Abstract
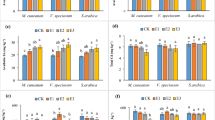
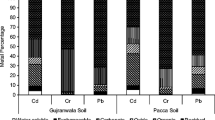
To increase the phytoextraction efficiency of heavy metals and to reduce the potential negative effects of mobilized metals on the surrounding environment are the two major objectives in a chemically enhanced phytoextraction process. In the present study, a biodegradable chelating agent, NTA, was added in a hot solution at 90°C to soil in which beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L., white bean) were growing. The concentrations of Cu, Zn and Cd, and the total phytoextraction of metals by the shoots of the plant from a 1 mmol kg−1 hot NTA application exceeded those in the shoots of plants treated with 5 mmol kg−1 normal NTA and EDTA solutions (without heating treatment). A significant correlation was found between the concentrations of metals in the shoots of beans and the relative electrolyte leakage rate of root cells, indicating that the root damage resulting from the application of a hot solution might play an important role in the process of chelate-enhanced metal uptake in plants. The application of hot NTA solutions did not significantly increase metal solubilization in soil in comparison with a normal application of solution of the same dosage. Therefore, the application of a hot NTA solution may provide a more efficient alternative in chemical-enhanced phytoextraction, although further studies of techniques of application in fields are sill required.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avery, B. W., & Bascomb, C. L. (1982). Soil survey laboratory methods. Harpenden, soil survey technical monograph No. 6. Rothamsted Experimental Station, Harpenden, Hertfordshire, U.K.
Bell, P. F., Chaney, R. L., & Angle, J. S. (1991). Free metal activity and total metal concentrations as indexes of micronutrient availability to barley [Hordeum vulgare (L.) ‘Klages’]’. Plant Soil, 130, 51–62.
Blaylock, M. J., Salt, D. E., Dushenkov, S., Zakharova, O., Gussman, C., & Kapulnik, Y., et al. (1997). Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 860–865.
Bucheli-Witschel, M., & Egli, T. (2001). Environmental fate and microbial degradation of aminopolycarboxylic acids. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 25, 69–106.
Chen, Y. H., Li, X. D., & Shen, Z. G. (2004a). Leaching and uptake of heavy metals by ten different species of plants during an EDTA-assisted phytoextraction process. Chemosphere, 57, 187–196.
Chen, Y. H., Shen, Z. G., & Li, X. D. (2004b). The use of vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides) in the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 1553–1565.
Chiu, K. K., Ye, Z. H., & Wong, M. H. (2005). Enhanced uptake of As, Zn and Cu by Vetiveria zizanioides and Zea mays using chelating agents. Chemosphere, 60, 1365–1375.
Cooper, E. M., Sims, J. T., Cunningham, S. D., Huang, J. W., & Berti, W. R. (1999). Chelate-assisted phytoextraction of lead from contaminated soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 28, 1709–1719.
Ensley, B. D., Blaylock, M. J., Dushenkov, S., Kumar, N. P. B. A., & Kapulnik, Y. (1999). Inducing hyperaccumulation of metals in plant shoots, S. U. Patent 5 917 117. Date issued: 29 June 1999.
Epstein, A. L., Gussman, C. D., Blaylock, M. J., Yermiyahu, U., Huang, J. W., & Kapulnik, Y., et al. (1999). EDTA and Pb-EDTA accumulation in Brassica juncea grown in Pb-amended soil. Plant Soil, 208, 87–94.
Garbisu, C., & Alkorta, I. (2001). Phytoextraction: A cost-effective plant-based technology for the removal of metals from the environment. Bioresource Technology, 77, 229–236.
Grčman, H., Velikonja-Bolta, Š., Vodnik, D., Kos, B., & Leštan, D. (2001). EDTA enhanced heavy metal phytoextraction: Metal accumulation, leaching and toxicity. Plant Soil, 235, 105–114.
Grčman, H., Vodnik, D., Velikonja-Bolta, Š., & Leštan, D. (2003). Ethylenediaminedissuccinate as a new chelate for environmentally safe enhanced lead phytoextraction. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 500–506.
Hewitt, E. J. (1966). Sand and water culture methods used in the study of plant nutrition (2nd ed), Technical Communication No. 22, Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, Farnham Royal, Bucks, U.K
Huang, J. W., Chen, J. J., Berti, W. R., & Cunningham, S. D. (1997). Phytoremediation of lead- contaminated soils: Role of synthetic chelates in lead phytoextraction. Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 800–805.
Kayser, A., Schulin, R., & Felix, H. (1999). Field trials for the phytoremediation of soils polluted with heavy metals. In Umweltbundesamt (Ed.), Proc. Int. Workshop am Fraunhofer Institut für Umweltchemic und Ökotoxikologie, Schmallenberg (pp. 170–182). Berlin, Germany: Erich Schmidt Verlag. Berlin, 1–2 Dec. 1997.
Kayser, A., Wenger, K., Keller, A., Attinger, W., Felix, H. R., & Gupta, S. K., et al. (2000). ‘Enhancement of phytoextraction of Zn, Cd, and Cu from calcareous soil: The use of NTA and sulfur amendments. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 1778–1783.
Kulli, B., Balmer, M., Krebs, R., Lothenbach, B., & Geiger, G., et al. (1999). The influence of nitrilotriacetate on heavy metal uptake of lettuce and ryegrass. Journal of Environmental Quality, 28, 1699–1705.
Li, X. D., Poon, C. S., & Liu, P. S. (2001). Concentration and chemical partitioning of road dusts and urban soils in Hong Kong. Applied Geochemistry, 16, 1361–1368.
