Abstract
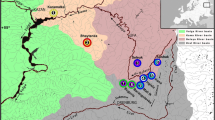
Triplophysa orientalis (Herzenstein) is one of the Nemacheilinae (Cypriniformes: Balitoridae) fish species distributed in the Tibetan Plateau area. In order to understand the impact of plateau uplift on population history and the isolation effect of plateau lakes on T. orientalis, we examined its genetic structure and phylogenetic relationships. A total of 98 individuals from five wild populations, three from plateau lakes and two from branch rivers in upper reaches of the Yangtze River, in the eastern peripheral of the Tibetan Plateau were sampled. An 848 base pair fragment from the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) control region was sequenced for analyses. Overall, very high intra-population genetic variability was found in all populations except for one lake population (Rannicuo); nucleotide diversity ranged from 0.0025 to 0.0159 and haplotype diversity ranged from 0.641 to 0.879. Furthermore, the genetic distance between river populations (0.0326) was much higher than that among lake populations (Rannicuo and Barencuo 0.0035, Bannicuo and Yibicuo 0.0038, Rannicuo and Yibicuo 0.0049). Additionally, the analysis of molecular variance demonstrated that most of the observed genetic variability occurred among populations, accompanied with significant Fst values except for that between the Yibicuo and Barencuo populations. This evidence suggested a strong population structure of the species and a lack of inter-population connection. Lastly, the rate of migration indicated there were large historic gene flows among lake populations. Demographic analysis also indicated there were bottlenecks or expansions in three lake populations, suggesting a potential isolation effect of plateau lakes on population differentiation. Molecular dating of intra-specific divergence showed the plateau uplift has shaped the genetic structure of T. orientalis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboim MA, Menezes GM, Schlitt T, Rogers AD (2005) Genetic structure and history of populations of the deep-sea fish Helicolenus dactylopterus (Delaroche, 1809) inferred from mtDNA sequence analysis. Mol Ecol 14:1343–1354
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 19:716–723
An ZS, Kutzbach JE, Prell WL, Porter SC (2001) Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau since Late Miocene times. Nature 411:62–66
Arbogast BS, Kenagy GJ (2001) Comparative phylogeography as an integrative approach to historical biogeography. J Biogeogr 28:819–825
Aris-Brosou S, Excoffier L (1996) The impact of population expansion and mutation rate heterogeneity on DNA sequence polymorphism. Mol Biol Evol 13:494–504
Aurelle D, Berrebi P (2001) Genetic structure of brown trout (Salmo trutta, L.) populations from south-western France: data from mitochondrial control region variability. Mol Ecol 10:1551–1561
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16:37–48
Beerli P (2008) Migrate version 3.0 − a maximum likelihood and Bayesian estimator of gene flow using the coalescent. Distributed over the internet at http://popgen.scs.edu/migrate.html
Beerli P, Felsentein J (1999) Maximum-likelihood estimation of migration rates and effective population numbers in two populations using a coalescent approach. Genetics 152:763–773
Bowen BW, Grant WS (1997) Phylogeography of the sardines (Sardinops spp.): assessing biogeographic models and population histories in temperate upwelling zones. Evolution 51:1601–1610
Brown GG, Gadaleta G, Pepe G, Saccone C, Sbisà E (1986) Structural conservation and variation in the D-loop-containing region of vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Biol 192:503–511
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol 7:214
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform Online 1:47–50
Fu YX (1997) Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 147:915–925
Fu YX, Li WH (1993) Maximum likelihood estimation of population parameters. Genetics 134:1261–1270
Grant WAS, Bowen BW (1998) Shallow population histories in deep evolutionary lineages of marine fishes: insights from sardines and anchovies and lessons for conservation. J Hered 89:415–426
Harpending HC (1994) Signature of ancient population growth in a low-resolution mitochondrial DNA mismatch distribution. Hum Biol 66:591–600
Harrison TM, Copeland P, Kidd WSF, Yin A (1992) Raising Tibet. Science 255:1663–1670
He CL (2008) Taxonomic revision of Triplophysa species in Sichuan Province, MS Dissertation. Sichuan University, China
He DK, Chen YF (2006) Biogeography and molecular phylogeny of the genus Schizothorax (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in China inferred from cytochrome b sequences. J Biogeogr 33:1448–1460
He DK, Chen YF (2007) Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of the highly specialized grade schizothoracine fishes (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) inferred from cytochrome b sequences. Chin Sci Bull 52:777–788
He SP, Cao WX, Chen YY (2001) The uplift of Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau and the vicariance speciation of glyptosternoid fishes (Siluriformes: Sisoridae). Sci China Ser C 44:644–651
He DK, Chen YF, Chen YY, Chen ZM (2004) Molecular phylogeny of the specialized schizothoracine fishes (Teleostei: Cyprinidae), with their implications for the uplift of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chin Sci Bull 49:39–48
He DK, Chen YX, Chen YF (2006) Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of the genus Triplophysa (Osteichthyes: Nemacheilinae) in the Tibetan Plateau inferred from cytochrome b DNA sequences. Prog Nat Sci 16:1395–1404
Herzenstein SM (1888) Fische. In: Wissenschaftliche Resultate der von N. M. Przewalski nach Central-Asien unternommenen Reisen. Zool Theil 3(2):1−90
