Abstract
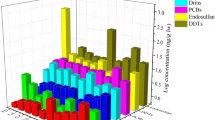
Organochlorine chemical residues and elemental concentrations were measured in piscivorous and benthivorous fish at 111 sites from large U.S. river basins. Potential contaminant sources such as urban and agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, mine drainage, and irrigation varied among the sampling sites. Our objectives were to provide summary statistics for chemical contaminants and to determine if contaminant concentrations in the fish were a risk to wildlife that forage at these sites. Concentrations of dieldrin, total DDT, total PCBs, toxaphene, TCDD-EQ, cadmium, chromium, mercury, lead, selenium, and zinc exceeded toxicity thresholds to protect fish and piscivorous wildlife in samples from at least one site; most exceedences were for total PCBs, mercury, and zinc. Chemical concentrations in fish from the Mississippi River Basin exceeded the greatest number of toxicity thresholds. Screening level wildlife risk analysis models were developed for bald eagle and mink using no adverse effect levels (NOAELs), which were derived from adult dietary exposure or tissue concentration studies and based primarily on reproductive endpoints. No effect hazard concentrations (NEHC) were calculated by comparing the NOAEL to the food ingestion rate (dietary-based NOAEL) or biomagnification factor (tissue-based NOAEL) of each receptor. Piscivorous wildlife may be at risk from a contaminant if the measured concentration in fish exceeds the NEHC. Concentrations of most organochlorine residues and elemental contaminants represented no to low risk to bald eagle and mink at most sites. The risk associated with pentachloroanisole, aldrin, Dacthal, methoxychlor, mirex, and toxaphene was unknown because NOAELs for these contaminants were not available for bald eagle or mink. Risk differed among modeled species and sites. Our screening level analysis indicates that the greatest risk to piscivorous wildlife was from total DDT, total PCBs, TCDD-EQ, mercury, and selenium. Bald eagles were at greater risk to total DDT and total PCBs than mink, whereas risks of TCDD-EQ, mercury, and selenium were greater to mink than bald eagle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adair, B. M., Reynolds, K. D., McMurry, S. T., & Cobb, G. P. (2003). Mercury occurrence in prothonotary warblers (Protonotaria citrea) inhabiting a national priority list site and reference areas in southern Alabama. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 44, 265–271.
Ambrose, R. E., Matz, A., Swem, T., & Bente, P. (2000). Environmental contaminants in American and arctic peregrine falcon eggs in Alaska, 1979–5. NAES-TR-00–2, US Fish and Wildlife Service, Fairbanks, Alaska.
Anderson, D. W., Jehl Jr., J. R., Risebrough, R. W., Woods Jr., L. A., DeWeese, L. R., & Edgecomb, W. G. (1975). Brown pelicans: improved reproduction off the southern California coast. Science, 190, 806–808.
Ankley, G. T., Tillitt, D. E., Giesy, J. P., Jones, P. D., & Verbrugge, D. A. (1991). Bioassay-derived 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin equivalents in PCB-containing extracts from the flesh and eggs of Lake Michigan chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) and possible implications for reproduction. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 48, 1685–1690.
Anthony, R. G., Garrett, M. G., & Schuler, C. A. (1993). Environmental contaminants in bald eagles in the Columbia River estuary. Journal of Wildlife Management, 57, 10–19.
Aulerich, R. J., & Ringer, R. K. (1977). Current status of PCB toxicity to mink, and effect on their reproduction. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 6, 279–292.
Barr, J. F. (1986). Population dynamics of the common loon (Gavia immer) associated with mercury-contaminated waters in northwestern Ontario. Canadian Wildlife Service Occasional Paper 56.
Baumann, P. C., & Gillespie, R. B. (1986). Selenium bioaccumulation in gonads of largemouth bass and bluegill from three power plant cooling reservoirs. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 5, 695–701.
Beckvar, N., Dillion, T. M., & Read, L. B. (2005). Approaches for linking whole-body fish tissue residues of mercury and DDT to biological effects thresholds. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 2094–2105.
Blus, L. J. (1996). DDT, DDD, and DDE in birds. In W. N. Beyer, G. H. Heinz, & A. W. Redmon-Norwood (Eds.), Environmental contaminants in wildlife: Interpreting tissue concentrations (pp. 49–71). Boca Raton, Florida: Lewis Publishers.
Björnberg, A., Hakanson, L., & Lundbergh, K. (1988). A theory on the mechanisms regulating the bioavailability of mercury in natural waters. Environmental Pollution, 49, 53–61.