Li, H. F., Wang, Q. R., Cui, Y. S., Dong, Y. T., & Christie, P. (2005). Slow release chelate enhancement of lead phytoextractio by corn (Zea mays L.) from contaminated soil – A preliminary study. Science of the Total Environment, 339, 179–187.
Lim, J.-M., Salido, A. L., & Butcher, D. J. (2004). Phytoextraction of lead using Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) with EDTA and electrodics. Microchemical Journal, 76, 3–9.
Luo, C. L., Shen, Z. G., Baker, A. J. M., & Li, X. D. (2006b). The role of root damage in the chelate-enhanced accumulation of lead by Indian mustard plants. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 8, 323–337.
Luo, C. L., Shen, Z. G., & Li, X. D. (2005). Enhanced phytoextraction of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd with EDTA and EDDS. Chemosphere, 59, 1–11.
Luo, C. L., Shen, Z. G., & Li, X. D. (2007). Plant uptake and the leaching of metals during the hot EDDS-enhanced phytoextraction process. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 9, 181–196.
Luo, C. L., Shen, Z. G., Li, X. D., & Baker, A. J. M. (2006c). Enhanced phytoextraction of Pb and other metals from artificially contaminated soils through the combined application of EDTA and EDDS. Chemosphere, 63, 1773–1784.
Luo, C. L., Shen, Z. G., Lou, L. Q., & Li, X. D. (2006a). EDDS and EDTA-enhanced phytoextraction of metals from artificially contaminated soil and residual effects of chelant compounds. Environmental Pollution, 144, 862–871.
McBride, M. B. (1994). Environmental chemistry of soils. New York: Oxford Univ. Press.
Meers, E., Hopgood, M., Lesage, E., Vervaeke, P., Tack, F. M. G., & Verloo, M. G. (2004). Enhanced phytoextraction: In search of EDTA alternatives. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 6, 95–109.
Meers, E., Ruttens, A., Hopgood, M. J., Samson, D., & Tack, F. M. G. (2005). Comparison of EDTA and EDDS as potential soil amendments for enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals. Chemosphere, 58, 1011–1022.
Puschenreiter, M., Stoger, G., Lombi, E., Horak, O., & Wenzel, W. W. (2001). Phytoextraction of heavy metal contaminated soils with Thlaspi goesingense and Amaranthus hybridus: rhizosphere manipulation using EDTA and ammonium sulfate. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 164, 615–621.
Quartacci, M. F., Baker, A. J. M., & Navari-Izzo, F. (2005). Nitrilotriacetate- and citric acid-assisted phytoremediation of cadmium by Indian mustard (Brassica juncea (L.) Czernj, Brassicaceae). Chemosphere, 59, 1249–1255.
Robinson, B. H., Mills, T. M., Petit, D., Fung, L. E., Green, S. R., & Clothier, B. E. (2000). ‘Natural and induced cadmium-accumulation in polar and willow: Implications for phytoremediation. Plant Soil, 227, 301–306.
Römheld, V., & Marschner, H. (1981). Effect of Fe stress on utilization of Fe chelates by efficient and inefficient plant-species. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 3, 551–556.
Sarret, G., Vangronsveld, J., Manceau, A., Musso, M., D’Haen, J., & Menthonnex, J.-J., et al. (2001). Accumulation forms of Zn and Pb in Phaseolus vulgaris in the presence and absence of EDTA. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 2854–2859.
Shen, Z. G., Li, X. D., Wang, C. C., Chen, H. M., & Chua, H. (2002). Lead phytoextraction from contaminated soil with high-biomass plant species. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 1893–1900.
Tandy, S., Bossart, K., Mueller, R., Ritschel, J., Hauser, L., & Schulin, R., et al. (2004). Extraction of heavy metals from soils using biodegradable chelating agents. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 937–944.
Tiedje, J. M., & Mason, B. B. (1974). Biodegradation of nitrilotriacetate (NTA) in soils. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings, 38, 278–283.
Vassil, A. D., Kapulnik, Y., Raskin, I., & Salt, D. E. (1998). The role of EDTA in lead transport and accumulation by Indian mustard. Plant Physiology, 117, 447–453.
Wenger, K., Gupta, S. K., Furrer, G., & Schulin, R. (2003). The role of nitrilotriacetate in copper uptake by tobacco. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 1669–1676.
Wenger, K., Kayser, A., Gupta, S. K., Furrer, G., & Schulin, R. (2002). Comparison of NTA and elemental sulfur as potential soil amendments in phytoremediation. Soil & Sediment Contamination, 11, 655–672.
Wu, J., Hsu, F. C., & Cunningham, S. D. (1999). Chelate-assisted Pb phytoextraction: Pb availability, uptake and translocation constraints. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 1898–1904.
Zhou, W. J., & Leul, M. (1998). Uniconazole-induced alleviation of freezing injury in relation to changes in hormonal balance, enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in winter rape. Plant Growth Regulation, 26, 41–47.
Zhu, G. R., Zhong, H. W., & Zhang, A. Q. (1990). Plant physiology experiment Peking University Press, Beijing, pp. 242–254.
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong SAR Government (PolyU5046/02E) and the Postdoctoral Research Fellowships from the Hong Kong Polytechnic University (G-YX07 and G-YY88).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, CL., Shen, ZG. & Li, XD. Hot NTA Application Enhanced Metal Phytoextraction from Contaminated Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 188, 127–137 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9529-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9529-3