Abstract
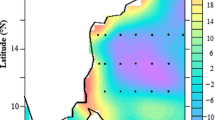
The biochemical effects of a cold-core eddy that was shed from the Kuroshio Current at the Luzon Strait bordering the South China Sea (SCS) were studied in late spring, a relatively unproductive season in the SCS. The extent of the eddy was determined by time-series images of SeaWiFS ocean color, AVHRR sea surface temperature, and TOPEX/Jason-1 sea surface height anomaly. Nutrient budgets, nitrate-based new production, primary production, and phytoplankton assemblages were compared between the eddy and its surrounding Kuroshio and SCS waters. The enhanced productivity in the eddy was comparable to wintertime productivity in the SCS basin, which is supported by upwelled subsurface nitrate under the prevailing Northeastern Monsoon. There were more Synechococcus, pico-eucaryotes, and diatoms, but less Trichodesmium in the surface water inside the eddy than outside. Prochlorococcus and Richelia intracellularis showed no spatial differences. Water column-integrated primary production (IPP) inside the eddy was 2–3 times that outside the eddy in the SCS (1.09 vs. 0.59 g C m−2d−1), as was nitrate-based new production (INP) (0.67 vs. 0.25 g C m−2d−1). INP in the eddy was 6 times that in the Kuroshio (0.12 g C m−2d−1). IPP and INP in the eddy were higher than the maximum production values ever measured in the SCS basin. Surface chlorophyll a concentration (0.40 mg m−3) in the eddy equaled the maximum concentration registered for the SCS basin and was higher than the wintertime average (0.29 ± 0.04 mg m−3). INP was 3.5 times as great and IPP was doubled in the eddy compared to the wintertime SCS basin. As cold core eddies form intermittently all year round as the Kuroshio invades the SCS, their effects on phytoplankton productivity and assemblages are likely to have important influences on the biogeochemical cycle of the region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, C. B., J. Kanda and E. A. Laws (1996): New production and photosynthetic rates within and outside a cyclonic mesoscale eddy in the North Pacific subtropical gyre. Deep-Sea Res. I, 43, 917–936.
Borgne, R. L., R. T. Barber, T. Delcroix, H. Y. Inoue, D. J. Mackey and M. Rodier (2002): Pacific warm pool and divergence: temporal and zonal variations on the equator and their effects on the biological pump. Deep-Sea Res. II, 49, 2471–2512.
Bustillos-Guzman, J., H. Claustre and J. C. Marty (1995): Specific phytoplankton signatures and their relationship to hydrographic conditions in the coastal northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 124, 247–258.
Campbell, L., H. A. Nolla and D. Vaulot (1994): The importance of Prochlorococcus to community structure in the central North Pacific Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr., 39, 954–961.
Chen, C. T. A. and M. H. Huang (1996): A mid-depth front separating the South China Sea water and the Philippine Sea water. J. Oceanogr., 52, 17–25.
Chen, Y. L. L. (2000): Comparisons of primary productivity and phytoplankton size structure in the marginal regions of southern East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res., 20, 437–458.
Chen, Y. L. L. (2005): Spatial and seasonal variations of nitrate-based new production and primary production in the South China Sea. Deep-Sea Res. I, 52, 319–340.
Chen, Y. L. L. and H. Y. Chen (2006): Seasonal dynamics of primary and new production in the northern South China Sea: the significance of river discharge and nutrient advection. Deep-Sea Res. I, 53, 971–986.
Chen, Y. L. L., H. Y. Chen and Y. H. Lin (2003): Distribution and downward flux of Trichodesmium in the South China Sea as influenced by the transport from the Kuroshio Current. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 259, 47–57.
Chen, Y. L. L., H. Y. Chen, D. M. Karl and M. Takahashi (2004): Nitrogen modulates phytoplankton growth in spring in the South China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res., 24, 527–541.
Chern, C. S. and J. Wang (2003): Numerical study of the upper-layer circulation in the South China Sea. J. Oceanogr., 59, 11–24.
Chu, P. C. and C. Fan (2001): Low salinity, cool-core cyclonic eddy detected northwest of Luzon during the South China Sea Monsoon Experiment (SCSMEX) in July 1998. J. Oceanogr., 57, 549–563.
Chu, P. C., C. Fan, C. J. Lozano and J. Kerling (1998): An airborne expandable bathythermograph (AXBT) survey of the South China Sea, May 1995. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 21637–21652.