Brumbaugh, W. G., Krabbenhoft, D. P., Helsel, D. R., Wiener, J. G., & Echols, K. R. (2001). A national pilot study of mercury contamination of aquatic ecosystems along multiple gradients: bioaccumulation in fish. Biological Science Report, 2001–009, US Geological Survey, Columbia, Missouri.
Bhavsar, S. P., Fletcher, R., Hayton, A., Reiner, E. J., & Jacoson, D. A. (2007a). Composition of dioxin-like PCBs in fish: An application for risk assessment. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 3096–3102.
Bhavsar, S. P., Hayton, A., Reiner, E. J., & Jackson, D. A. (2007b). Estimating dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyl toxic equivalents from total polychlorinated biphenyl measurements in fish. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 26, 1622–1628.
Buck, J. A., Anthony, R. G., Schular, C. A., Isaacs, F. B., & Tillitt, D. E. (2005). Changes in productivity and contaminants in bald eagles nesting along the lower Columbia River, USA. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 1779–1792.
Chapman, P. M., Wang, F., Janssen, C., Persoonne, J., & Allen, H. E. (1998). Ecotoxicology of metals in aquatic sediments: binding and release, bioavailability, risk assessment, and remediation. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 55, 2221–2243.
Eisler, R. (1985). Cadmium hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: A synoptic review. Biological report, 85(1.2), US Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington, D.C.
Eisler, R. (1986). Chromium hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: A synoptic review. Biological report, 85(1.6), US Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington, D.C.
Eisler, R. (1990). Chlordane hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: A synoptic review. Biological report, 85(1.21), US Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington, D.C.
Eisler, R. (2004). Mercury hazards from gold mining to humans, plants, and animals. Review of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 181, 139–198.
Elliott, J. E., & Harris, M. L. (2001). An ecotoxicological assessment of chlorinated hydrocarbon effects on bald eagle populations. Reviews in Toxicology, 4, 1–60.
Giesy, J. P., Bowerman, W. W., Mora, M. A., Verbrugge, D. A., Othoudt, R. A., Newsed, J. L., et al. (1995). Contaminants in fishes from Great Lakes-influenced sections and above dams of three Michigan rivers: III. Implications for health of bald eagles. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 29, 309–321.
Gilderhus, P. A. (1966). Some effects of sublethal concentrations of sodium arsenate on bluegills and the aquatic environment. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 95, 289–296.
Grubb, T. G. (1995). Food habits of bald eagles breeding in the Arizona desert. Wilson Bulletin, 107, 258–274.
Grubb, T. G., Wiemeyer, S. N., & Kiff, L. F. (1990). Eggshell thinning and contaminant levels in bald eagle eggs from Arizona, 1977 to 1985. Southwest Naturalist, 35, 298–301.
Halbrook, R. S., Jenkins, J. H., Bush, P. B., & Seabolt, N. D. (1994). Sublethal concentrations of mercury in river otters: Monitoring environmental contamination. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 27, 306–310.
Hamilton, S. J. (2004). Review of selenium toxicity in the aquatic food chain. Science of the Total Environment, 326, 1–31.
Hansen, J. A., Welsh, P. G., Lipton, J., & Suedkamp, M. J. (2002). The effects of long-term cadmium exposure on the growth and survival of juvenile bull trout (Salvelinus confluentus). Aquatic Toxicology, 58, 165–174.
Haywood, D. D., & Ohmart, R. D. (1986). Utilization of benthic-feeding fish by inland breeding bald eagles. Condor, 88, 35–42.
Heaton, S. N., Bursian, S. J., Giesy, J. P., Tillitt, D. E., Render, J. A., Jones, P. D., et al. (1995). Dietary exposure of mink to carp from Saginaw Bay, Michigan: 1. Effects on reproduction and survival, and potential risks to wild mink populations. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 28, 334–343.
Heekyoung Choi, M., Cehc Jr., J. J., & Lagunas-Solar, M. C. (1998). Bioavailability of methylmercury to Sacramento blackfish (Orthodon microlepidotus): Dissolved organic carbon effects. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17, 695–701.
Heinz, G. H. (1979). Methyl mercury: reproductive and behavioral effects on three generations of mallard ducks. Journal of Wildlife Management, 43, 394–401.
Henny, C. J., Grove, R. A., Kaiser, J. L., & Bentley, V. R. (2004). An evaluation of osprey eggs to determine spatial residue patterns and effects of contaminants along the lower Columbia River, U.S.A. In R. D. Chancellor, & B.U. Meyburg (Eds.), Raptors Worldwide (pp. 369–388). Berlin, Germany: Hancock House Publishers.
