Abstract
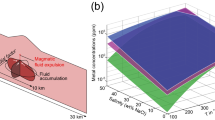
Porphyry copper systems, which provide most of the world’s copper resource, are commonly associated with characteristic concentric zonation of alteration and mineralization. In-depth knowledge of the distribution and transport mechanism of elements in the alteration zones is essential for understanding the ore-forming processes. We employed flow-reaction apparatus to simulate the fluid-rock interactions during porphyry ore formation so as to investigate the mechanisms that govern the transport of elements and the development of zonation. The results indicate more heterogeneous distribution of elements in the experimental products at 450°C compared to those at lower temperatures, which implies a crucial role of temperature in controlling elements redistribution in hydrothermal systems. Heating advances potassic alteration and Ca leaching of wall rocks. To achieve the same degree of sodic alteration, it requires a higher concentration of Na+ in the fluid toward higher temperature. Temperature also facilitates the incorporation of Ti, Sr and Pb into silicate minerals through cation substitution. We infer from experimental results that from the center of intermediate to mafic volcanic wall rocks toward periphery, the contents of K and Ti should decrease and the contents of Ca, Zn and Mn should increase, whereas the trend for Si and Na could be non-monotonic. This study provides experimental and theoretical insights into a variety of vital geological observations, including anhydrite formation and the widespread development of potassic rather than sodic alteration in porphyry copper deposits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagaard P, Helgeson H C. 1982. Thermodynamic and kinetic constraints on reaction rates among minerals and aqueous solutions: I, Theoretical considerations. Am J Sci, 282: 237–285
Ague J J, Brimhall G H. 1989. Geochemical modeling of steady state fluid flow and chemical reaction during supergene enrichment of porphyry copper deposits. Econ Geol, 84: 506–528
Airy G B. 1855. On the computation of the effect of the attraction of mountain-masses, as disturbing the apparent astronomical latitude of stations in geodetic surveys. Philos Trans R Soc Lond, 145: 101–104
Barnes H L. 1997. Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. 3rd ed. John Wiley & Sons. 1
Bondar R J, Sanchez P L, Moncada D, Macinnis M S. 2014. Fluid inclusions in hydrothermal ore deposits. Treat Geochem, 13: 119–142
Bickle M, Baker J. 1990. Migration of reaction and isotopic fronts in infiltration zones: Assessments of fluid flux in metamorphic terrains. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 98: 1–13
Bird D K, Schiffman P, Elders W A, Williams A E, McDowell S D. 1984. Calc-silicate mineralization in active geothermal systems. Econ Geol, 79: 671–695
Brimhall G H. 1977. Early fracture-controlled disseminated mineralization at Butte, Montana. Econ Geol, 72: 37–59
Carmichael D M. 1987. Induced stress and secondary mass transfer: Thermodynamic basis for the tendency toward constant-volume constraint in diffusion metasomatism. In: Helgeson H C, ed. Chemical Transport in Metasomatic Processes. NATO ASI Series (Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences). Dordrecht: Springer
Carten R B. 1986. Sodium-calcium metasomatism; chemical, temporal, and spatial relationships at the Yerington, Nevada, porphyry copper deposit. Econ Geol, 81: 1495–1519
Chang J, Li J W, Audétat A. 2018. Formation and evolution of multistage magmatic-hydrothermal fluids at the Yulong porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, eastern Tibet: Insights from LA-ICP-MS analysis of fluid inclusions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 232: 181–205
Chen H Y, Xiao B. 2014. Metallogenesis of subduction zone: The progress and future. Geosci Front, 21: 13–22
Cooke D R, Hollings P, Walshe J L. 2005. Giant porphyry deposits: Characteristics, distribution, and tectonic controls. Econ Geol, 100: 801–818
Cooke D R, Baker M, Hollings P, Sweet G, Chang Z, Danyushevsky L, Gilbert G, Zhou T, White N C, Gemmell J B, Inglis S. 2014a. New advances in detecting systems-epidote mineral chemistry as a tool for vectoring and fertility assessments. Soc Econ Geologists Spec Publ, 18: 127–152
Cooke D R, Agnew P, Hollings P. 2017. Porphyry indicator minerals (PIMS) and porphyry vectoring and fertility tools (PVFTS)-indicators of mineralization styles and recorders of hypogene geochemical dispersion halos. In: Exploration 17: Sixth Decennial International Conference on Mineral Exploration.
