Abstract
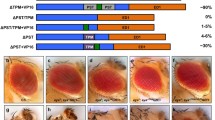
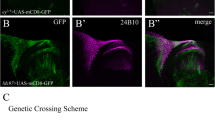
Transglutaminases (TGs) catalyze the cross-linking of proteins and are involved in various biological processes in mammals. In invertebrates, except for the involvement in the hemolymph clotting, the functions of TG have not been revealed. Drosophila has a single TG gene (CG7356), from which two kinds of mRNAs (dTG-RA and dTG-RB) are formed. RT-PCR analyses indicated that both dTGs-RA and -RB are synthesized in all the developmental stages tested. To reveal the roles of dTG during the development, we examined a phenotype induced through the ectopic expression of dTG by using a GAL4-UAS targeted expression system. Over-expression of dTG-A in the eye imaginal disc of larva induced a rough eye phenotype in adult compound eyes. Co-expression of P35, an inhibitor of apoptosis, suppressed the rough eye phenotype, suggesting that the rough eye phenotype induced by the over-expression of dTG-A in the eye imaginal disc is due to the occurrence of apoptosis. The rough eye phenotype induced by the over-expression of dTG-A was suppressed by the crossing with mutant fly lines lacking Drosophila JNK gene basket (bsk) or Drosophila JNKK gene hemipterous. FLP-out experiments using an enhancer trap line showed that the over-expression of dTG-A in the eye imaginal disc increased the puckered enhancer activity, a reporter of Bsk activity. These results suggested that the rough eye phenotype induced by the over-expression of dTG-A is related to an enhancement of JNK signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fesus L, Piacentini M (2002) Transglutaminase 2: an enigmatic enzyme with diverse functions. Trends Biochem Sci 27:534–539
Griffin M, Casadio R, Bergamini CM (2002) Transglutaminases: nature’s biological glues. Biochem J 368:377–396
Lorand L, Graham RM (2003) Transglutaminases: crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:140–156
Esposito C, Caputo I (2005) Mammalian transglutaminases: identification of substrates as a key to physiological function and physiopathological relevance. FEBS J 272:615–631
Grenard P, Bates MK, Aeschlimann D (2001) Evolution of transglutaminase genes: identification of a transglutaminase gene cluster on human chromosome 15q15. J Biol Chem 276:33066–33078
Tokunaga F, Yamada M, Miyata T, Ding YL, Hiranaga-Kawabata M, Muta T, Iwanaga S, Ichinose A, Davie EW (1993) Limulus hemocyte transglutaminase: its purification and characterization, and identification of the intracellular substrates. J Biol Chem 268:252–261
Tokunaga F, Muta T, Iwanaga S, Ichinose A, Davie EW, Kuma K, Miyata T (1993) Limulus hemocyte transglutaminase: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence, and tissue localization. J Biol Chem 268:262–268
Osaki T, Okino N, Tokunaga F, Iwanaga S, Kawabata S (2002) Proline-rich cell surface antigens of horseshoe crab hemocytes are substrates for protein cross-linking with a clotting protein coagulin. J Biol Chem 277:40084–40090
Singer MA, Hortsch M, Goodman CS, Bentley D (1992) Annulin, a protein expressed at limb segment boundaries in the grasshopper embryo, is homologous to protein cross-linking transglutaminase. Dev Biol 154:143–159
Matsuda Y, Koshiba T, Osaki T, Suyama H, Arisaka F, Toh Y, Kawabata S (2007) An arthropod cuticular chitin-binding protein endows injured sites with transglutaminase-dependent mesh. J Biol Chem 282:37316–37324
Lin X, Soderhall K, Soderhall I (2008) Transglutaminase activity in the hematopoietic tissue of a crustacean, Pacifastacus leniuscurs, importance in hemocyte homeostasia. BMC Immunol 9:58
Karlsson C, Korayem AM, Scherfer C, Loseva O, Dushay MS, Theopold U (2004) Proteomic analysis of the Drosophila larval hemolymph clot. J Biol Chem 279:52033–52041
