Abstract
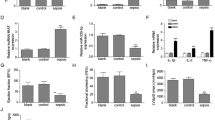
The research aims to explore the roles and underlying mechanisms of microRNA-21 (miR-21) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in MH7A cells. Cells were treated with LPS and/or transfected with miR-21 mimic/inhibitor or pc-sucrose nonfermentable 5 (SNF5). Cell viability was detected by CCK-8. ELISA and western blot were respectively conducted to measure the protein levels of pro-inflammatory factors, NF-κB or PTEN/PI3K/AKT key proteins and SNF5. miR-21/U6 was measured by qRT-PCR. The association between miR-21 and SNF5 was determined by luciferase reporter assay. Cell viability and the protein expression levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, and p/t-p65, p/t-IκBα, p/t-PI3K, and p/t-AKT were significantly elevated by LPS, but with an inhibition of p-PTEN. Besides, LPS upregulated miR-21, whose overproduction or silence enhanced or alleviated the LPS stimulation on those elements above, respectively. miR-21 mimic notably inhibited SNF5, which was accelerated by miR-21 inhibitor, and abundant SNF5 abolished the effect of miR-21 mimic on cell viability, pro-inflammatory mediators, and sensitivity of signaling pathways, representing a negative relationship between them. miR-21 augmented LPS-induced inflammation response through activating NF-κB and PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathways by silencing SNF5 in MH7A cell line.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahn, J.K., B. Huang, E.K. Bae, E.J. Park, J.W. Hwang, J. Lee, E.M. Koh, and H.S. Cha. 2013. The role of alpha-defensin-1 and related signal transduction mechanisms in the production of IL-6, IL-8 and MMPs in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52 (8): 1368–1376. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ket147.
Balzano, F., M. Deiana, S. Dei Giudici, A. Oggiano, S. Pasella, S. Pinna, A. Mannu, N. Deiana, B. Porcu, A.G.E. Masala, P.V. Pileri, F. Scognamillo, C. Pala, A. Zinellu, C. Carru, and L. Deiana. 2017. MicroRNA expression analysis of centenarians and rheumatoid arthritis patients reveals a common expression pattern. International Journal of Medical Sciences 14 (7): 622–628. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.18972.
Boilard, E., P.A. Nigrovic, K. Larabee, G.F. Watts, J.S. Coblyn, M.E. Weinblatt, E.M. Massarotti, E. Remold-O’Donnell, R.W. Farndale, J. Ware, and D.M. Lee. 2010. Platelets amplify inflammation in arthritis via collagen-dependent microparticle production. Science 327 (5965): 580–583. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1181928.
Chatzikyriakidou, A., P.V. Voulgari, I. Georgiou, and A.A. Drosos. 2012. miRNAs and related polymorphisms in rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Autoimmunity Reviews 11 (9): 636–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2011.11.004.
Cheng, Y., P. Zhu, J. Yang, X. Liu, S. Dong, X. Wang, B. Chun, J. Zhuang, and C. Zhang. 2010. Ischaemic preconditioning-regulated miR-21 protects heart against ischaemia/reperfusion injury via anti-apoptosis through its target PDCD4. Cardiovascular Research 87 (3): 431–439. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvq082.
Churov, A.V., E.K. Oleinik, and M. Knip. 2015. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: altered expression and diagnostic potential. Autoimmunity Reviews 14 (11): 1029–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2015.07.005.
Dong, L., X. Wang, J. Tan, H. Li, W. Qian, J. Chen, Q. Chen, J. Wang, W. Xu, C. Tao, and S. Wang. 2014. Decreased expression of microRNA-21 correlates with the imbalance of Th17 and Treg cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 18 (11): 2213–2224. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12353.
Fulci, V., G. Scappucci, G.D. Sebastiani, C. Giannitti, D. Franceschini, F. Meloni, T. Colombo, et al. 2010. miR-223 is overexpressed in T-lymphocytes of patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Human Immunology 71 (2): 206–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2009.11.008.
Furer, V., J.D. Greenberg, M. Attur, S.B. Abramson, and M.H. Pillinger. 2010. The role of microRNA in rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. Clinical Immunology 136 (1): 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2010.02.005.