Toronto Cooke D R, Hollings P, Wilkinson J J, Tosdal R M. 2014b. Geochemistry of porphyry deposits. Treat Geochem, 13: 357–381
Dang Z, Hou Y. 1995. Experimental study on the dissolution kinetics of basalt-water interaction. Acta Petrol Sin, 11: 9–15
Du L T. 1986. Geochemistry of alkaline metasomatism. Sci China, 1: 83–92
Du J G. 2010. High Pressure Geoscience. Beijing: Seismological Press
Ferry J M, Dipple G M. 1991. Fluid flow, mineral reactions, and metaso-matism. Geology, 19: 211–214
Ferry J M, Dipple G M. 1992. Models for coupled fluid flow, mineral reaction, and isotopic alteration during contact metamorphism: The Notch Peak aureole, Utah. Ame Miner, 77: 577–591
Fournier R O. 1999. Hydrothermal processes related to movement of fluid from plastic into brittle rock in the magmatic-epithermal environment. Econ Geol, 94: 1193–1211
Fournier R O, Marshall W L. 1983. Calculation of amorphous silica solubilities at 25 to 300°C and apparent cation hydration numbers in aqueous salt solutions using the concept of effective density of water. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 47: 587–596
Frank M R, Candela P A, Piccoli P M. 1998. K-feldspar-muscovite-andalusite- quartz-brine phase equilibria: An experimental study at 25 to 60 MPa and 400 to 550°C. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 62: 3717–3727
Frank M R, Vaccaro D M. 2012. An experimental study of high temperature potassic alteration. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 83: 195–204
Gautier J M, Oelkers E H, Schott J. 1994. Experimental study of K-feldspar dissolution rates as a function of chemical affinity at 150°C and pH 9. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 58: 4549–4560
Gislason S R, Oelkers E H. 2003. Mechanism, rates, and consequences of basaltic glass dissolution: II. An experimental study of the dissolution rates of basaltic glass as a function of pH and temperature. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 67: 3817–3832
Gudbrandsson S, Wolff-Boenisch D, Gislason S R, Oelkers E H. 2011. An experimental study of crystalline basalt dissolution from 2=pH=11 and temperatures from 5 to 75°C. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 75: 5496–5509
Harris N B W, Inger S, Ronghua X. 1990. Cretaceous plutonism in Central Tibet: An example of post-collision magmatism? J Volcanol Geotherm Res, 44: 21–32
Halter W E, Pettke T, Heinrich C A. 2002. The origin of Cu/Au ratios in porphyry-type ore deposits. Science, 296: 1844–1846
Haselton Jr H T, Cygan G L, Jenkins D M. 1995. Experimental study of muscovite stability in pure H2O and 1 molal KCl-HCl solutions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 59: 429–442
Helgeson H C. 1969. Thermodynamics of hydrothermal systems at elevated temperatures and pressures. Am J Sci, 267: 729–804
Heinrich C A. 1990. The chemistry of hydrothermal tin(-tungsten) ore deposition. Econ Geol, 85: 457–481
Heinrich C A. 2005. The physical and chemical evolution of low-salinity magmatic fluids at the porphyry to epithermal transition: A thermodynamic study. Miner Deposita, 39: 864–889
Heinrich C A. 2006. From fluid inclusion microanalysis to large-scale hydrothermal mass transfer in the Earth’s interior. J Mineral Petrol Sci, 101: 110–117
Hemley J J, Montoya J W, Marinenko J W, Luce R W. 1980. Equilibria in the system Al2O3-SiO2-H2O and some general implications for alteration/mineralization processes. Econ Geol, 75: 210–228
Heinrich C A, Walshe J L, Harrold B P. 1996. Chemical mass transfer modelling of ore-forming hydrothermal systems: Current practise and problems. Ore Geol Rev, 10: 319–338