Lindgren M, Riazi R, Lesch C, Wilhelmsson C, Theopold U, Dushay MS (2008) Fondue and transglutaminase in the Drosophila larval clot. J Insect Physiol 54:586–592
Ikle J, Elwell JA, Bryantsev AL, Cripps RM (2008) Cardiac expression of the Drosophila transglutaminase (CG7356) gene is directly controlled by myocyte enhancer factor-2. Dev Dyn 237:2090–2099
Brand AH, Perrimon N (1993) Targeted gene expression as means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118:401–415
Hirose F, Ohshima N, Shiraki M, Inoue YH, Taguchi O, Nishi Y, Matsukage A, Yamaguchi M (2001) Ectopic expression of DREF induced DNA synthesis, apoptosis, and unusual morphogenesis in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc: possible interaction with polycomb and trithorax group proteins. Mol Cell Biol 21:7231–7242
Adachi-Yamada T (2002) Puckered-GAL4 driving in JNK-active cells. Genesis 34:19–22
Spradling AC (1986) P-element-mediated transformation. In: Roberts DB (ed) Drosophila, a practical approach. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 175–197
Robertson HM, Preston CR, Phillis RW, Johnson-Schlitz DM, Benz WK, Engels WR (1988) A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 118:461–470
Ikura K, Yanagawa S, Okumura K, Sasaki R, Chiba H (1984) Production of monoclonal antibodies to guinea pig liver transglutaminase. Agric Biol Chem 48:1835–1840
Sun J, Tower J (1999) FLP recombinase-mediated induction of Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase transgene expression can extend the life span of adult Drosophila melanogaster flies. Mol Cell Biol 19:216–228
Piacentini M, Amendola A, Ciccosanti F, Falasca L, Farrace MG, Mastroberardino PG, Nardacci R, Oliverio S, Piredda L, Rodolfo C, Autuori F (2005) Type 2 transglutaminase and cell death. In: Mehta K, Eckert R (eds) Transglutaminases. Family of enzymes with diverse functions. Karger, Basel, pp 58–74
Yamaguchi M, Yoshida H, Hirose F, Inoue YH, Hayashi Y, Yamagishi M, Nishi Y, Tamai K, Sakaguchi K, Matsukage A (2001) Ectopic expression of BEAF32A in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc inhibits differentiation of photoreceptor cells and induces apoptosis. Chromosoma 110:313–321
Hay BA, Wolff T, Rubin GM (1994) Expression of baculovirus P35 prevents cell death in Drosophila. Development 120:2121–2129
Roibitaille K, Daviau A, Tucholski J, Johnson GVW, Rancourt C, Blouin R (2004) Tissue transglutaminase triggers oligomerization and activation of dual leucine zipper-bearing kinase in calphostin C-treated cells to facilitate apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 11:539–542
Martin-Blanco E, Gampel A, Ring J, Virdee K, Kirov N, Tolkovski AM, Martinez-Arias A (1998) Puckered encodes a phosphatase that mediates a feedback loop regulating JNK activity during dorsal closure in Drosophila. Genes Dev 12:557–570
Matsumoto K (1999) Distortion of proximodistal information causes JNK-dependent apoptosis in Drosophila wing. Nature 400:166–169
Tateno M, Nishida Y, Adachi-Yamada T (2000) Regulation of JNK by Src during Drosophila development. Science 287:324–327
Igaki T, Kanda H, Yamamoto-Goto Y, Kanuka H, Kuranaga E, Aigaki T, Miura M (2002) Eiger, a TNF superfamily ligand that triggers the Drosophila JNK pathway. EMBO J 21:3009–3018
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in Aid for Scientific Research (C) 18580092 (to K. I.) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umehara, M., Ichikawa, A., Sakamoto, H. et al. Over-expression of transglutaminase in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc induces a rough eye phenotype. Mol Cell Biochem 342, 223–232 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0487-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0487-5