Hill, E. F., & Camardese, M. B. (1986). Lethal dietary toxicities of environmental contaminants and pesticides to coturnix. Technical report 2, US Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington D.C.
Hinck, J. E., Blazer, V. S., Denslow, N. D., Echols, K. R., Gale R. W., Wieser, C., et al. (2008). Chemical contaminants, health indicators, and reproductive biomarker responses in fish from rivers in the Southeastern U.S. Science of the Total Environment, 390(2–), 538–557.
Hinck, J. E., Blazer, V. S., Denslow, N. D., Echols, K. R., Gross, T. S., May, T. W., et al. (2007). Chemical contaminants, health indicators, and reproductive biomarker responses in fish from the Colorado River and its tributaries. Science of the Total Environment, 378, 376–402.
Hinck, J. E., Schmitt, C. J., Blazer, V. S., Denslow, N. D., Bartish, T. M., Anderson, P. J., et al. (2006a). Environmental contaminants and biomarker responses in fish from the Columbia River and its tributaries: Spatial and temporal trends. Science of the Total Environment, 366, 549–578.
Hinck, J. E., Schmitt, C. J., Echols, K. R., May, T. W., Orazio, C. E., & Tillitt, D. E. (2006b). Environmental contaminants in fish and their associated risk to piscivorous wildlife in the Yukon River Basin, Alaska. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 51, 661–672.
Holcombe, G. W., Benoit, D. A., Leonard, E. N., & McKim, J. M. (1976). Long-term effects of lead exposure on three generations of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). Journal of Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 33, 1731–1741.
Hornshaw, T. C., Aulerich, R. J., & Johnson, H. E. (1983). Feeding great lakes fish to mink: effects on mink and accumulation and elimination of PCBs by mink. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, 11, 933–946.
Keith, L. H. (1991). Environmental Sampling and Analysis. (Boca Raton, Florida: Lewis Publishers).
Lemly, A. D. (1996). Selenium in aquatic organisms. In W. N. Beyer, G. H. Heinz, & A. W. Redmon-Norwood (Eds.), Environmental contaminants in wildlife: Interpreting tissue concentrations (pp. 427–445). Boca Raton, Florida: Lewis Publishers.
Leonards, P. E. G., de Vries, T. H., Minnaard, W., Stuijfzand, S., de Voogt, P., Cofino, W. P., et al. (1995). Assessment of experimental data on PCB-induced reproduction inhibition in mink, based on an isomer- and congener-specific approach using 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin toxic equivalency. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 14, 639–652.
Linder, R., Scotti, T., Goldstein, J., McElroy, K., & Walsh, D. (1980). Acute and subchronic toxicity of pentachlorobenzene. Journal of Environmental Pathology and Toxicology, 4, 183–196.
Mason, R. P., Laporte, J. M., & Andres, S. (1999). Factors controlling the bioaccumulation of mercury, methylmercury, arsenic, selenium, and cadmium by freshwater invertebrates and fish. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 38, 283–297.
Mayer, F. L., Jr., Mehrle, P. M., Jr., & Dwyer, W. P. (1975). Toxaphene effects on reproduction, growth, and mortality of brook trout. Report EPA-600/3-75/013, US Environmental Protection Agency, Duluth, Minnesota.
McGreachy, S. M., & Dixon, D. G. (1992). Whole-body arsenic concentrations in rainbow trout during acute exposure to arsenate. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 24, 301–308.
Newell, A. J., Johnson, D. W., & Allen, L. K. (1987). Niagara River biota contamination project: fish flesh criteria for piscivorous wildlife. Bureau of Environmental Protection Technical Report 87–, New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, Buffalo, New York.
Nocera, J. J., & Taylor, P. D. (1998). In situ behavioral responses of common loons associated with elevated mercury (Hg) exposure. Conservation Ecology, 2, 10.
Nosek, J. A., Craven, S. R., Sullivan, J. R., Hurley, S. S., & Peterson, R. E. (1992). Toxicity and reproductive effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in ring-necked pheasant hens. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, 35, 187–198.
Orihel, D., Paterson, M. J., Blanchfield, P. J., Bodaly, R. J., & Hintelmann, H. (2007). Experimental evidence of a linear relationship between inorganic mercury loading and methylmercury accumulation in aquatic biota. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 4952–4958.
