Abstract
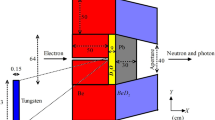
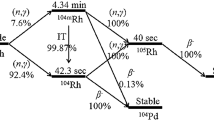
Stray neutron distribution in a medical cyclotron vault room was evaluated by neutron activation analysis (NAA). Neutrons were generated in the production of radioactive nuclides, such as 18F, 11C, 13N and 15O, for diagnostic usage. Indium foil was adopted to evaluate the stray fast and thermal neutron intensity based on 115In(nf, n′)115mIn and 115In(nth, γ)116m1In reactions, respectively. The indium foils were weighed, sealed and placed at 62 points around the 6.7×8.2 m2 cyclotron room. Additionally, each indium foil was exposed for over 80 minutes during cyclotron operation and γ-peaks were analyzed using an HPGe detector to evaluate the number of stray fast (Φ f) or thermal (Φ th) neutrons. The minimum to maximum numbers of fast and thermal neutrons were (3.47±0.11)×103 to (1.06±0.21)×104 n·cm−2·s−1 and 9 to 965 n·cm−2·s−1, respectively. The minimum detectable limit for stray neutrons was included herein to demonstrate the reliability. Accordingly, 60 and two points, respectively, the confidence level associated with the reported intensities of fast and thermal neutrons reached 95%. The low qualified ratio in the evaluation of stray thermal neutrons might have been caused by either the high Compton scattering plateau or the low intensity of the gamma-ray peak in the relevant spectrum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. G. O’donnell, L. L. Vintro, G. J. Duffy, et al., Appl. Radiat. Isotopes, 60 (2004) 539.
C. Birattari, M. C. Cantone, A. Ferrari, et al., Nucl. Instr. Methods, B43 (1989) 119.
M. Silari, Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 96[4] (2001) 381.
K. Kondo, H. Hirayama, S. Ban, et al., Health Phys., 46[6] (1984) 1221.
B. Mukherjee, A. Barber, Appl. Radiat. Isotopes, 46(12) (1995) 1333.
B. Mukherjee, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 231 (1998) 179.
I. Tilquin, P. Fromrnt, M. Cogneau, et al., Nucl. Instr. Meth. A545 (2005) 339.
H. R. Vega-Carrillo, Nucl. Instr. Methods, A463 (2001) 375.
L. K. Pan, Nucl. Tech., 89 (1990) 116.
C. Y. CHEN, Y. Y. WEI, S. P. CHANGLAI, et al., J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 257 (2003) 405.
Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Environmental radiation report, Taichung Taiwan, Republic of China, 2007.
International Commission on Radiological Protection, Recommendation of the ICRP, ICRP Publication 60, Annals of the ICRP, 21. No. 1–3, Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 1991.
CTI, Radioisotope delivery system RDS-111. Technical description, Knoxville, T. N. USA, 1995.
J. H. Chao, W. S. Liu, C. Y. Chen, Radiat. Meas., 42 (2007) 1538.
S. S. Hanna, C. J. Martoff, D. Pocanic, et al., Nucl. Instr. Methods, A401 (1997) 345.
American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM), Neutron measurements around high energy X-ray radiotherapy machine, AAPM No.19, New York, 1986.
C. Konno, F. Maekawa, Y. Oyama, et al., Fusion Eng. Des., 28 (1995) 745.
V. S. Shieley, C. M. Lederer, Table of Isotopes, Wiley-Interscience Publishing, New York, 1978.
R. B. Sharma, C. M. Culver, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 183 (1994) 329.
J. H. Chao, P. C. Hsu, H. M. Liu, Appl. Radiat. Isotopes, 55 (2001) 549.
O. Z. Assatel, N. M. Spyrou, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 217 (1997) 255.
L. K. Pan, Nucl. Tech., 124 (1998) 276.
C. Chung, L. J. Yuan, K. B. Chen, Nucl. Instr. Methods, A243 (1986) 102.
C. Chumg, C. J. Lee, Nucl. Instr. Methods, A273 (1988) 436.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, JB., Lee, JP., Lin, DB. et al. Evaluation of stray neutron distribution in medical cyclotron vault room by neutron activation analysis approach. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 280, 481–487 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-7461-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-7461-2