Abstract
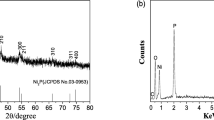
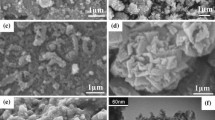
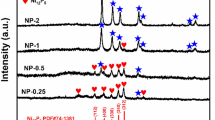
The controlled synthesis of transition metal phosphides has been pursued to obtain excellent performances in application. Herein, we report a simple and effective method to synthesize nickel phosphide nanoparticles with target phases. Pure-phase nickel phosphide nanoparticles were obtained in different crystalline states (Ni2P and Ni12P5), and the crystalline phase of nickel phosphide could be controlled by varying the reaction conditions such as the temperature and duration of thermal treatment or the ratio between Ni and P. In addition, the nickel phosphide particles after thermal treatment maintained their sizes without serious agglomeration. In the hydrogenation of nitrobenzene, the phosphides with pure-phase (Ni2P or Ni12P5) and high crystallinity showed high catalytic activities. This proves that the crystalline phase of nickel phosphide plays an important role in the catalytic activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang L, Li X, Wang AJ, Prins R, Wang Y, Chen YY, Duan XP (2014) J Catal 317:144–152
Peroni M, Lee I, Huang X, Barath E, Gutierrez OY, Lercher JA (2017) ACS Catal 7:6331–6341
Chung DY, Jun SW, Yoon G, Kim H, Yoo JM, Lee K-S, Kim T, Shin H, Shin H, Kwon SG, Kang K, Hyeon T, Sung Y-E (2017) J Am Chem Soc 139:6669–6674
Guo HN, Chen CC, Chen K, Cai HC, Chang XY, Liu S, Li WQ, Wang YJ, Wang CY (2017) J Mater Chem A 5:22316–22324
Bai J, Xi BJ, Mao HZ, Lin Y, Ma XJ, Feng JK, Xiong SL (2018) Adv Mater 30:1802310
Moon J-S, Kim E-G, Lee Y-K (2014) J Catal 311:144–152
Li HM, Lu SQ, Sun JY, Pei JJ, Liu D, Xue YR, Mao JJ, Zhu W, Zhuang ZB (2018) Chem Eur J 24:11748–11754
Wang XD, Zhou HP, Zhang DK, Pi MY, Feng JJ, Chen SJ (2018) J Power Sources 387:1–8
Liu P, Wei T, Xu J, Xue B, Zhang W, Li Y (2013) Reac Kinet Mech Cat 109:105–115
Ma JJ, Ni SB, Lv XH, Yang XL, Zhang LL (2014) Mater Lett 133:94–96
Aso K, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2011) Inorg Chem 50:10820–10824
Layan Savithra GH, Muthuswamy E, Bowker RH, Carrillo BA, Bussell ME, Brock SL (2013) Chem Mater 25:825–833
Senevirathne K, Burns AW, Bussell ME, Brock SL (2007) Adv Funct Mater 17:3933–3939
Badari CA, Lonyi F, Drotar E, Kaszonyi A, Valyon J (2015) Appl Catal B 164:48–60
Li D, Senevirathne K, Aquilina L, Brock SL (2015) Inorg Chem 54:7968–7975
Pan Y, Liu Y, Zhao J, Yang K, Liang J, Liu D, Hu W, Liu D, Liu Y, Liu C (2015) J Mater Chem A 3:1656–1665
Muthuswamy E, Savithra GHL, Brock SL (2011) ACS Nano 5:2402–2411
Yun G, Guan Q, Li W (2017) RSC Adv 7:8677–8687
Deng Y, Zhou Y, Yao Y, Wang J (2013) New J Chem 37:4083–4088
Wang B, Huang X, Zhu Z, Huang H, Dai J (2012) Appl Nanosci 2:423–427
Liu P, Chang W-T, Liang X-Y, Wang J, Li Y-X (2016) Catal Commun 76:42–45
Iino A, Cho A, Takagaki A, Kikuchi R, Oyama ST (2014) J Catal 311:17–27
Huang Z, Chen Z, Chen Z, Lv C, Meng H, Zhang C (2014) ACS Nano 8:8121–8129
Liu P, Chen Y-L, Zhang Z-X, Liu H-F, Li Y-X (2018) Reac Kinet Mech Cat 125:595–603
Prekob Á, Muránszky G, Hutkai ZG, Pekker P, Kristály F, Fiser B, Viskolcz B, Vanyorek L (2018) Reac Kinet Mech Cat 125:583–593
Acknowledgements
Authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21406019), Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (No. 2016M601794), Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Jiangsu province, Jiangsu Shuangchuang Program, and Advanced Catalysis and Green Manufacturing Collaborative Innovation Center, Changzhou University for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Zhang, ZX., Jun, S.W. et al. Controlled synthesis of nickel phosphide nanoparticles with pure-phase Ni2P and Ni12P5 for hydrogenation of nitrobenzene. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 126, 453–461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-018-1496-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-018-1496-8