Osowski, S. L., Brewer, L. W., Baker, O. E., & Cobb, G. P. (1995). The decline of mink in Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina: the role of contaminants. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 29, 418–423.
Paller, M. H., Bowers, J. A., Littrell, J. W., & Guanlao, A. V. (2004). Influences on mercury bioaccumulation factors for the Savannah River. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 46, 236–243.
Peakall, D. B. (1996). Dieldrin and other cyclodiene pesticides in wildlife. In W. N. Beyer, G. H. Heinz, & A. W. Redmon-Norwood (Eds.), Environmental contaminants in wildlife: Interpreting tissue concentrations (pp. 73–98). Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, Florida.
Peterson, R. E., Theobold, H. M., & Kimmel, G. L. (1993). Developmental and reproductive toxicity of dioxins and related compounds: Cross species comparisons. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 23, 283–335.
Reichel, W. L., Schmeling, S. K., Cromartie, E., Kaiser, T. E., Krynitsky, A. J., Lamont, T. G., et al. (1984). Pesticide, PCB, and lead residues and necropsy data for bald eagles from 32 states 1978–981. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 4, 395–403.
Rose, J., Hutcheson, M. S., Rowan West, C., Pancorbo, O., Hulme, K., Cooperman, A., et al. (1999). Fish mercury distribution in Massachusetts, USA Lakes. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 1370–1379.
Rudd, J. W. (1995). Sources of mercury to freshwater ecosystems: A review. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 80, 697–713.
Safe, S. (1990). Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzofurans (PCDFs), and related compounds: environmental and mechanistic considerations which support the development of toxic equivalency factors (TEFs). Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 21, 51–88.
Sample, B. E., & Suter, G. W. (1999). Ecological risk assessment in a large river-reservoir: 4. piscivorous wildlife. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 610–620.
Sample, B. E., Opresko, D. M., & Suter, G. W. (1996). Toxicological benchmarks for wildlife: 1996 revision. Report ES/ER/TM-86/R3, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee.
Scheuhammer, A. M., Atchison, C. M., Wong, A. H. K., & Evers, D. C. (1998). Mercury exposure in breeding Common Loons (Gavia immer) in central Ontario, Canada. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17, 191–196.
Scheuhammer, A. M., & Blancher, P. J. (1994). Potential risk to Common Loons (Gavia immer) from methylmercury exposure in acidified lakes. Hydrobiologia, 279/280, 445–455.
Schmitt, C. J. (2002). Organochlorine chemical residues in fish from the Mississippi River Basin, 1995. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 43, 81–97.
Schmitt, C. J. (2004). Concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, copper, lead, selenium, and zinc in fish from the Mississippi River Basin, 1995. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 90, 289–321.
Schmitt, C. J., Brumbaugh, W. G., Linder, G. L., & Hinck, J. E. (2006). A screening-level assessment of lead, cadmium, and zinc in fish and crayfish from northeastern Oklahoma, USA. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28, 445–471.
Schmitt, C. J., Hinck, J. E., Blazer, V. S., Denslow, N. D., Dethloff, G. M., Bartish, T. M., et al. (2005). Environmental contaminants and biomarker responses in fish from the Rio Grande and its U.S. tributaries: Spatial and temporal trends. Science of the Total Environment, 350, 161–193.
Schmitt, C. J., Zajicek, J. L., May, T. W., & Cowman, D. F. (1999). National contaminant biomonitoring program: Concentrations of organochlorine chemical residues and elemental contaminants in U.S. freshwater fish, 1976–986. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 162, 43–104.
Shubat, P. J., & Curtis, L. R. (1986). Ration and toxicant preexposure influence dieldrin accumulation by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 5, 69–77.
Sorenson, E. (1991). Metal poisoning in fish. (Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press).
Spehar, R. L. (1976). Cadmium and zinc toxicity to flagfish (Jordanella floridae). Journal of Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 33, 1939–1945.
Stephens, D. W., Waddell, B., Peltz, L. A., & Miller, J. B. (1992). Detailed study of selenium and selected elements in water, bottom sediment, and biota associated with irrigation drainage in the middle Green River basin, Utah, 1988–0. Water Resources Investigations Report, 92–084, US Geological Survey, Denver, Colorado.
Stouthart, X. J. H. X., Haans, J. L. M., Lock, R. A. C., & Wendelaar-Bonga, S. E. (1996). Effects of water pH on copper toxicity to early life stages of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 15, 376–383.