Hewitt G (2000) The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature 405:907–913
Hudson RR, Slatkin M, Maddison WP (1992) Estimation of levels of gene flow from DNA sequence data. Genetics 132:583–589
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Liu HZ, Tzeng CS, Teng HY (2002a) Sequence variations in the mitochondrial DNA control region and their implications for the phylogeny of the Cypriniformes. Can J Zool 80:569–581
Liu JQ, Gao TG, Chen ZD, Lu AM (2002b) Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau endemic Nannoglottis (Asteraceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 23:307–325
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Pang JF, Wang YZ, Zhong Y, Hoelzel AR, Papenfuss TJ, Zeng XM, Ananjeva NB, Zhang YP (2003) A phylogeny of Chinese species in the genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae) inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 27:398–409
Peng ZG, Ho SYW, Zhang YG, He SP (2006) Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from divergence times of glyptosternoid catfishes. Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:568–572
Posada D (2008) jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25:1253–1256
Qi DL, Guo SC, Zhao XQ, Yang J, Tang WJ (2007) Genetic diversity and historical population structure of Schizopygopsis pylzovi (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) in the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Freshw Biol 52:1090–1104
Qu YH, Ericson PGP, Lei FM, Li SH (2005) Postglacial colonization of the Tibetan Plateau inferred from the matrilineal genetic structure of the endemic red-necked snow finch, Pyrgilauda ruficollis. Mol Ecol 14:1767–1781
Qu JY, Liu NF, Bao XK, Wang XL (2009) Phylogeography of the ring-necked pheasant (Phasianus colchicus) in China. Mol Phylogenet Evol 52:125–132
Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2007) Tracer v 1.4 http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer
Recuero E, Martínez SÍ, Parra OG, García PM (2006) Phylogeography of Pseudacris regilla (Anura: Hylidae) in western North America, with a proposal for a new taxonomic rearrangement. Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:293–304
Rogers AR, Harpending H (1992) Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Mol Biol Evol 9:552–569
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioniformatics 19:1572–1574
Rozas J, Sánchez DJC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 19:2496–2497
Saccone C, Attimonelli M, Sbisà E (1987) Structural elements highly preserved during the evolution of the D-loop-containing region in vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Biol 26:205–211
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Schneider S, Excoffier L (1999) Estimation of past demographic parameters from the distribution of pairwise differences when the mutation rates vary among sites: application to human mitochondrial DNA. Genetics 152:1079–1089
Shi YF, Li JJ, Li BY (1998) Uplift and environmental changes of Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau in the Late Cenozoic. Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou
Song ZB, Song J, Yue BS (2008) Population genetic diversity of Prenant’s schizothoracin, Schizothorax prenanti, inferred from the mitochondrial DNA control region. Environ Biol Fish 81:247–252
Stepien CA (1995) Population genetic divergence and geographic patterns from DNA sequences: Examples from marine and freshwater fishes. Am Fish Soc Symp 17:263–287
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585–595
Tang QY, Liu HZ, Mayden R, Xiong BX (2006) Comparison of evolutionary rates in the mitochondrial DNA cytochrome b gene and control region and their implications for phylogeny of the Cobitoidea (Teleostei: Cypriniformes). Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:347–357
Wu YF, Wu CZ (1992) The fishes of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, Chengdu
Yang SJ, Lei FM, Qu YH, Yin ZH (2006a) Intraspecific phylogeography of the white-rumped snowfinch (Onychostruthus taczanowskii) endemic to the Tibetan Plateau based on mtDNA sequences. J Zool 268:187–192
Yang SJ, Yin ZH, Ma XM, Lei FM (2006b) Phylogeography of ground tit (Pseudopodoces humilis) based on mtDNA: Evidence of past fragmentation on the Tibetan Plateau. Mol Phylogenet Evol 41:257–265
Yang SJ, Dong HL, Lei FM (2009) Phylogeography of regional fauna on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. Prog Nat Sci 19:789–799
Yu N, Zheng CL, Zhang YP, Li WH (2000) Molecular systematics of pikas (Genus Ochotona) inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 16:85–95
Zhang JB, Cai ZP, Huang LM (2006) Population genetic structure of crimson snapper Lutjanus erythropterus in East Asia, revealed by analysis of the mitochondrial control region. ICES J Mar Sci 63:693–704
Zhu SQ (1989) The loaches of the subfamily Nemacheilinae in China (Cypriniformes: Cobitidae). Jiangsu Science and Technology Publishing House, Nanjing
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30670290), Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry (No. 2008890-19-13), and Sichuan Youth Science and Technology Foundation (No. 08ZQ026-019). We would like to thank Chunlin He for his help in sample collection. We are grateful for Emily H. King, Jinzhong Fu and Cameron Hudson for their help in English corrections, three anonymous reviewers and David. L. G. Noakes for their comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, F., Zhang, X., Zhang, X. et al. High intra-population genetic variability and inter-population differentiation in a plateau specialized fish, Triplophysa orientalis . Environ Biol Fish 93, 519–530 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-011-9947-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-011-9947-3