Abstract
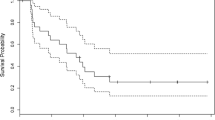
We evaluated the efficacy of temozolomide (TMZ) or lomustine (CCNU) in combination with 6-thioguanine, capecitabine, and celecoxib for the treatment of recurrent high-grade glioma. Forty-three patients with recurrent glioblastoma and 31 patients with recurrent anaplastic glioma (AG) were enrolled in this open-label, non-comparative study. Patients previously treated with TMZ received CCNU while all others received TMZ; all patients received 6-thioguanine, capecitabine, and celecoxib. Endpoints were 12-month progression-free survival (PFS) for patients with AG, 6-month PFS for patients with glioblastoma, duration of PFS, and MRI-based objective response rates. Results from the TMZ and CCNU treatment arms were combined in the final analysis because there was no statistically significant difference between them. Thirty-eight patients with glioblastoma were treated with the lomustine-based regimen, and five received the TMZ-based regimen. For the 43 glioblastoma patients, the objective response rate was 12 and 33% had stable disease; the 6-month PFS was 14% and median overall survival 32 weeks. For the 31 AG patients, the combined objective response rate was 26 and 42% had stable disease; the 12 month PFS was 44%. Treatment was reasonably well tolerated with hematological toxicity common and more frequent with CCNU than TMZ. The combination therapy with 6-thioguanine, capecitabine and celecoxib plus CCNU or TMZ does not appear to be more effective than other alkylating agent schedules for patients with recurrent glioblastoma. The combination, however, is promising for patients with recurrent high-grade AG.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
CBTRUS (2009–2010) CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in Eighteen States in 2002–2006. Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States, 2009
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Levin VA, Hoffman WF, Pischer TL, Seager ML, Boldrey EB, Wilson CB (1978) BCNU-5-fluorouracil combination therapy for recurrent malignant brain tumors. Cancer Treat Rep 62:2071–2076
van den Bent MJ, Carpentier AF, Brandes AA, Sanson M, Taphoorn MJ, Bernsen HJ, Frenay M, Tijssen CC, Grisold W, Sipos L, Haaxma-Reiche H, Kros JM, van Kouwenhoven MC, Vecht CJ, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Gorlia T (2006) Adjuvant procarbazine, lomustine, and vincristine improves progression-free survival but not overall survival in newly diagnosed anaplastic oligodendrogliomas and oligoastrocytomas: a randomized European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 24:2715–2722
Prados MD, Seiferheld W, Sandler HM, Buckner JC, Phillips T, Schultz C, Urtasun R, Davis R, Gutin P, Cascino TL, Greenberg HS, Curran WJ Jr (2004) Phase III randomized study of radiotherapy plus procarbazine, lomustine, and vincristine with or without BUdR for treatment of anaplastic astrocytoma: final report of RTOG 9404. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:1147–1152
Prados MD, Gutin PH, Phillips TL, Wara WM, Larson DA, Sneed PK, Davis RL, Ahn DK, Lamborn K, Wilson CB (1992) Highly anaplastic astrocytoma: a review of 357 patients treated between 1977 and 1989. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23:3–8
Yung WK, Albright RE, Olson J, Fredericks R, Fink K, Prados MD, Brada M, Spence A, Hohl RJ, Shapiro W, Glantz M, Greenberg H, Selker RG, Vick NA, Rampling R, Friedman H, Phillips P, Bruner J, Yue N, Osoba D, Zaknoen S, Levin VA (2000) A phase II study of temozolomide vs procarbazine in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Br J Cancer 83:588–593
Wong ET, Hess KR, Gleason MJ, Jaeckle KA, Kyritsis AP, Prados MD, Levin VA, Yung WK (1999) Outcomes and prognostic factors in recurrent glioma patients enrolled onto phase II clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 17:2572–2578
Levin VA, Ictech S, Hess KR (2007) Impact of phase II trials with progression-free survival as end-points on survival-based phase III studies in patients with anaplastic gliomas. BMC Cancer 7:106
Kreisl TN, Kim L, Moore K, Duic P, Royce C, Stroud I, Garren N, Mackey M, Butman JA, Camphausen K, Park J, Albert PS, Fine HA (2009) Phase II trial of single-agent bevacizumab followed by bevacizumab plus irinotecan at tumor progression in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:740–745
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, Hau P, Brandes AA, Gijtenbeek J, Marosi C, Vecht CJ, Mokhtari K, Wesseling P, Villa S, Eisenhauer E, Gorlia T, Weller M, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Mirimanoff RO (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10:459–466
Levin VA, Prados MD (1992) Treatment of recurrent gliomas and metastatic brain tumors with a polydrug protocol designed to combat nitrosourea resistance. J Clin Oncol 10:766–771
Goerne R, Bogdahn U, Hau P (2008) Procarbazine–a traditional drug in the treatment of malignant gliomas. Curr Med Chem 15:1376–1387
Bodell WJ, Morgan WF, Rasmussen J, Williams ME, Deen DF (1985) Potentiation of 1, 3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea (BCNU)-induced cytotoxicity in 9L cells by pretreatment with 6-thioguanine. Biochem Pharmacol 34:515–520