Garchow, B.G., O. Bartulos Encinas, Y.T. Leung, P.Y. Tsao, R.A. Eisenberg, R. Caricchio, S. Obad, A. Petri, S. Kauppinen, and M. Kiriakidou. 2011. Silencing of microRNA-21 in vivo ameliorates autoimmune splenomegaly in lupus mice. EMBO Molecular Medicine 3 (10): 605–615. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201100171.
Gregersen, P.K., C.I. Amos, A.T. Lee, Y. Lu, E.F. Remmers, D.L. Kastner, M.F. Seldin, L.A. Criswell, R.M. Plenge, V.M. Holers, T.R. Mikuls, T. Sokka, L.W. Moreland, Bridges SL Jr, G. Xie, A.B. Begovich, and K.A. Siminovitch. 2009. REL, encoding a member of the NF-kappaB family of transcription factors, is a newly defined risk locus for rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Genetics 41 (7): 820–823. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.395.
Gupta, O.P., S.G. Karkute, S. Banerjee, N.L. Meena, and A. Dahuja. 2017. Contemporary understanding of miRNA-based regulation of secondary metabolites biosynthesis in plants. Frontiers in Plant Science 8: 374. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00374.
Hu, S.L., A.C. Chang, C.C. Huang, C.H. Tsai, C.C. Lin, and C.H. Tang. 2017. Myostatin promotes interleukin-1beta expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through inhibition of miR-21-5p. Frontiers in Immunology 8: 1747. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01747.
Jin, S., H. Chen, Y. Li, H. Zhong, W. Sun, J. Wang, T. Zhang, J. Ma, S. Yan, J. Zhang, Q. Tian, X. Yang, and J. Wang. 2018. Maresin 1 improves the Treg/Th17 imbalance in rheumatoid arthritis through miR-21. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 77 (11): 1644–1652. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213511.
Jung, E.J., and G.A. Calin. 2010. The meaning of 21 in the MicroRNA world: perfection rather than destruction? Cancer Cell 18 (3): 203–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.08.015.
Kawano, Seiji, and Yuji Nakamachi. 2011. miR-124a as a key regulator of proliferation and MCP-1 secretion in synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 70 (Suppl 1): i88–i91.
Kohashi, K., H. Yamamoto, R. Kumagai, Y. Yamada, Y. Hotokebuchi, T. Taguchi, Y. Iwamoto, and Y. Oda. 2014. Differential microRNA expression profiles between malignant rhabdoid tumor and epithelioid sarcoma: miR193a-5p is suggested to downregulate SMARCB1 mRNA expression. Modern Pathology 27 (6): 832–839. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2013.213.
Krichevsky, A.M., and G. Gabriely. 2009. miR-21: a small multi-faceted RNA. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 13 (1): 39–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00556.x.
Li, G., Y. Zhang, Y. Qian, H. Zhang, S. Guo, M. Sunagawa, T. Hisamitsu, and Y. Liu. 2013. Interleukin-17A promotes rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes migration and invasion under hypoxia by increasing MMP2 and MMP9 expression through NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha pathway. Molecular Immunology 53 (3): 227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2012.08.018.
Lorenzen, J.M., H. Haller, and T. Thum. 2011. MicroRNAs as mediators and therapeutic targets in chronic kidney disease. Nature Reviews. Nephrology 7 (5): 286–294. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2011.26.
Ma, X., M. Kumar, S.N. Choudhury, L.E. Becker Buscaglia, J.R. Barker, K. Kanakamedala, M.F. Liu, and Y. Li. 2011. Loss of the miR-21 allele elevates the expression of its target genes and reduces tumorigenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108 (25): 10144–10149. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1103735108.
McInnes, Iain B., and Georg Schett. 2011. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine 365 (23): 2205–2219.
McKenna, Elizabeth S, Pablo Tamayo, Yoon-Jae Cho, Erik J Tillman, E Lorena Mora-Blanco, Courtney G Sansam, Edward C Koellhoffer, Scott L Pomeroy, and Charles WM Roberts. 2012. Epigenetic inactivation of the tumor suppressor BIN1 drives proliferation of SNF5-deficient tumors. Cell Cycle 11 (10):1956–1965.
