Abstract
Background
The Modifiable Activity Questionnaire (MAQ) is a physical activity questionnaire shown to be both valid and reliable in French. After translation and adaptation to Dutch, the objective of the study was to see whether this questionnaire was valid and reliable in the Dutch language and thus could be used as a tool for the detection of exercise levels in a Dutch native-speaking population.
Methods
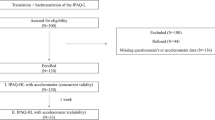
After translating and back translating the valid French version of the MAQ into Dutch, the final product of the Dutch version was tested twice in the same population (n = 101) interrupted by 1 week for the assessment of the test–retest reliability. To measure concurrent validity, the valid Dutch version of the IPAQ was filled in at the same time as the MAQ. To measure the construct validity of this assessment tool, a smaller sample size (n = 28) of the total population carried an accelerometer for 1 week.
Results
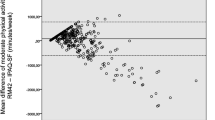
The intraclass correlation coefficient for the test–retest reliability was 0.78 (p < 0.01), suggesting a good test–retest reliability. Pearson’s rho correlation coefficient between the IPAQ and the MAQ was 0.41 (p < 0.01), suggesting a medium concurrent validity. Pearson correlation statistics showed a low, non-significant correlation coefficient (r = 0.243, p = 0.213) when measuring construct validity.
Conclusion
The present study shows that the Dutch language of the MAQ is reliable and has a medium concurrent validity. Although the construct validity is low, these results are in line with previous validation studies of physical activity questionnaires.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helmerhorst HJ, Brage S, Warren J, Besson H, Ekelund U (2012) A systematic review of reliability and objective criterion-related validity of physical activity questionnaires. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 9:103
Plasqui G, Bonomi AG, Westerterp KR (2013) Daily physical activity assessment with accelerometers: new insights and validation studies. Obes Rev 14(6):451–462
Pereira MA, FitzerGerald SJ, Gregg EW, Joswiak ML, Ryan WJ, Suminski RR et al (1997) A collection of Physical Activity Questionnaires for health-related research. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29(6 Suppl):S1–S205
Kriska AM, Knowler WC, LaPorte RE, Drash AL, Wing RR, Blair SN et al (1990) Development of questionnaire to examine relationship of physical activity and diabetes in Pima Indians. Diabetes Care 13(4):401–411
Zanuso S, Jimenez A, Pugliese G, Corigliano G, Balducci S (2010) Exercise for the management of type 2 diabetes: a review of the evidence. Acta Diabetol 47(1):15–22
Pettee Gabriel K, McClain JJ, Schmid KK, Storti KL, Ainsworth BE (2011) Reliability and convergent validity of the past-week Modifiable Activity Questionnaire. Public Health Nutr 14(3):435–442
Vuillemin A, Oppert JM, Guillemin F, Essermeant L, Fontvieille AM, Galan P et al (2000) Self-administered questionnaire compared with interview to assess past-year physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32(6):1119–1124
Oyeyemi AL, Oyeyemi AY, Adegoke BO, Oyetoke FO, Aliyu HN, Aliyu SU et al (2011) The Short International Physical Activity Questionnaire: cross-cultural adaptation, validation and reliability of the Hausa language version in Nigeria. BMC Med Res Methodol 11:156
Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjostrom M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE et al (2003) International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(8):1381–1395
Santos-Lozano A, Marin PJ, Torres-Luque G, Ruiz JR, Lucia A, Garatachea N (2012) Technical variability of the GT3X accelerometer. Med Eng Phys 34(6):787–790
Chinapaw MJ, Slootmaker SM, Schuit AJ, van Zuidam M, van Mechelen W (2009) Reliability and validity of the Activity Questionnaire for Adults and Adolescents (AQuAA). BMC Med Res Methodol 9:58
Sirard JR, Melanson EL, Li L, Freedson PS (2000) Field evaluation of the Computer Science and Applications, Inc. physical activity monitor. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32(3):695–700
Bassett DR Jr, Ainsworth BE, Swartz AM, Strath SJ, O’Brien WL, King GA (2000) Validity of four motion sensors in measuring moderate intensity physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32(Suppl 9):S471–S480
Plasqui G, Westerterp KR (2007) Physical activity assessment with accelerometers: an evaluation against doubly labeled water. Obesity (Silver Spring) 15(10):2371–2379
Momenan AA, Delshad M, Sarbazi N, Rezaei Ghaleh N, Ghanbarian A, Azizi F (2012) Reliability and validity of the Modifiable Activity Questionnaire (MAQ) in an Iranian urban adult population. Arch Iran Med 15(5):279–282
Terwee CB, Roorda LD, Dekker J, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Peat G, Jordan KP et al (2010) Mind the MIC: large variation among populations and methods. J Clin Epidemiol 63(5):524–534
Terwee CB, Mokkink LB, van Poppel MN, Chinapaw MJ, van Mechelen W, de Vet HC (2010) Qualitative attributes and measurement properties of physical activity questionnaires: a checklist. Sports Med 40(7):525–537
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd edn. Lawrence erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale
Lee PH, Macfarlane DJ, Lam TH, Stewart SM (2011) Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF): a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 8:115
Kurtze N, Rangul V, Hustvedt BE (2008) Reliability and validity of the international physical activity questionnaire in the Nord-Trondelag health study (HUNT) population of men. BMC Med Res Methodol 8:63
Mader U, Martin BW, Schutz Y, Marti B (2006) Validity of four short physical activity questionnaires in middle-aged persons. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38(7):1255–1266
Dinger MK, Behrens TK (2006) Accelerometer-determined physical activity of free-living college students. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38(4):774–779
Deng HB, Macfarlane DJ, Thomas GN, Lao XQ, Jiang CQ, Cheng KK et al (2008) Reliability and validity of the IPAQ-Chinese: the Guangzhou Biobank Cohort study. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40(2):303–307
van Poppel MN, Chinapaw MJ, Mokkink LB, van Mechelen W, Terwee CB (2010) Physical activity questionnaires for adults: a systematic review of measurement properties. Sports Med 40(7):565–600
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the funding through the Vrije Universiteit Brussel (OZR2096BOF). Bart Roelands is a postdoctoral fellow of the Research Fund of Flanders (FWO). We also thank Prof. Dr. J. Nijs for his constructive advice concerning the study protocol.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest for all authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tonoli, C., Heyman, E., Roelands, B. et al. Validation and reliability of the Dutch language version of the Modifiable Activity Questionnaire in healthy subjects. Sport Sci Health 9, 139–144 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-013-0160-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11332-013-0160-y