Wang AM, Elion GB, Friedman HS, Bodell WJ, Bigner DD, Schold SC Jr (1991) Positive therapeutic interaction between thiopurines and alkylating drugs in human glioma xenografts. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 27:278–284
Prados MD, Larson DA, Lamborn K, McDermott MW, Sneed PK, Wara WM, Chang SM, Mack EE, Krouwer HG, Chandler KL, Warnick RE, Davis RL, Rabbitt JE, Malec M, Levin VA, Gutin PH, Phillips TL, Wilson CB (1998) Radiation therapy and hydroxyurea followed by the combination of 6-thioguanine and BCNU for the treatment of primary malignant brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 40:57–63
Kyritsis AP, Yung WK, Jaeckle KA, Bruner J, Gleason MJ, Ictech SE, Flowers A, Levin VA (1996) Combination of 6-thioguanine, procarbazine, lomustine, and hydroxyurea for patients with recurrent malignant gliomas. Neurosurgery 39:921–926
Shono T, Tofilon PJ, Bruner JM, Owolabi O, Lang FF (2001) Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human gliomas: prognostic significance and molecular correlations. Cancer Res 61:4375–4381
Deininger MH, Weller M, Streffer J, Mittelbronn M, Meyermann R (1999) Patterns of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 expression in human gliomas in vivo. Acta Neuropathol 98:240–244
Hida T, Kozaki K, Muramatsu H, Masuda A, Shimizu S, Mitsudomi T, Sugiura T, Ogawa M, Takahashi T (2000) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor induces apoptosis and enhances cytotoxicity of various anticancer agents in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 6:2006–2011
Masferrer JL, Leahy KM, Koki AT, Zweifel BS, Settle SL, Woerner BM, Edwards DA, Flickinger AG, Moore RJ, Seibert K (2000) Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Cancer Res 60:1306–1311
Joki T, Heese O, Nikas DC, Bello L, Zhang J, Kraeft SK, Seyfried NT, Abe T, Chen LB, Carroll RS, Black PM (2000) Expression of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) in human glioma and in vitro inhibition by a specific COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398. Cancer Res 60:4926–4931
Kardosh A, Blumenthal M, Wang WJ, Chen TC, Schonthal AH (2004) Differential effects of selective COX-2 inhibitors on cell cycle regulation and proliferation of glioblastoma cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther 3:55–62
Chen JC, Chen Y, Su YH, Tseng SH (2007) Celecoxib increased expression of 14–3-3sigma and induced apoptosis of glioma cells. Anticancer Res 27:2547–2554
Gaiser T, Becker MR, Habel A, Reuss DE, Ehemann V, Rami A, Siegelin MD (2008) TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in malignant glioma cells is augmented by celecoxib through proteasomal degradation of survivin. Neurosci Lett 442:109–113
Kang SG, Kim JS, Park K, Groves MD, Nam DH (2006) Combination celecoxib and temozolomide in C6 rat glioma orthotopic model. Oncol Rep 15:7–13
Mizutani Y, Kamoi K, Ukimura O, Kawauchi A, Miki T (2002) Synergistic cytotoxicity and apoptosis of JTE-522, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, and 5-fluorouracil against bladder cancer. J Urol 168:2650–2654
Wilgus TA, Breza TS Jr, Tober KL, Oberyszyn TM (2004) Treatment with 5-fluorouracil and celecoxib displays synergistic regression of ultraviolet light B-induced skin tumors. J Invest Dermatol 122:1488–1494
Zhang YC, Wang S, Zhang H, Ye YJ, Liang B, Cui ZR (2004) Effects of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor NS-398 on 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy and progression of colon cells: an experimental study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 84:583–586
Irie T, Tsujii M, Tsuji S, Yoshio T, Ishii S, Shinzaki S, Egawa S, Kakiuchi Y, Nishida T, Yasumaru M, Iijima H, Murata H, Takehara T, Kawano S, Hayashi N (2007) Synergistic antitumor effects of celecoxib with 5-fluorouracil depend on IFN-gamma. Int J Cancer 121:878–883
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr, Cairncross JG (1990) Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8:1277–1280
Wick W, Steinbach JP, Kuker WM, Dichgans J, Bamberg M, Weller M (2004) One week on/one week off: a novel active regimen of temozolomide for recurrent glioblastoma. Neurology 62:2113–2115
Yung WK, Prados MD, Yaya-Tur R, Rosenfeld SS, Brada M, Friedman HS, Albright R, Olson J, Chang SM, O’Neill AM, Friedman AH, Bruner J, Yue N, Dugan M, Zaknoen S, Levin VA (1999) Multicenter phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with anaplastic astrocytoma or anaplastic oligoastrocytoma at first relapse Temodal Brain Tumor Group. J Clin Oncol 17:2762–2771
Brandes AA, Tosoni A, Amista P, Nicolardi L, Grosso D, Berti F, Ermani M (2004) How effective is BCNU in recurrent glioblastoma in the modern era? A phase II trial. Neurology 63:1281–1284
Acknowledgments
We thank Bryan Tutt for editorial support preparing this manuscript and Siew Ju See for help in protocol design and development.
Funding
This study was supported by The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center institutional funds and Core Grant CA 16672 to support clinical trials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walbert, T., Gilbert, M.R., Groves, M.D. et al. Combination of 6-thioguanine, capecitabine, and celecoxib with temozolomide or lomustine for recurrent high-grade glioma. J Neurooncol 102, 273–280 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0313-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0313-7