Abstract
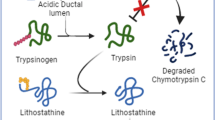
Symptoms of choledochal cysts are caused by protein plugs. We performed proteomic analysis of protein plugs to elucidate formation mechanism. Protein plugs were obtained from three pediatric patients with choledochal cyst. Proteins were separated using sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Gel bands common to the samples were excised for mass spectrometry. Mass spectra were compared with the NCBI database for protein identification. Gel bands of protein plug samples were predominant at 14 kilodaltons (kDa), followed by 29 kDa. Four other thin bands were common to the plug samples. Four bands (including 14 and 29 kDa) were identified as lithostathine, and one band as serum albumin. Plugs consisted mostly of lithostathine, a protein secreted by pancreatic acinar cells into pancreatic juice. The mechanism involves trypsinogen and lithostathine regurgitating into the cyst through an aberrant union of pancreaticobiliary ducts. Activated trypsin cleaves soluble lithostathine into insoluble forms that aggregate to form plugs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Todani T, Watanabe Y, Naruse M, Tabuchi K, Okajima K (1977) Congenital bile duct cysts: classification, operative procedures, and review of thirty-seven cases including cancer arising from choledochal cyst. Am J Surg 134:263–269
Todani T (1997) Congenital choledochal dilatation: classification, clinical features, and long-term results. J Hepatobil Pancreat Surg 4:276–282
Visser BC, Suh I, Way LW, Kang SM (2004) Congenital choledochal cysts in adults. Arch Surg 139:855–862
Japanese Study Group on Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction (JSPBM), Committee of JSPBM for Diagnostic Criteria (1994) Diagnostic criteria of pancreaticobiliary maljunction. J Hepatobil Pancreat Surg 1:219–221
Kaneko K, Ando H, Ito T, Watanabe Y, Seo T, Harada T, Ito F (1997) Protein plugs cause symptoms in patients with choledochal cysts. Am J Gastroenterol 92:1018–1021
Kaneko K, Ando H, Ito T, Kasai K, Watanabe Y, Seo T (1996) Increased cell proliferation and transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF alpha) in the gall-bladder epithelium of patients with pancreaticobiliary maljunction. Pathol Int 46:253–260
Kaneko K, Ando H, Seo T, Ono Y, Ochiai K, Ogura Y (2005) Bile infection contributes to intrahepatic calculi formation after excision of choledochal cysts. Pediatr Surg Int 21:8–11
Maki T (1966) Pathogenesis of calcium bilirubinate stone: role of E. coli, b-glucuronidase and coagulation by inorganic ions, polyelectrolytes and agitation. Ann Surg 164:90–100
Ando H, Ito T, Kaneko K, Seo T, Ito F (1996) Intrahepatic bile duct stenosis causing intrahepatic calculi formation following excision of a choledochal cyst. J Am Coll Surg 183:56–60
Uno K, Tsuchida Y, Kawarasaki H, Ohmiya H, Honna T (1996) Development of intrahepatic cholelithiasis long after primary excision of choledochal cysts. J Am Coll Surg 183:583–588
Watanabe Y, Toki A, Todani T (1999) Bile duct cancer developed after cyst excision for choledochal cyst. J Hepatobil Pancreat Surg 6:207–212
Kobayashi S, Asano T, Yamasaki M, Kenmochi T, Nakagohri T, Ochiai T (1999) Risk of bile duct carcinogenesis after excision of extrahepatic bile ducts in pancreaticobiliary maljunction. Surgery 126:939–944
Goto N, Yasuda I, Uematsu T, Kanemura N, Takai S, Ando K, Kato T, Osada S, Takao H, Saji S, Shimokawa K, Moriwaki H (2001) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma arising 10 years after the excision of congenital extrahepatic biliary dilation. J Gastroenterol 36:856–862
Tsuchida A, Kasuya K, Endo M, Saito H, Inoue K, Nagae I, Aoki T, Koyanagi Y (2003) High risk of bile duct carcinogenesis after primary resection of a congenital biliary dilatation. Oncol Rep 10:1183–1187
Ando H, Ito T, Watanabe Y, Seo T, Kaneko K, Nagaya M (1995) Spontaneous perforation of choledochal cyst. J Am Coll Surg 181:125–128
Ando H, Ito T, Nagaya M, Watanabe Y, Seo T, Kaneko K (1995) Pancreaticobiliary maljunction without choledochal cysts in infants and children: clinical features and surgical therapy. J Pediatr Surg 30:1658–1662
Shevchenko A, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mann M (1996) Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem 68:850–858
Giorgi D, Bernard JP, Rouquier S, Iovanna J, Sarles H, Dagorn JC (1989) Secretory pancreatic stone protein messenger RNA. Nucleotide sequence and expression in chronic calcifying pancreatitis. J Clin Invest 84:100–106
Watanabe T, Yonekura H, Terazono K, Yamamoto H, Okamoto H (1990) Complete nucleotide sequence of human reg gene and its expression in normal and tumoral tissues: the reg protien, pancreatic stone protein, and pancreatic thread protein are one and the same product of the gene. J Biol Chem 265:7432–7439
Patard L, Lallemand JY, Stoven V (2003) An insight into the role of human pancreatic lithostathine. JOP 4:92–103
Provansal-Cheylan M, Mariani A, Bernard JP, Sarles H, Dupuy P (1989) Pancreatic stone protein: quantification in pancreatic juice by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and comparison with other methods. Pancreas 4:680–689
Schmiegel W, Burchert M, Kalthoff H, Roeder C, Butzow G, Grimm H, Kremer B, Soehendra N, Schreiber HW, Thiele HG, Greten H (1990) Immunochemical characterization and quantitative distribution of pancreatic stone protein in sera and pancreatic secretions in pancreatic disorders. Gastroenterology 99:1421–1430