Draper, N. R. and H. Smith (1981): Applied Regression Analysis. Wiley, New York, 709 pp.
Dugdale, R. C. and F. P. Wilkerson (1986): The use of 15N to measure nitrogen uptake in eutrophic oceans: experimental considerations. Limnol. Oceanogr., 31, 673–689.
Dugdale, R. C., A. Morel, A. Bricaud and F. P. Wilkerson (1989): Modeling new production in upwelling centers: a case study of modeling new production from remotely sensed temperature and color. J. Geophys. Res., 94, 18119–18132.
DuRand, M. D., R. J. Olson and S. W. Chisholm (2001): Phytoplankton population dynamics at the Bermuda Atlantic time-series station in the Sargasso Sea. Deep-Sea Res. II, 48, 1983–2003.
Fu, L. L., E. J. Christensen, C. A. Yamarone, M. Lefebvre, Y. Menard, M. Dorrer and P. Escudier (1994): TOPEX/POSEIDON mission overview. J. Geophys. Res., 99, 24369–24381.
Garside, C. (1982): A chemiluminescent technique for the determination of nanomolar concentrations of nitrate and nitrite in seawater. Mar. Chem., 11, 159–167.
Glover, H. E., B. B. Prézelin, L. Campbell, M. Wyman and C. Garside (1988): A nitrate-dependent Synechococcus bloom in surface Sargasso Sea water. Nature, 331, 161–163.
Goericke, R. and N. A. Welschmeyer (1993): The marine prochlorophyte Prochlorococcus contributes significantly to phytoplankton biomass and primary production in the Sargasso Sea. Deep-Sea Res., 40, 2283–2294.
Hama, T., T. Miyazaki, Y. Ogawa, T. Iwakumi, M. Takahashi, A. Otsuki and S. Ichimura (1983): Measurement of photosynthetic production of a marine phytoplankton population using a stable 13C isotope. Mar. Biol., 73, 31–36.
Jia, Y. and Q. Liu (2004): Eddy shedding from the Kuroshio bend at Luzon Strait. J. Oceanogr., 60, 1063–1069.
Jia, Y., Q. Liu and W. Liu (2005): Primary study of the mechanism of eddy shedding from the Kuroshio bend in Luzon Strait. J. Oceanogr., 61, 1017–1027.
Letelier, R. M., R. R. Bidigare, D. V. Hebel, M. Ondrusek, C. D. Winn and D. M. Karl (1993): Temporal variability of phytoplankton community structure based on pigment analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr., 38, 1420–1437.
Li, L., W. D. Nowlin, Jr. and J. Su (1998): Anticyclonic rings from the Kuroshio in the South China Sea. Deep-Sea Res. I, 45, 1469–1482.
Li, Y., L. Li, M. Lin and W. Cai (2002): Observation of mesoscale eddy fields in the sea south west of Taiwan by TOPEX/POSEIDON altimeter data. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 24, 163–170 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lindell, D. and A. E. Post (1995): Ultraphytoplankton succession is triggered by deep winter mixing in the Gulf of Aqaba (Eilat), Red Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr., 40, 1130–1141.
Liu, H., L. Campbell, M. R. Landry, H. A. Nolla, S. L. Brown and J. Constantinou (1998): Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus growth rates and contributions to production in the Arabian Sea during the 1995 Southwest and Northeast Monsoons. Deep-Sea Res. II, 45, 2327–2352.
Liu, K. K., S. Y. Chao, P. T. Shaw, G. C. Gong, C. C. Chen and T. Y. Tang (2002): Monsoon-forced chlorophyll distribution and primary production in the South China Sea: observations and a numerical study. Deep-Sea Res. I, 49, 1387–1412.
McGillicuddy, D. and A. R. Robinson (1997): Eddy induced nutrient supply and new production in the Sargasso Sea. Deep-Sea Res. I, 44, 1427–1449.
McGillicuddy, D., A. R. Robinson, D. A. Siegel, H. W. Jannasch, R. Johnson, T. D. Dickey, J. McNeil, A. F. Michaels and A. H. Knap (1998): Influence of mesoscale eddies on new production in the Sargasso Sea. Nature, 394, 263–265.
McGillicuddy, D., R. Johnson, D. A. Siegel, A. F. Michaels, N. R. Bates and A. H. Knap (1999): Mesoscale variations of biogeochemical properties in the Sargasso Sea. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 13381–13394.
