Abstract
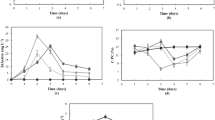
The dry weight per unit biovolume of 810 single, living cells of the ubiquitous soil algae Klebsormidium flaccidum from 80 experiments were determined using a Mach–Zehnder double-beam interference microscope. Different substrates such as agarized nutrient solution, different soils, and slag heap material, different pH values, temperatures and light intensities were used and cells from both growth and stationary phase were measured. The total possible range of dry weight with respect to carbon per unit biovolume (C/ubv) values was 93–226 fg μm−3. The mean value of all data was 147 fg μm−3, which concurs with the average value as taken from literature data of several planktonic algal species and groups within the respective size range (cell volume 300–1,000 μm3). We could show that C/ubv is suitable to quantify environmental stress conditions: C/ubv values ≤140 fg μm−3 are characteristic of cells grown under optimum conditions, and values ≥160 fg μm−3 reflect quantitatively graded stress situations. We propose integrating the microscope interferometric method using K. flaccidum as a test organism into a soil test system to determine the prevailing environmental conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bischoff HW, Bold HC (1963) Phycological studies IV. Some soil algae from enchanted rock and related algae species. The University of Texas Publication No. 6318, pp 1–95
Bölter M, Bloem J, Meinetrs K, Möller R (2006) Enumeration and biovolume determination of micreobial cells. In: Bloem J, Hopkins DW, Benedetti A (eds) Microbiological methods for assessing soil quality. CABI, Wallingford, pp 93–113
Børsheim KY, Bratbak G (1987) Cell volume to cell carbon conversion factors for a bacteriovorous Monas sp. enriched from seawater. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 36:171–175
Cain JR, Mattox KR, Stewart KD (1973) The cytology of zoosporogenesis in the filamentous green algal genus Klebsormidium. Trans Amer Micros Soc 92:398–404
Cain JR, Mattox KR, Stewart KD (1974) Conditions of illumination and zoosporogenesis in Klebsormidium flaccidum. J Phycol 10:134–136
Cullimore DR (1966a) Influence of ionic phosphate diffusion in the soil on the growth of Hormidium flaccidum. Nature 209:326–327
Cullimore DR (1966b) A qualitative method of assessing the available nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus in the soil. J Sci Food Agric 17:321–323
Cullimore DR (1975) The in vivo sensitivity of some species of Chlorophyceae to a selected range of herbicides. Weed Res 15:401–406
De Winder B, Matthijs HCP, Mur LR (1989) The role of water retaining substrata on the photosynthetic response of three drought tolerant phototrophic micro-organisms isolated from a terrestrial habitat. Arch Microbiol 152:458–462
De Winder B, Matthijs HCP, Mur LR (1990) The effect of dehydration and ion stress on carbon dioxide fixation in drought-tolerant phototrophic micro-organisms. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:33–38
Elster J, Degma P, Kováčik L, Valentová L, Sramková K, Pereira AB (2008) Freezing and desiccation injury resistance in the filamentous green alga Klebsormidium from the Antarctic, Arctic and Slovakia. Biologia 63:843–851
Esser D, Mahlmann D, Wortmann D, Gottmann J (2009) Interference microscopy of femtosecond laser written waveguides in phosphate glass. Appl Phys B 96:453–457
Ettl H, Gärtner G (1995) Syllabus der Boden-, Luft-und Flechtenalgen. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart
Ghiglia DC, Pritt MD (1998) Two-dimensional phase unwrapping: theory, algorithms, and software. Wiley, New York
Jahnke J, Priefer UB (2002) Phototrophic biofilms of restored fields in the rhenish lignite mining area: development of soil algal, bacterial, and fungal biomasses. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1157–1165
Jahnke J, Mahlmann DM (2010) Differences in the cellular dry weight per unit biovolume of Phormidium autumnale (Caynobacteria) dependent on growth conditions. J Appl Phycol 22:117–122
Jahnke J, Wehren T, Priefer UB (2007) In vitro studies of the impact of the naked soil amoeba Thecamoeba similis Greef, feeding on phototrophic soil biofilms. Eur J Soil Biol 43:14–22
Lohmann H (1908) Untersuchungen zur Feststellung des vollständigen Gehaltes des Meeres an Plankton. Wiss Meeresunters Kiel NF 10:129–370
Mahlmann DM, Jahnke J, Loosen P (2008) Rapid determination of the dry weight of single, living cyanobacterial cells using the Mach–Zehnder double-beam interference microscope. Eur J Phycol 43:355–364
Menden-Deuer S, Lessard EJ (2000) Carbon to volume relationships for dinoflagellates, diatoms, and other protist plankton. Limnol Oceanogr 45:569–579
Nagao M, Matsui K, Uemura M (2008) Klebsormidium flaccidum, a charophycean green alga, exhibits cold acclimation that is closely associated with compatible solute accumulation and ultrastructural changes. Plant Cell Environ 31:872–885
Paul EA, Clark FE (1989) Soil microbiology and biochemistry. Academic, San Diego
Paul EA, Harris D, Klug MJ, Ruess RW (1999) The determination of microbial biomass. In: Robertson GP, Coleman DC, Bledsoe CS, Sollins P (eds) Standard soil methods for long-term ecological research. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 219–317
Podola B, Melkonian M (2003) A long-term operating algal biosensor for the rapid detection of volatile toxic compounds. J Appl Phycol 15:415–424
Podola B, Nowack ECM, Melkonian M (2004) The use of multiple-strain algal sensor chips for the detection and identification of volatile organic compounds. Biosens Bioelectron 19:1253–1260
Reynolds CS (1984) The ecology of freshwater phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rocha A, Duncan A (1985) The relationship between cell carbon and cell volume in freshwater algal species used in zooplanktonic studies. J Plankt Res 7:279–294
Sicko-Goad L, Stoermer EF, Ladewski BG (1977) A morphometric method for correcting phytoplankton cell volume estimates. Protoplasma 93:147–163
Škaloud P (2006) Variation and taxonomic significance of some morphological features in european strains of Klebsormidium (Klebsormidiophyceae, Streptophyta). Nova Hedwigia 83:533–550
Sluiman HJ, Guihal C (2008) Assessing phylogenetic affinities and species deliminations in Klebsormidiales (Streptophyta): a nuclear-encoded rDNA phylogenies and its secondary structure models in Klebsormidium, Hormidiella, and Entransia. J Phycol 44:183–195
Stramski D (1999) Refractive index of planktonic cells as a measure of cellular carbon and chlorophyll a content. Deep-Sea Res 46:335–351
Thompson PA, Harrison PJ, Parslow JS (1991) Influence of irradiance on cell volume and carbon quota for ten species of marine phytoplankton. J Phycol 27:351–360
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Maria Bugaro for excellent technical assistance. B. Kosier are acknowledged for critically reading and correcting the manuscript. We wish to thank two anonymous referees for their critical suggestions which lead to a substantial improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahnke, J., Mahlmann, D.M., Jacobs, P. et al. The influence of growth conditions on the cell dry weight per unit biovolume of Klebsormidium flaccidum (Charophyta), a typical ubiquitous soil alga. J Appl Phycol 23, 655–664 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9557-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9557-z