Abstract
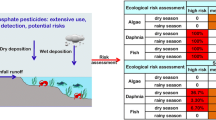
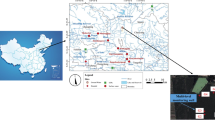
Organophosphorus pesticides (OPs), which are some of the most extensively used pesticides, have drawn much attention in recent years owing to their ubiquity as well as the potential ecological and health risks they pose to aquatic organisms and even to humans. In this study, we investigated the residue of five OPs in 49 river cross sections in Shangyu, Zhejiang province, China, a rainy region with relatively developed agriculture. Correlations analysis, principal component analysis, and cluster analysis were conducted. The results showed that dichlorvos exhibited the highest concentrations (0.01 to 5.63 μg/L) among the OPs in most monitoring sites. Weak positive correlations were found between methyl parathion and dichlorvos as well as malathion and dimethoate. The principal component analysis and cluster analysis indicated a correlation among these river cross sections. We then calculated the hazard index (HI) to estimate the potential adverse health effects. The mean HI presented no risk to adults but showed potential health risks to children, with values of 0.285, 0.228, and 0.166 for dichlorvos, methyl parathion, and dimethoate, respectively. Our study will help elucidate the potential risks of OPs and their residues in the rivers of Shangyu in the Zhejiang province in China and will be beneficial for managing water quality and will provide valuable suggestions to local policy makers.

Comparison of the ∑5OPs concentrations among 49 river cross sections






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adigun, A. A., Wrench, N., Seidler, F. J., & Slotkin, T. A. (2010). Neonatal organophosphorus pesticide exposure alters the developmental trajectory of cell-signaling cascades controlling metabolism: differential effects of diazinon and parathion. Environmental Health Perspectives, 118(2), 210–215.
Antonio, V., Jorge, R., Rocío, C., & Irmene, O. (2012). Residues of organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides in sugarcane crop soils and river water. Journal of Environmental Science & Health Part B Pesticides Food Contaminants & Agricultural Wastes, 47(9), 833–841.
Banks, C. N., & Lein, P. J. (2012). A review of experimental evidence linking neurotoxic organophosphorus compounds and inflammation. Neurotoxicology, 33(3), 575–584.
Benoit, F., Raphael, M., & Jeanne, G. (2006). Development of a zebrafish 4-day embryo-larval bioassay to assess toxicity of chemicals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 63(2), 253–267.
Bonvallot, N., Tremblay-Franco, M., Chevrier, C., Canlet, C., Warembourg, C., Cravedi, J. P., & Cordier, S. (2013). Metabolomics tools for describing complex pesticide exposure in pregnant women in Brittany (France). PloS One, 8(5), e64433.
Gao, J. J., Liu, L. H., Liu, X. R., Zhou, H. D., Lu, J., Huang, S. B., & Wang, Z. J. (2009). The occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphorous pesticides in Chinese surface water. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 82(2), 223–229.
GB13192–91, Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. (1991). Water quality-determination of organic phosphorus pesticide in water-gas chromatography. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China.
GB5749—2006, Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. (2006). Standards for drinking water quality. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China.
He, W., Qin, N., He, Q. S., Wang, Y., Kong, X. Z., & Xu, F. L. (2012). Evaluation of the hazard quotient method for risk assessment of seleniu characterization, ecological and health risks of DDTs and HCHs in water from a large shallow Chinese lake. Ecological Informatics, 12(12), 77–84.
Lemly, A. D. (1996). Evaluation of the hazard quotient method for risk assessment of selenium. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 35(2), 156–162.
Leong, K. H., Tan, L. L. B., & Mustafa, A. M. (2007). Contamination levels of selected organochlorine and organophosphate pesticides in the Selangor River, Malaysia between 2002 and 2003. Chemosphere, 66(6), 1153–1159.
Li, H. Z., Tyler Mehler, W., Lydy, M. J., & You, J. (2011). Occurrence and distribution of sediment-associated insecticides in urban waterways in the Pearl River Delta, China. Chemosphere, 82(10), 1373–1379.
Liess, M., Schulz, R., Liess, H. D., Rother, B., & Kreuzig, R. (1999). Determination of insecticide contamination in agricultural headwater streams. Water Research, 33(1), 239–247.
Ling, K. D., Liu, W. P., Ling, L., & Gan, J. (2008). Single and joint acute toxicity of isocarbophos enantiomers to Daphnia magna. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(11), 4273–4277.