Lee BI, Mustafi D, Cho W, Nakagawa Y (2003) Characterization of calcium binding properties of lithostathine. J Biol Inorg Chem 8:341–347
Gregoire C, Marco S, Thimonier J, Duplan L, Laurine E, Chauvin JP, Michel B, Peyrot V, Verdier JM (2001) Three-dimensional structure of the lithostathine protofibril, a protein involved in Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J 20:3313–3321
Graf R, Schiesser M, Scheele GA, Marquardt K, Frick TW, Ammann RW, Bimmler D (2001) A family of 16-kDa pancreatic secretory stress proteins form highly organized fibrillar structures upon tryptic activation. J Biol Chem 276:21028–21038
Iovanna JL, Dagorn JC (2005) The multifunctional family of secreted proteins containing a C-type lectin-like domain linked to a short N-terminal peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1723:8–18
Guy O, Robles-Diaz G, Adrich Z, Sahel J, Sarles H (1983) Protein content of precipitates present in pancreatic juice of alcoholic subjects and patients with chronic calcifying pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 84:102–107
Multigner L, Daudon M, Montalto G, De Caro A, Etienne JP, Sarles H (1986) Radiolucent pancreatic stones. N Engl J Med 314:248
Mariani A, Bernard JP, Provansal-Cheylan M, Nitsche S, Sarles H (1991) Differnces of pancreatic stone morphology and content in patients with pancreatic lithiasis. Dig Dis Sci 36:1509–1516
Ozturk M, de la Monte SM, Gross J, Wands JR (1989) Elevated leveld of an exocrine pancreatic secretory protein in Alzheimer disease brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:419–423
Laurine E, Gregoire C, Fandrich M, Engemann S, Marchal S, Thion L, Mohr M, Monsarrat B, Michel B, Dobson CM, Wanker E, Erard M, Verdier JM (2003) Lithostathine quadruple-helical filaments form proteinase K-resistant deposits in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Bio Chem 51:51770–51778
Duplan L, Michel B, Boucraut J, Barthellemy S, Desplat-Jego S, Marin V, Gambarelli D, Bernard D, Berthezene P, Alescio-Lautier B, Verdier JM (2001) Lithostathine and pancreatitis-associated protein are involved in the very early stages of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 22:79–88
Kaneko K, Ando H, Watanabe Y, Seo T, Harada T (2000) Pathologic changes in the common bile duct of an experimental model with pancreaticobiliary maljunction. Pediatr Surg Int 16:26–28
Kristiansen TZ, Bunkenborg J, Gronborg M, Molina H, Thuluvath PJ, Argani P, Goggins MG, Maitra A, Pandey A (2004) A proteomic analysis of human bile. Mol Cell Proteomics 3:715–728
Zhou H, Chen B, Li RX, Sheng QH, Li SJ, Zhang L, Li L, Xia QC, Wang HY, Zeng R (2005) Large-scale identification of human biliary proteins from a cholesterol stone patient using a proteomic approach. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 19;3569–3578
Grønborg M, Bunkenborg J, Kristiansen TZ, Jensen ON, Yeo CJ, Hruban RH, Maitra A, Goggins MG, Pandey A (2004) Comprehensive proteomic analysis of human pancreatic juice. J Proteome Res 3:1042–1055
He XM, Carter DC (1992) Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 358:209–215
Smits ME, Groen AK, Mok KS, van Marle J, Tytgat GN, Huibregtse K (1997) Analysis of occluded pancreatic stents and juices in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 45:52–58
Farnbacher MJ, Voll RE, Faissner R, Wehler M, Hahn EG, Lohr M, Schneider HT (2005) Composition of clogging material in pancreatic endoprostheses. Gastrointest Endosc 61:862–866
Ochiai K, Kaneko K, Kitagawa M, Ando H, Hayakawa T (2004) Activated pancreatic enzyme and pancreatic stone protein (PSP/reg) in bile of patients with pancreaticobiliary maljunction/choledochal cyst. Dig Dis Sci 49:1953–1956
Bensimon G, Lacomblez L, Meininger V (1994) A controlled trial of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med 330:585–591
Heiser V, Engemann S, Brocker W, Dunkel I, Boeddrich A, Waelter S, Nordhoff E, Lurz R, Schugardt N, Rautenberg S, Herhaus C, Barnickel G, Bottcher H, Lehrach H, Wanker EE (2002) Identification of benzothiazoles as potential polyglutamine aggregation inhibitors of Huntington's disease by using an automated filter retardation assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16400–16406
Huntington Study Group (2003) Dosage effects of riluzole in Huntington's disease. A multicenter placebo-controlled study. Neurology 61:1551–1556
Tsuchida A, Itoi T, Kasuya K, Endo M, Katsumata K, Aoki T, Suzuki M, Aoki T (2005) Inhibitory effect of meloxicam, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on N-nitrosobis (2-oxopropyl) amine induced biliary carcinogenesis in Syrian hamsters. Carcinogenesis 26:1922–1928
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by a grant-in-aid (17591860) for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, and Culture, Japan. We thank Kenji Yamamoto, Ikuko Sagawa, and Satoru Kuboi (APRO Life Science Institute, Naruto, Japan) for peptide mass fingerprinting analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaneko, K., Ando, H., Seo, T. et al. Proteomic Analysis of Protein Plugs: Causative Agent of Symptoms in Patients with Choledochal Cyst. Dig Dis Sci 52, 1979–1986 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9398-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9398-4