Tillitt, D. E., Gale, R. W., Meadows, J. C., Zajicek, J. L., Peterman, P. H., Heaton, S. N., et al. (1996). Dietary exposure of mink to carp from Saginaw Bay 3, characterization of dietary exposure to planar halogenated hydrocarbons, dioxin equivalents, and biomagnifications. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 283–291.
Tillitt, D. E., Giesy, J. P., & Ankley, G. T. (1991). Characterization of the H4IIE rat hepatic cell bioassay as a tool for assessing toxic potency of planar halogenated hydrocarbons in environmental samples. Environmental Science and Technology, 25, 87–92.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1993). Wildlife exposure factors handbook. EPA/600/R093/187, Office of Health and Environmental Assessment and Office of Research and Development, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1995). Great lakes water quality initiative criteria documents for the protection of wildlife. EPA-820\b-95\008, Office of Water, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1997). Mercury study report to Congress. EPA-452/R-97–03, Office of Research and Development, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1998). Guidelines for ecological risk assessment. EPA/630/R-95/002F, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2005a). Ecological soil screening levels for arsenic. Interim Final OSWER Directive 9285.7–2, Office of solid waste and emergency response, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2005b). Ecological soil screening levels for cadmium. Interim Final OSWER Directive 9285.7–5, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2005c). Ecological soil screening levels for chromium. Interim final OSWER Directive 9285.7–6, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2005d). Ecological soil screening levels for lead. Interim final OSWER Directive 9285.7-70, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2007a). Ecological soil screening levels for copper. Interim final OSWER Directive 9285.7-68, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2007b). Ecological soil screening levels for nickel. Interim final OSWER Directive 9285.7-76, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, D.C.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (1996). An investigation into the uptake of contaminants in largemouth bass and sediment from the lower Tombigbee and Mobile Rivers. Ecological Services Office Report 06-196-03-00-A, Daphne, Alabama.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (2007). Endangered and threatened wildlife and plants; Removing the bald eagle in the lower 48 states from the list of endangered and threatened wildlife, 50 CFR Part 17. Federal Register, 72, 37346–37372.
van den Berg, M., Birnbaum, L., Bosveld, A. T. C., Brunström, B., Cook, P., Feeley, M., et al. (1998). Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environmental Health Perspectives, 106, 775–792.
van den Berg, M., Birnbaum, L. S., Denison, M., De Vito, M., Farland, W., Feeley, M., et al. (2006). The 2005 World Health Organization re-evaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicological Science, 93, 223–241.
Walker, M. A., Cook, P. M., Butterworth, B. C., Zabel, E. W., & Peterson, R. E. (1996). Potency of a complex mixture of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin, dibenzofuran, and biphenyl congeners compared 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in causing fish early life stage mortality. Fundamental and Applied Toxicology, 30, 178–187.
Warner, K. A., Bonzongo, J. J., Roden, E. E., Ward, G. M., Green, A. C., Chaubey, I., et al. (2005). Effect of watershed parameters on mercury distribution in different environmental compartments in the Mobile Alabama River Basin, USA. Science of the Total Environment, 347, 187–207.
Whyte, J. J., Schmitt, C. J., & Tillitt, D. E. (2004). The H4IIE cell bioassay as an indicator of dioxin-like chemicals in wildlife and the environment. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 34, 1–83.
Wiemeyer, S. N., Lamont, T. G., Bunck, C. M., Sindelar, C. R., Gramlich, F. J., Fraser, J. D., et al. (1984). Organochlorine pesticide, polychlorobiphenyl, and mercury residues in bald eagle eggs-1969-79- and their relationships to shell thinning and reproduction. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 13, 529–549.
Wren, C. D., Hunter, D. B., Leatherland, J. F., & Stokes, P. M. (1987). The effects of polychlorinated biphenyls and methylmercury, singly and in combination, on mink. I: Uptake and toxic responses. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 16, 441–447.
Yeardley Jr., R. B., Lazorchak, J. M., & Paulsen, S. G. (1998). Elemental fish tissue contamination in northeastern U.S. lakes: evaluation of an approach to regional assessment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17, 1875–1884.
Zappia, H. (2002). Organochlorine compounds and trace elements in fish tissue and streambed sediment in the mobile river basin, Alabama, Mississippi, and Georgia, 1998. Water-resources investigations Report 02–160, US Geological Survey, Montgomery, Alabama.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hinck, J.E., Schmitt, C.J., Chojnacki, K.A. et al. Environmental contaminants in freshwater fish and their risk to piscivorous wildlife based on a national monitoring program. Environ Monit Assess 152, 469–494 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0331-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0331-5