Liu, W. P., Lin, K. D., & Gan, J. (2006). Separation and aquatic toxicity of enantiomers of the organophosphorus insecticide trichloronate. Chirality, 18(9), 713–716.
Liu, H., Yuan, B., & Li, S. (2012). Altered quantities and in vivo activities of cholinesterase from Daphnia magna in sub-lethal exposure to organophosphorus insecticides. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 80(3), 118–125.
Repetto, R., & Baliga, S. (1996). Pesticides and the immune system: the public health risks. Central European Journal of Public Health, 4(4), 263–265.
Rezg, R., Mornagui, B., El-Fazaa, S., & Gharbi, N. (2010). Organophosphorus pesticides as food chain contaminants and type 2 diabetes: a review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 21(7), 345–357.
Shilpa, N., Zeyan, L., Kimberly, P., Lee, P. C., Sinsheimer, J. S., Bronstein, J. M., & Beate, R. (2013). Household organophosphorus pesticide use and Parkinson’s disease. International Journal of Epidemiology, 42(5), 1476–1485.
Ündeğer, Ü., & Başaran, N. (2005). Effects of pesticides on human peripheral lymphocytes in vitro: induction of DNA damage. Archives of Toxicology, 79(3), 169–176.
USEPA (2014). National recommended water quality criteria—aquatic life criteria table. United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Varol, M., & Şen, B. (2012). Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River, Turkey. Catena, 92(1), 1–10.
Venerosi, A., Ricceri, L., Tait, S., & Calamandrei, G. (2012). Sex dimorphic behaviors as markers of neuroendocrine disruption by environmental chemicals: the case of chlorpyrifos. Neurotoxicology, 33(6), 1420–1426.
Vinggaard, A. M., Breinholt, V., & Larsen, J. C. (1999). Screening of selected pesticides for oestrogen receptor activation in vitro. Food Additives & Contaminants, 16(12), 533–542.
Wang, C., Li, Z. Y., Zhang, Q., Zhao, M. R., & Liu, W. P. (2013). Enantioselective induction of cytotoxicity by o,p’-DDD in PC12 cells: implications of chirality in risk assessment of POPs metabolites. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(8), 3909–3917.
Yen, J., Donerly, S., Levin, E. D., & Linney, E. A. (2011). Differential acetylcholinesterase inhibition of chlorpyrifos, diazinon and parathion in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 33(6), 735–741.
Zeng, X. X., Liu, Y. G., You, S. H., Zeng, G. M., Tan, X. F., Hu, X. J., Hu, X., Huang, L., & Li, F. (2015). Spatial distribution, health risk assessment and statistical source identification of the trace elements in surface water from the Xiangjiang River, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(12), 9400–9412.
Zhang, Z., Dai, M., Hong, H., Zhou, J. L., & Yu, G. (2002a). Dissolved insecticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in the Pearl River Estuary and South China Sea. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 4(6), 922–928.
Zhang, Z. L., Hong, H. S., Zhou, J. L., & Yu, G. (2002b). Occurrence and behaviour of organophosphorus insecticides in the River Wuchuan, southeast China. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 4(4), 498–504.
Zhang, Q., Ye, J. J., Chen, J. Y., Xu, H. J., Wang, C., & Zhao, M. R. (2013a). Risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in soils of an abandoned e-waste site in China. Environmental Pollution, 185, 258–265.
Zhang, X. N., Gao, L., Yang, K. F., Hua, T., Wang, W., & Ru, S. G. (2013b). Monocrotophos pesticide modulates the expression of sexual differentiation genes and causes phenotypic feminization in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Toxicology & Pharmacology, 157(1), 33–40.
Zhang, Q., Lu, M. Y., Dong, X. W., Wang, C., Zhang, C. L., Liu, W. P., & Zhao, M. R. (2014a). Potential estrogenic effects of phosphorus-containing flame retardants. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(12), 6995–7001.
Zhang, Q., Lu, M. Y., Wang, C., Du, J., Zhou, P. X., & Zhao, M. R. (2014b). Characterization of estrogen receptor α activities in polychlorinated biphenyls by invitro dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. Environmental Pollution, 189, 169–175.
Zhang, Q., Zhu, J. Q., Ye, J. J., Qian, Y., Chen, F., Wang, J. H., & Zhao, M. R. (2015). Temporal trends and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in a solid waste site in Taizhou, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(1), 1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Zhu, J., Li, Z. et al. The occurrence and risk assessment of five organophosphorus pesticides in river water from Shangyu, China. Environ Monit Assess 188, 614 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5612-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5612-9