Hemley J J. 1959. Some mineralogical equilibria in the system K2O-Al2O3- SiO2-H2O. Am J Sci, 257: 241–270
Hemley J J, Jones W R. 1964. Chemical aspects of hydrothermal alteration with emphasis on hydrogen metasomatism. Econ Geol, 59: 538–569
Hildreth W, Moorbath S. 1988. Crustal contributions to arc magmatism in the Andes of central Chile. Contr Mineral Petrol, 98: 455–489
Holyland P W. 1987. Dynamic modelling at the Renison tin mine. Pacific Rim Congress’87. 189–193
Hu S M, Zhang R H, Zhang X T, Hang W B. 2010. Experimental study of water-basalt interaction in Luzong volcanic basin and its application. Acta Petrol Sin, 26: 2681–2693
Huang W B, Zhang R H, Hu S M. 2011. Chemical dynamics of basaltseawater interaction near critical states. Acta Mineral Sin, Suppl: 692
Hutcheon I, Shevalier M, Abercrombie H J. 1993. pH buffering by metastable mineral-fluid equilibria and evolution of carbon dioxide fugacity during burial diagenesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 57: 1017–1027
Kerrich R. 2000. The geodynamics of world-class gold deposits, characteristics, space-time distribution, and origins. Rev. Econ Geol, 13: 501–551
Korzhinskii D S. 1959. Acid-basic interaction of components in silicate melts and the direction of the cotectic lines. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 128: 383–386
Korzhiniskii D S. 1970. Theory of Metasomatie Zoning. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Landtwing M R, Pettke T, Halter W E, Heinrich C A, Redmond P B, Einaudi M T, Kunze K. 2005. Copper deposition during quartz dissolution by cooling magmatic-hydrothermal fluids: The Bingham porphyry. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 235: 229–243
Landtwing M R, Furrer C, Redmond P B, Pettke T, Guillong M, Heinrich C A. 2010. The Bingham Canyon porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit. III. Zoned copper-gold ore deposition by magmatic vapor expansion. Econ Geol, 105: 91–118
Liang H Y, Sun W, Su W C, Zartman R E. 2009. Porphyry copper-gold mineralization at Yulong, China, promoted by decreasing redox potential during magnetite alteration. Econ Geol, 104: 587–596
Lasaga A C, Rye D M. 1993. Fluid flow and chemical reaction kinetics in metamorphic systems. Am J Sci, 293: 361–404
Liu Y, Liu H C, Li X H. 1996. Simultaneous and precise determination of 40 trace elements in rock Samples using ICP-MS. Geochimica, 6: 552–558
Liu Y J. 1984. Geochemistry of Elements. Beijing: Science Press
Liu Y S, Zhang G L. 1996. An Experimental study on sea water-basalt interaction at 250–500°C and 100 MPa. Geochimica, 1: 53–62
Lowell J D, Guilbert J M. 1970. Lateral and vertical alteration-mineralization zoning in porphyry ore deposits. Econ Geol, 65: 373–408
Luhmann A J, Tutolo B M, Tan C, Moskowitz B M, Saar M O, Seyfried Jr. W E. 2017. Whole rock basalt alteration from CO2-rich brine during flow-through experiments at 150°C and 150 bar. Chem Geol, 453: 92–110
Merino E, Moore C, Ortoleva P, Ripley E. 1986. Mineral zoning in sediment- hosted copper-iron sulfide deposits—A quantitative kinetic approach. In: Geology and Metallogeny of Copper Deposits. Special Publication No. 4 of the Society for Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits. Berlin: Springer. 559–571
Montoya J W, Hemley J J. 1975. Activity relations and stabilities in alkali feldspar and mica alteration reactions. Econ Geol, 70: 577–583