Mora-Blanco, E.L., Y. Mishina, E.J. Tillman, Y.J. Cho, C.S. Thom, S.L. Pomeroy, W. Shao, and C.W. Roberts. 2014. Activation of beta-catenin/TCF targets following loss of the tumor suppressor SNF5. Oncogene 33 (7): 933–938. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.37.
Okada, Y., D. Wu, G. Trynka, T. Raj, C. Terao, K. Ikari, Y. Kochi, K. Ohmura, A. Suzuki, S. Yoshida, R.R. Graham, A. Manoharan, W. Ortmann, T. Bhangale, J.C. Denny, R.J. Carroll, A.E. Eyler, J.D. Greenberg, J.M. Kremer, D.A. Pappas, L. Jiang, J. Yin, L. Ye, D.F. Su, J. Yang, G. Xie, E. Keystone, H.J. Westra, T. Esko, A. Metspalu, X. Zhou, N. Gupta, D. Mirel, E.A. Stahl, D. Diogo, J. Cui, K. Liao, M.H. Guo, K. Myouzen, T. Kawaguchi, M.J. Coenen, P. van Riel, M. van de Laar, H.J. Guchelaar, T.W. Huizinga, P. Dieudé, X. Mariette, Bridges SL Jr, A. Zhernakova, R.E. Toes, P.P. Tak, C. Miceli-Richard, S.Y. Bang, H.S. Lee, J. Martin, M.A. Gonzalez-Gay, L. Rodriguez-Rodriguez, S. Rantapää-Dahlqvist, L. Arlestig, H.K. Choi, Y. Kamatani, P. Galan, M. Lathrop, RACI consortium, GARNET consortium, S. Eyre, J. Bowes, A. Barton, N. de Vries, L.W. Moreland, L.A. Criswell, E.W. Karlson, A. Taniguchi, R. Yamada, M. Kubo, J.S. Liu, S.C. Bae, J. Worthington, L. Padyukov, L. Klareskog, P.K. Gregersen, S. Raychaudhuri, B.E. Stranger, P.L. de Jager, L. Franke, P.M. Visscher, M.A. Brown, H. Yamanaka, T. Mimori, A. Takahashi, H. Xu, T.W. Behrens, K.A. Siminovitch, S. Momohara, F. Matsuda, K. Yamamoto, and R.M. Plenge. 2014. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery. Nature 506 (7488): 376–381. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12873.
Pauley, Kaleb M., and Seunghee Cha. 2011. miRNA-146a in rheumatoid arthritis: a new therapeutic strategy. Immunotherapy 3 (7): 829–831.
Peters, M.A., D. Wendholt, S. Strietholt, S. Frank, N. Pundt, A. Korb-Pap, L.A. Joosten, W. van den Berg, G. Kollias, B. Eckes, and T. Pap. 2012. The loss of alpha2beta1 integrin suppresses joint inflammation and cartilage destruction in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 64 (5): 1359–1368. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.33487.
Peters, Marvin A, Doreen Wendholt, Simon Strietholt, Svetlana Frank, Noreen Pundt, Adelheid Korb-Pap, Leo AB Joosten, Wim B van den Berg, George Kollias, and Beate Eckes. 2012. The loss of α2β1 integrin suppresses joint inflammation and cartilage destruction in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 64 (5):1359–1368.
Radwan-Oczko, M., and I. Dus-Ilnicka. 2019. Rheumatoid arthritis patients’ oral health and disease activity. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185x.13590.
Ramirez-Carrozzi, V.R., A.A. Nazarian, C.C. Li, S.L. Gore, R. Sridharan, A.N. Imbalzano, and S.T. Smale. 2006. Selective and antagonistic functions of SWI/SNF and Mi-2beta nucleosome remodeling complexes during an inflammatory response. Genes & Development 20 (3): 282–296. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1383206.
Roubille, C., V. Richer, T. Starnino, C. McCourt, A. McFarlane, P. Fleming, S. Siu, J. Kraft, C. Lynde, J. Pope, W. Gulliver, S. Keeling, J. Dutz, L. Bessette, R. Bissonnette, and B. Haraoui. 2015. The effects of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors, methotrexate, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids on cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 74 (3): 480–489. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206624.