McGillicuddy, D., L. A. Anderson, S. C. Doney and M. E. Maltrud (2003): Eddy-driven sources and sinks of nutrients in the upper ocean: results from a 0.1° resolution model of the North Atlantic. Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 17(2), 1035, doi:10.1029/2002GB001987.
McNeil, J., H. W. Jannasch, T. D. Dickey, D. J. McGillicuddy, M. Brzezinski and C. M. Sakamoto (1999): New chemical bio-optical and physical observations of upper ocean response to the passage of a mesoscale eddy. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 15537–15548.
Metzger, E. J. and H. E. Hurlburt (1996): Coupled dynamics of the South China Sea, the Sulu Sea and the Pacific Ocean. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 12331–12352.
Metzger, E. J. and H. E. Hurlburt (2001): The nondeterministic nature of Kuroshio penetration and eddy shedding in the South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 31, 1712–1732.
Moore, L. R., A. F. Post, G. Rocap and S. W. Chisholm (2002): Utilization of different nitrogen sources by the marine cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Limnol. Oceanogr., 47, 989–996.
O’Reilly, J. E., S. Maritorena, B. G. Mitchell, D. A. Siegel, K. L. Carder, S. A. Garver, M. Kahru and C. McClain (1998): Ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for SeaWiFS. J. Geophys. Res., 103(C11), 24937–24953.
Partensky, F., J. Blanchot, F. Lantoine, J. Neveux and D. Marie (1996): Vertical structure of picophytoplankton at different trophic sites of the tropical northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Deep-Sea Res., 43, 1191–1213.
Partensky, F., J. Blanchot and D. Vaulot (1999): Differential Phytoplankton Production and Assemblage in a Cyclonic Eddy 683 distribution and ecology of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus in oceanic waters: A review. p. 457–475. In Marine Cyanobacteria, ed. by L. Charpy and A. W. D. Larkum, Bulletin de Institut Oceanographique.
Rao, C. R. N. and J. Chen (1996): Post launch calibration of the visible and near-infrared channels of the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer on the NOAA-14 spacecraft. Intl. J. Remote Sens., 17, 2743–2747.
Siegel, D. A., D. J. McGillicuddy, Jr. and E. A. Fields (1999): Mesoscale eddies, satellite altimetry, and new production in the Sargasso Sea. J. Geophys. Res., 104(C6), 13359–13379.
Strickland, J. D. H. and T. R. Parsons (1972): A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada, 167, 1–310.
Sweeney, E., D. McGillicuddy and K. Buesseler (2003): Biogeochemical impacts due to mesoscale eddy activity in the Sargasso Sea as measured at the Bermuda Atlantic Timeseries (BATS) site. Deep-Sea Res. II, 50, 3017–3039.
Takahashi, M., J. Ishizaka, T. Ishimaru, L. P. Atkinson, T. N. Lee, Y. Yamaguchi, Y. Fujita and S. Ichimura (1986): Temporal change in nutrient concentrations and phytoplankton biomass in short time scale local upwelling around the Izu Peninsula, Japan. J. Plankton Res., 8, 1039–1049.
Thomson-Bulldis, A. and D. Karl (1998): Application of a novel method for phosphorus determinations in the oligotrophic North Pacific Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr., 43, 1565–1577.
Vaillancourt, R. D., J. Marra, M. P. Seki, M. L. Parsons and R. R. Bidigare (2003): Impact of a cyclonic eddy on phytoplankton community structure and photosynthetic competency in the subtropical North Pacific Ocean. Deep-Sea Res. I, 50, 829–847.
Vaulot, D., C. Courties and F. Partensky (1989): A simple method to preserve oceanic phytoplankton for flow cytometric analyses. Cytom., 10, 629–635.
Wu, C. R., P. T. Shaw and S. Y. Chao (1999): Assimilating altimeter data into a South China Sea model. J. Geophys. Res., 104(C12), 29987–30005.
Wu, J., S. W. Chung, L. S. Wen, K. K. Liu, Y. L. Lee Chen, H. Y. Chen and D. M. Karl (2003): Dissolved inorganic phosphorus, dissolved iron, and Trichodesmium in the oligotrophic South China Sea. Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 17(1), 1008, doi:10.1029/2002GB001924.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YL.L., Chen, HY., Lin, I.I. et al. Effects of cold eddy on phytoplankton production and assemblages in Luzon strait bordering the South China Sea. J Oceanogr 63, 671–683 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-007-0059-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-007-0059-9