Mottl M J, Holland H D. 1978. Chemical exchange during hydrothermal alteration of basalt by seawater—I. Experimental results for major and minor components of seawater. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 42: 1103–1115
Murphy W M, Oelkers E H, Lichtner P C. 1989. Surface reaction versus diffusion control of mineral dissolution and growth rates in geochemical processes. Chem Geol, 78: 357–380
Nash J T. 1976. Fluid-inclusion petrology—Data from porphyry copper deposits and applications to exploration: A summary of new and published descriptions of fluid inclusions from 36 porphyry copper deposits and discussion of possible applications to exploration for copper deposits. US Govt. Print. Off
Oelkers E H. 2001. General kinetic description of multioxide silicate mineral and glass dissolution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 65: 3703–3719
Oelkers E H, Schott J. 2001. An experimental study of enstatite dissolution rates as a function of pH, temperature, and aqueous Mg and Si concentration, and the mechanism of pyroxene/pyroxenoid dissolution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 65: 1219–1231
Oelkers E H, Schott J, Devidal J L. 1994. The effect of aluminum, pH, and chemical affinity on the rates of aluminosilicate dissolution reactions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 58: 2011–2024
Orville P M. 1962. Alkali metasomatism and feldspars. Norsk Geologisk Tidsskrift. 283–316
Pollard P J. 2001. Sodic(-calcic) alteration in Fe-oxide-Cu-Au districts: An origin via unmixing of magmatic H2O-CO2-NaCl±CaCl2-KCl fluids. Miner Depos, 36: 93–100
Ré C L, Kaszuba J P, Moore J N, McPherson B J. 2014. Fluid-rock interactions in CO2-saturated, granite-hosted geothermal systems: Implications for natural and engineered systems from geochemical experiments and models. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 141: 160–178
Reed M H. 1997. Hydrothermal alteration and its relationship to ore fluid composition. Geochem Hydrothermal Ore Deposits, 1: 303–365
Redmond P B, Einaudi M T, Inan E E, Landtwing M R, Heinrich C A. 2004. Copper deposition by fluid cooling in intrusion-centered systems: New insights from the Bingham porphyry ore deposit, Utah. Geology, 32: 217–220
Redmond P B, Einaudi M T. 2010. The Bingham Canyon porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit. I. Sequence of intrusions, vein formation, and sulfide deposition. Econ Geol, 105: 43–68
Richards J P. 2011. Magmatic to hydrothermal metal fluxes in convergent and collided margins. Ore Geol Rev, 40: 1–26
Richards J P, Kerrich R. 2007. Special paper: Adakite-like rocks: Their diverse origins and questionable role in metallogenesis. Econ Geol, 102: 537–576
Ringwood A E. 1977. Petrogenesis in Island Arc Systems. Island Arcs, Deep Sea Trenches and Back-arc Basins. Washington: American Geophysical Union. 311–324
Roedder E. 1971. Fluid inclusion studies on the porphyry-type ore deposits at Bingham, Utah, Butte, Montana, and Climax, Colorado. Econ Geol, 66: 98–118
Rogers K L, Neuhoff P S, Pedersen A K, Bird D K. 2006. CO2 metasomatism in a basalt-hosted petroleum reservoir, Nuussuaq, West Greenland. Lithos, 92: 55–82
Rusk B G, Reed M H, Dilles J H, Klemm L M, Heinrich C A. 2004. Compositions of magmatic hydrothermal fluids determined by LA-ICPMS of fluid inclusions from the porphyry copper-molybdenum deposit at Butte, MT. Chem Geol, 210: 173–199
Rusk B G, Reed M H, Dilles J H. 2008. Fluid inclusion evidence for magmatic-hydrothermal fluid evolution in the porphyry copper-molybdenum deposit at Butte, Montana. Econ Geol, 103: 307–334