Ruan, Q., T. Wang, V. Kameswaran, Q. Wei, D.S. Johnson, F. Matschinsky, W. Shi, and Y.H. Chen. 2011. The microRNA-21-PDCD4 axis prevents type 1 diabetes by blocking pancreatic beta cell death. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108 (29): 12030–12035. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1101450108.
Sapi, Z., G. Papp, M. Szendroi, Z. Papai, V. Plotar, T. Krausz, and C.D. Fletcher. 2016. Epigenetic regulation of SMARCB1 by miR-206, -381 and -671-5p is evident in a variety of SMARCB1 immunonegative soft tissue sarcomas, while miR-765 appears specific for epithelioid sarcoma. A miRNA study of 223 soft tissue sarcomas. Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer 55 (10): 786–802. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22379.
Singh, Ram Pyare, Israel Massachi, Sudhir Manickavel, Satendra Singh, Nagesh P Rao, Sascha Hasan, Deborah K Mc Curdy, Sherven Sharma, David Wong, and Bevra H Hahn. 2013. The role of miRNA in inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmunity Reviews 12 (12):1160–1165.
Stanczyk, J., C. Ospelt, E. Karouzakis, A. Filer, K. Raza, C. Kolling, R. Gay, C.D. Buckley, P.P. Tak, S. Gay, and D. Kyburz. 2011. Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation. Arthritis and Rheumatism 63 (2): 373–381. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.30115.
Sun, S., Y. Wu, K. Zeng, and Y. Zhao. 2019. Expression and potential role of SNF5 in endometrial carcinoma. BMC Womens Health 19 (1): 16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-019-0718-1.
Tang, Y., X. Luo, H. Cui, X. Ni, M. Yuan, Y. Guo, X. Huang, H. Zhou, N. de Vries, P.P. Tak, S. Chen, and N. Shen. 2009. MicroRNA-146A contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis and Rheumatism 60 (4): 1065–1075. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24436.
van Loo, G., and R. Beyaert. 2011. Negative regulation of NF-kappaB and its involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 13 (3): 221. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3324.
Wöhrle, Simon, Andreas Weiss, Moriko Ito, Audrey Kauffmann, Masato Murakami, Zainab Jagani, Anne Thuery, Beatrice Bauer-Probst, Flavia Reimann, and Christelle Stamm. 2013. Fibroblast growth factor receptors as novel therapeutic targets in SNF5-deleted malignant rhabdoid tumors. PLoS One 8 (10): e77652.
Wang, G., L.S. Tam, E.K. Li, B.C. Kwan, K.M. Chow, C.C. Luk, P.K. Li, and C.C. Szeto. 2010. Serum and urinary cell-free MiR-146a and MiR-155 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. The Journal of Rheumatology 37 (12): 2516–2522. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.100308.
Wu, Shupeng, Jing Wang, and Fang Li. 2017. Role of SNF5 in rheumatoid arthritis by upregulation of p16 and inactivation of JNK pathway. Turkish Journal of Biology 41 (3): 535–542.
Wu, Z., H. Lu, J. Sheng, and L. Li. 2012. Inductive microRNA-21 impairs anti-mycobacterial responses by targeting IL-12 and Bcl-2. FEBS Letters 586 (16): 2459–2467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.06.004.
Yamamura, S., M. Imai-Sumida, Y. Tanaka, and R. Dahiya. 2018. Interaction and cross-talk between non-coding RNAs. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 75 (3): 467–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2626-6.
Zeng, Zhenguo, Honghan Gong, Yong Li, Kemin Jie, Chengzhi Ding, Qiang Shao, Fen Liu, Yian Zhan, Nie Cheng, and Weifeng Zhu. 2013. Upregulation of miR-146a contributes to the suppression of inflammatory responses in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Experimental Lung Research 39 (7): 275–282.
Zhang, W., Z. Du, J. Zhu, J. Yu, and Y. Xu. 2015. Sprouty2 suppresses the inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through regulating the Raf/ERK and PTEN/AKT signals. Mol Immunol 67 (2 Pt B):532-539. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2015.07.033.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Wang, J., Li, J. et al. microRNA-21 Aggravates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in MH7A Cells Through Targeting SNF5. Inflammation 43, 441–454 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01117-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01117-8