Abstract
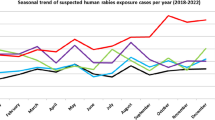
To assess the epidemiological features of wildlife rabies in Zimbabwe, a retrospective study covering a period of 12 years (1992–2003) was conducted using rabies records of the Central Veterinary Laboratories (CVL), Department of Veterinary Technical Services at Harare. Records of monthly and annual wildlife rabies were perused with regard to total samples submitted to the CVL and corresponding positive cases. Positive cases were analyzed in relation to the animal species involved, seasonal trends, and land-use categories. A total of 2107 samples were submitted and 1 540 (73.1%) were positive. Jackals (Canis mesomelas and C. adustus), with a peak occurrence of rabies between January and March were the major maintenance host, representing approximately 91% of the total rabies cases confirmed. The Canidae family recorded the highest number of cases followed by the Viverridae, Mustelidae, Felidae, Herpestidae and Hyaenidae families in that order. During the present study rabies cases were confirmed in 7 additional wild animals. The majority of the positive cases (83.7%) were recorded in commercial farming areas in the northeast parts of the country.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon., 2002. Central Veterinary Laboratory Report for 2002. Department of Veterinary Technical Services, Ministry of Lands, Agriculture and Rural Resettlement, P.O. Box, CY551, Causeway, Harare, Zimbabwe.
Bingham, J., 1999. The control of rabies in jackals in Zimbabwe. PhD Thesis. University of Zimbabwe, Harare, Zimbabwe.
Bingham, J., 2005. Canine rabies ecology in southern Africa. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 11, 1337–1342.
Bingham, J. and Foggin, C.M., 1993. Jackal rabies in Zimbabwe. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 60, 365–366.
Bingham, J., Foggin, C.M., Wandeler, A.I. and Hill, F.W.G., 1999. The epidemiology of rabies in Zimbabwe. 2. Rabies in jackals (Canis adustus and Canis mesomelas). Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 66, 11–23.
Bingham, J., Javangwe, S., Sabeta, C.T., Wandeler, A.I. and Nel, L.H., 2001. Report of isolations of unusual lyssaviruses (rabies and Mokola viruses) identified retrospectively from Zimbabwe. Journal of the South African Veterinary Association, 72, 92–94.
Bishop, G.C., Durreheim, G.N., Kloeck, P.E., Godlonton, J.D., Bingham, J., Speare, R. and The Rabies Advisory Group, 2002. Rabies guide for the medical, veterinary and allied professions. Department of Agriculture, Government Printer, Pretoria.
Childs, J.E., Krebs, J.W., Real, L.A. and Gordon, E.R., 2007. Animal-based national surveillance for zoonotic disease: Quality, limitations, and implications of a model system for monitoring rabies. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 78, 246–261. doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2006.10.014
Foggin, C.M., 1988. Rabies and rabies-related viruses in Zimbabwe: historical, virological and ecological aspects. DPhil Thesis, Faculty of Medicine, University of Zimbabwe.
Hofmeyr, M., Hofmeyr, D., Nel, L. and Bingham, J., 2004. A second outbreak of rabies in African wild dogs (Lycaon pictus) in Madikwe Game Reserve, South Africa, demonstrating the efficacy of vaccination against natural rabies challenge. Animal Conservation, 7, 193–198. doi:10.1017/S1367943004001234
King, A.A., Meredith, C.D. and Thomson, G.R., 1994. The biology of southern African lyssavirus variants. In: C.E. Rupprecht, B. Dietzschold and H. Koprowski (Editors), Lyssaviruses, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Lloyd, H.G., 1976. Wildlife rabies in Europe and the British situation. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 70, 179–187. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(76)90036-5
Nel, L.H., Thomson, G.R. and von Teichman, B.F., 1993. Molecular epidemiology of rabies in South Africa. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 60, 301–306.
Nel, L.H., Sabeta, C.T., von Teichman, B., Jaftha, J.B., Rupprecht, C.E. and Bingham, J., 2005. Mongoose rabies in Southern Africa: a re-evaluation based on molecular epidemiology. Virus Research, 109, 165–173. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2004.12.003
Pfukenyi, D.M., Pawandiwa, D., Makaya, P.V. and Ushewokunze-Obatolu, Unesu, 2007. A retrospective study of rabies in humans in Zimbabwe, between 1992 and 2003. Acta Tropica, 102, 190–196. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2007.04.013
Randall, D.A., Williams, S.D., Kuzmin, I.V., Rupprecht, C.E., Tallents, L.A. and Tefera, Z., 2004. Rabies in endangered Ethiopian wolves. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 10, 2214–2217.
Rottcher, D. and Sawchuk, A.M., 1978. Wildlife rabies in Zambia. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 14, 513–517.
Rupprecht, C.E., 2002. Rabies: reemergence of the disease. Compendium on Continuing Education for the Practicing Veterinarian (Supplement No.1A), 24, 57–60.
Sabeta, C.T., Bingham, J. and Nel, L.H., 2003. Molecular epidemiology of canid rabies in Zimbabwe and South Africa. Virus Research, 91, 203–211. doi:10.1016/S0168-1702(02)00272-1
Swanepoel, R., Barnard, B.J.H., Meredith, C.D., Bishop, G.C., Bruchner, G.K., Fogging, C.M. and Hubschle, O.J.B., 1993. Rabies in Southern Africa. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 60, 323–346.
Thomson, G.R. and Meredith, C.D., 1993. Rabies in bat-eared foxes in South Africa. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 60, 399–403.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Rabies Unit, Pathology Section, within the Central Veterinary Laboratory, Diagnostic and Research Branch, Department of Veterinary Technical Services for allowing access to the rabies records.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfukenyi, D.M., Pawandiwa, D., Makaya, P.V. et al. A retrospective study of wildlife rabies in Zimbabwe, between 1992 and 2003. Trop Anim Health Prod 41, 565–572 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-008-9224-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-008-9224-4