Schott J, Pokrovsky O S, Oelkers E H. 2009. The link between mineral dissolution/precipitation kinetics and solution chemistry. Rev Mineral Geochem, 70: 207–258
Seedorff E, Dilles J H, Proffett J M. 2005. Porphyry deposits: Characteristics and origin of hypogene features. Econ Geol, 100: 251–298
Sillitoe R H. 1972. A plate tectonic model for the origin of porphyry copper deposits. Econ Geol, 67: 184–197
Sillitoe R H. 1973. The tops and bottoms of porphyry copper deposits. Econ Geol, 68: 799–815
Sillitoe R H. 2010. Porphyry copper systems. Econ Geol, 105: 3–41
Stern C R, Funk J A, Skewes M A, Arevalo A. 2007. Magmatic anhydrite in plutonic rocks at the El Teniente Cu-Mo deposit chile, and the role of sulfur- and copperrich magmas in its formation. Econ Geol, 102: 1335–1344
Sun S, McDonough W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ, 42: 313–345
Sun W D, Ling M X, Yang X Y, Fan W M, Ding X, Liang H Y. 2010. Ridge subduction and porphyry copper-gold mineralization: An overview. Sci China Earth Sci, 53: 475–484
Sverjensky D A, Hemley J J, D’angelo W M. 1991. Thermodynamic assessment of hydrothermal alkali feldspar-mica-aluminosilicate equilibria. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 55: 989–1004
Tan K X, Zhang Z R, Wang Z G. 1994. The Mechanism of surface chemical kinetics of dissolution of minerals. Acta Mineral Sin, 3: 207–214
Wang Y F, Chen H Y, Xiao B, Han J S. 2016. Porphyritic-overlapped mineralization of Tuwu and Yandong copper deposits in Eastern Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang. Mineral Deposits, 35: 51–68
Wang Y R, Wang Z X, Zhang S. 2000. Water-rock reaction experiment and mineralization. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem, 19: 426–427
Wilkinson J J, Chang Z, Cooke D R, Baker M J, Wilkinson C C, Inglis S, Chen H, Bruce Gemmell J. 2015. The chlorite proximitor: A new tool for detecting porphyry ore deposits. J Geochem Exploration, 152: 10–26
Winkler H G F, von Platen H. 1961. Experimentelle gesteinsmetamorphose —V. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 24: 250–259
Xiao B, Chen H Y, Hollings P, Han J S, Wang Y F, Yang J T, Cai K D. 2015. Magmatic evolution of the Tuwu-Yandong porphyry Cu belt, NW China: Constraints from geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes. Gondwana Res, 43: 74–91
Yang Z, Hou Z, White N C, Chang Z S, Li Z Q, Song Y C. 2009. Geology of the post-collisional porphyry copper-molybdenum deposit at Qulong, Tibet. Ore Geol Rev, 36: 133–159
Zhang D H, Xu J H, Yu X Q, Li J K, Mao S D, Wang K Q, Li Y Q. 2011. The diagenetic and metallogenic depth: Main constraints and the estimation methods. Geol Bull China, 30: 112–125
Zhang Y X. 2010. Geochemical Kinetics. Beijing: Higher Education Press
Acknowledgements
Zhang Dongwei, Li Dengfeng, Zhang Shitao, Zhao Liandang, Xu Chao and Huang Jianhan are thanked for the laboratory assistance. We also appreciate the constructive comments from three anonymous reviewers which significantly improved this manuscript. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U1603244), Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB1803206) and Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2017B030314175).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Chen, H., Su, L. et al. Experimental study of high to intermediate temperature alteration in porphyry copper systems and geological implications. Sci. China Earth Sci. 62, 550–570 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-018-9295-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-018-9295-1