–3521
Asher DR, Cerny AM, Weiler SR, et al. Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor is essential for cardiomyocyte development. Genesis, 2005,42(2):77–85
Chen JW, Zhou B, Yu QC, et al. Cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor results in hyperplasia of the embryonic left ventricle and abnormalities of sinuatrial valves. Circ Res, 2006,98(7): 923–930
Fan LS, Chen G, Ma D. Research advance on role of Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor (CAR) in tumor progression. Aizheng (Chinese), 2009,28(3):333–336
Hotta Y, Honda T, Naito M, et al. Developmental distribution of coxsackie virus and adenovirus receptor localized in the nervous system. Brain Res Dev Brain Res, 2003,143(1):1–13
Giaginis CT, Zarros AC, Papaefthymiou MA, et al. Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor expression in human endometrial adenocarcinoma: possible clinical implications. World J Surg Oncol, 2008,17(6):59
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402–408
Anders M, Vieth M, Röcken C, et al. Loss of the coxsackie and adenovirus receptor contributes to gastric cancer progression. Br J Cancer, 2009,100(2):352–359
Yamashita M, Ino A, Kawabata K, et al. Expression of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor reduces the lung metastatic potential of murine tumor cells. Int J Cancer, 2007,121(8):1690–1696
Sachs MD, Rauen KA, Ramamurthy M, et al. Integrin alpha(v) and coxsackie adenovirus receptor expression in clinical bladder cancer. Urology, 2002, 60(3):531–536
Korn WM, Macal M, Christian C, et al. Expression of the coxsackievirus- and adenovirus receptor in gastrointestinal cancer correlates with tumor differentiation. Cancer Gene Ther, 2006,13(8):792–797
Fok PT, Huang KC, Holland PC, et al. The Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor binds microtubules and plays a role in cell migration. J Biol Chem, 2007,282(10):7512–7521
Stecker K, Koschel A, Wiedenmann B, et al. Loss of Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor downregulates alpha-catenin expression. Br J Cancer, 2009,101(9):1574–1579
Farmer C, Morton PE, Snippe M, et al. Coxsackie adenovirus receptor (CAR) regulates integrin function through activation of p44/42 MAPK. Exp Cell Res, 2009, 315(15):2637–2647
Zen K, Liu Y, McCall IC, et al. Neutrophil migration across tight junctions is mediated by adhesive interactions between epithelial coxsackie and adenovirus receptor and a junctional adhesion molecule-like protein on neutrophils. Mol Bio Cell, 2005,16:2694–2703
Lessey BA, Castelbaum AJ. Integrins and implantation in the human. Rev Endocr Metab Disorders, 2002,3(2): 107–117
Walters RW, Freimuth P, Moninger TO, et al. Adenovirus fiber disrupts CAR-mediated intercellular adhesion allowing virus escape. Cell, 2002, 110(6):789–799
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhao, H., Wang, B. et al. Down-regulation of coxsakie and adenovirus receptor during embryo implantation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 32, 103–106 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-012-0018-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-012-0018-6