Abstract
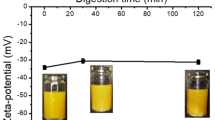
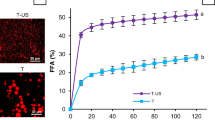
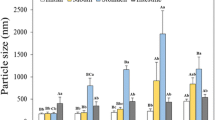
The objective of this study was to investigate the influence of interfacial composition and electrical charge on the in vitro digestion of emulsified fats by pancreatic lipase. An electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition technique was used to prepare corn oil-in-water emulsions (3 wt% oil) that contained droplets coated by (1) lecithin, (2) lecithin–chitosan, or (3) lecithin–chitosan–pectin. Pancreatic lipase (1.6 mg mL−1) and/or bile extract (5.0 mg mL−1) were added to each emulsion, and the particle charge, droplet aggregation, and free fatty acids released were measured. In the presence of bile extract, the amount of fatty acids released per unit amount of emulsion was much lower in the emulsions containing droplets coated by lecithin–chitosan (38 ± 16 μmol mL−1) than those containing droplets coated by lecithin (250 ± 70 μmol mL−1) or lecithin–chitosan–pectin (274 ± 80 μmol mL−1). In addition, there was much more extensive droplet aggregation in the lecithin–chitosan emulsion than in the other two emulsions. We postulated that lipase activity was reduced in the lecithin–chitosan emulsion as a result of the formation of a relatively thick cationic layer around each droplet, as well as the formation of large flocs, which restricted the access of the pancreatic lipase to the lipids within the droplets. Our results also suggest that droplets initially coated by a lecithin–chitosan–pectin layer did not inhibit lipase activity, which may have been because the chitosan–pectin desorbed from the droplet surfaces thereby allowing the enzyme to reach the lipids; however, further work is needed to establish this. This information could be used to create food emulsions with low caloric level, or to optimize diets for individuals with lipid digestion problems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.J. McClements, Food Emulsions: Principles, Practice and Techniques (CRC Press, Boca Raton 2004).
D. Lairon, Eur J Clin Nutr 50, 125 (1996).
G.A. Van Aken, Coalescence mechanisms in protien-stabilized emulsion, In: Food Emulsions, edited by S. Friberg, K. Larsson and J. Sjoblom (Marcel Dekker, New York, NY 2004), 4th ed, chap 8.
M. Armand, P. Borel, C. Dubois, M. Senft, J. Peyrot, J. Salducci, H. Lafont and D. Lairon, Am J Physiol 266, G372 (1994).
M. Armand, B. Pasquier, M. Andre, P. Borel, M. Senft, J. Peyrot, J. Salducci, H. Portugal, V. Jaussan and D. Lairon, Am J Clin Nutr 70, 1096 (1999).
H.L. Brockman, Biochimie 82, 987 (2000).
M. Armand, P. Borel, P. Ythier, G. Dutot, M. Melin, H. Senft, H. Lafont and D. Lairon, J Nutr Biochem 3, 333 (1992).
H. Mu and C.-E. Høy, Prog Lipid Res 43, 105 (2004).
S. Labourdenne, O. Brass, M. Ivanova, A. Cagna and G. Verger, Biochemistry 36, 3423 (1997).
C. Chapus, M. Rovery, L. Sarda and R. Verger, Biochimie 70, 1223 (1988).
M. Wickham, M. Garrood, J. Leney, P.D.G. Wilson and A. Fillery-Travis, J Lipid Res. 39, 623 (1998).
L.-K. Han, Y. Kimura and H. Okuda, Int J Obes 23, 174 (1999).
C.M. Gallaher, J. Munion, R. Hasslink, J. Wise and D.D. Gallaher, J Nutr 130, 2753 (2000).
S. Kobayashi, Y. Terashima and H. Itoh, Br Poult Sci 43, 270 (2002).
M. Sugano, S. Watanabe, A. Kishi, M. Izume and A. Ohtakara, Lipids 23, 187 (1998).
P. Faldt, B. Bergenstahl and P.M. Claesson, Colloids Surf A 71, 187 (1993).
C. Peniche, W. Aruelles-Monal, H. Peniche and N. Acosta, Macromol Biosci 3, 511 (2003).
S. Ogawa, E.A. Decker and D.J. McClements, J Agric Food Chem 51, 2806 (2003).
S. Ogawa, E.A. Decker and D.J. McClements, J Agric Food Chem 52, 3595 (2004).
D.A. Garrett, M.L. Failla and R.J. Sarama, J Agric Food Chem 47, 4301 (1999).
N. Saisuburamaniyan, L. Krithika, K.P. Dileena, S. Sivasubramanian and R. Puvanakrishnan, Anal Biochem 330, 70 (2004).
A. Lykidis, A. Antonis and P. Arzoglou, Comp Biochem Physiol B 116, 51 (1997).
A. Tavridou, A. Avranas and P. Arzoglou, Biochem Biophys Res Commun 186, 746 (1992).
F. Shahidi, J.K.V. Arachchi and Y.J. Jeon, Trends Food Sci Technol 10, 37 (1999).
G. Skjak-Braek, T. Anthonsen and P. Sandford, Chtin and Chitosan (Elsevier, London, 1989).
M.S. Rodriguez, L.A. Albertengo, I. Vitale and E. Agullo, JFood Sci 68, 665 (2003).
T. Aoki, E.A. Decker and D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll 19, 209 (2005).
Acknowledgments
This material is based upon work supported by the Cooperative State Research, Extension, Education Service, United State Department of Agriculture, Massachusetts Agricultural Experiment Station (project No. 831), by an United States Department of Agriculture, CREES, IFAFS Grant (Award Number 2001-4526) and an United States Department of Agriculture, CREES, NRI Grant (Award Number 2002-01655). This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by Korea Government (MOEHRD, Basic Research Promotion Fund) (KRF-2004-214-M01-2004-000-10380-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mun, S., Decker, E.A., Park, Y. et al. Influence of Interfacial Composition on in Vitro Digestibility of Emulsified Lipids: Potential Mechanism for Chitosan's Ability to Inhibit Fat Digestion. Food Biophysics 1, 21–29 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-005-9001-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-005-9001-0