Abstract
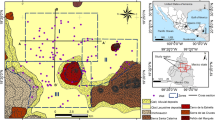
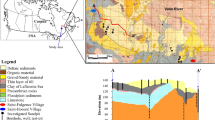
We present a method of aquifer characterization that is able to utilize multiple sources of conditioning data to build a more realistic model of heterogeneity. This modeling approach (InMod) uses geophysical data to delineate bounding surfaces within sedimentary deposits. The depositional volumes between bounding surfaces are identified automatically from the geophysical data by a region growing algorithm. Simple geometric rules are used to constrain the growth of the regions in 3-D. The nodes within the depositional volume are assigned to categorical lithologies using geostatistical realizations and a dynamic lookup routine that can be conditioned to field data. The realizations created with this method preserve geologically expected features and produces sharp juxtapositions of high and low hydraulic conductivity lithologies along bounding surfaces. The realizations created with InMod also have higher variance than models created only with geostatistics and honor the volumetric distribution of sediments measured from field data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annan, A.P.: GPR methods for hydrogeological studies. In: Rubin, Y., Hubbard, S.S. (eds.) Hydrogeophysics, pp. 185–213. Springer, New York (2005)
Barrash, W., Clemo, T.: Hierarchical geostatistics and multifacies systems: Boise hydrogeophysical research site, Boise, Idaho. Water Resour. Res. 38(11), 1196 (2002)
Bersezio, R., Giudici, M., Mele, M.: Combining sedimentological and geophysical data for high-resolution 3-D mapping of fluvial architectural elements in the Quaternary Po plain (Italy). Sediment. Geol. 202, 230–248 (2007)
Bridge, J.J., Hyndman, D.W.: Aquifer characterization. In: Bridge, J.J., Hyndman, D.W. (eds.) Aquifer Characterization, pp. 1–2. SEPM special publication No. 80 (2004)
Cardenas, M.B., Zlotnik, V.A.: Three-dimensional model of modern channel bend deposits. Water Resour. Res. 39(6), 1141 (2003)
Carle, S.F., Fogg, G.E.: Transition probability-based indicator geostatistics. Math. Geol. 28(4), 453–476 (1996)
Carle, S.F., Fogg, G.E.: Modeling spatial variability with one and multidimensional continuous-lag markov chains. Math. Geol. 29(7), 891–918 (1997)
Carle, S.F.: T-PROGS: transition probability geostatistical software, users manual version 2.1, p. 84. University of California, Davis (1999)
Close, M.E., Nobes, D.C., Pang L.: Presence of preferential flow paths in shallow groundwater systems as indicated by tracer experiments and geophysical surveys. In: Bridge, J.J., Hyndman, D.W. (eds.) Aquifer Characterization, pp. 79–91. SEPM special publication No. 80 (2004)
Cortis, A., Gallo, C., Scher, H., Berkowitz, B.: Numerical simulation of non-Fickian transport in geological formations with multiple-scale heterogeneities. Water Resour. Res. 40, W04209 (2004)
Dai, X., Ritzi, R.W., Dominic, D.F.: Estimating parameters for hierarchical permeability correlation models. In: Bridge, J.J., Hyndman, D.W. (eds.) Aquifer Characterization, pp. 41–54. SEPM special publication No. 80 (2004)
Deutsch, C.V.: Geostatistical Reservoir Modeling, p. 376. Oxford University Press, New York (2002)
Deutsch, C.V., Journel, A.G.: GSLIB—Geostatistical Software Library Users Guide, p. 384. Oxford University Press, New York (1998)
Engdahl, N.B.: Heterogeneity effects on flow and transport within a shallow fluvial aquifer, p. 199. M.S. Thesis, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque (2009)
Fleckenstein, J.H., Niswonger, R.G., Fogg, G.E.: River-aquifer interactions, geologic heterogeneity, and low-flow management. Ground Water 44(4), 837–852 (2006)
Heinz, J., Kleineidam, S., Teutsch, G., Aigner, T.: Heterogeneity patterns of Quaternary glaciofluvial gravel bodies (SW-Germany): Application to hydrogeology. Sediment. Geol. 158, 1–23 (2003)
Gaud, M.N., Smith, G.A., McKenna, S.A.: Realting small-scale permeability heterogeneity to lithofacies distribution. In: Bridge, J.J., Hyndman, D.W. (eds.) Aquifer Characterization, pp. 55–66. SEPM special publication No. 80 (2004)
Guardiano, F.B., Srivastava, R.M.: Multivariate geostatistics: Beyond bivariate moments. Quant. Geol. Geostat. 5, 133–144 (1993)
Huggenberger, P.: Radar facies: recognition of facies patterns ad heterogeneities within Pleistocene rhine gravels, NE Switzerland. In: Best, C.L., Bristow, C.S. (eds.) Braided Rivers. Geological Society Special Publication, vol. 75, pp. 163–176. Geological Society, London (1993)
Journel, A.G., Huijbregts, Ch.J.: Mining Geostatistics, p. 600. Academic, San Diego (1978)
Knight, R., Tercier,P., Jol, H.: The role of ground penetrating radar and geostatistics in reservoir description. In: The Leading Edge, pp. 1576–1582 (1997)
Koltermann, C.E., Gorelick, S.M.: Heterogeneity in sedimentary deposits: a review of structure-imitating, process-imitating, and descriptive approaches. Water Resour. Res. 32(9), 2617–2658 (1996)
Kowalsky, M.B., Rubin,Y., Dietrich, P.: The use of ground-penetrating radar for characterizing sediments under transient flow conditions. In: Bridge, J.J., Hyndman, D.W. (eds.) Aquifer Characterization, pp. 107–127. SEPM special publication No. 80 (2004)
Lesmes, D.P., Friedman, S.P.: Relationships between the electrical and hydrogeological properties of rocks and soils. In: Rubin, Y., Hubbard, S.S. (eds.) Hydrogeophysics, pp. 87–128. Springer, New York (2005)
Levy, M., Berkowitz, B.: Measurement and analysis of non-Fickian dispersion in heterogeneous porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 64, 203–226 (2003)
Lira, J., Frulla, L.: An automated region growing algorithm for segmentation of texture regions in SAR images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 19(18), 3595–3606 (1997)
Lunt, I.A., Bridge, J.S., Tye, R.S.: Development of a 3-D depositional model of braided-river gravels and sands to improve aquifer characterization. In: Bridge, J.J., Hyndman, D.W. (eds.) Aquifer Characterization, pp. 139–169. SEPM special publication No. 80 (2004)
Lunt, I.A., Bridge, J.S., Tye, R.S.: A qualitative, three-dimensional depositional model of gravelly braided rivers. Sedimentology 51, 377–414 (2004)
Mehnert, A., Jackway, P.: An improved seeded region growing algorithm. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 18(10), 1065–1071 (1997)
Neal, A.: Ground-penetrating radar and its use in sedimentology: principles, problems, and progress. Earth Sci. Rev. 66, 261–330 (2004)
Novakovic, D., White, C.D., Corbeanu, R.M., Hammon III, W.S., Bhattacharya, J.P., McMechan, G.A.: Hydraulic effects of shales in fluvial-deltaic deposits: ground-penetrating radar, outcrop observations, geostatistics, and three-dimensional flow modeling for the ferron sandstone, Utah. Math. Geol. 34(7), 857–893 (2002)
Rea, J., Knight, R.: Geostatistical analysis of ground-penetrating radar data: a means of describing spatial variation in the subsurface. Water Resour. Res. 34(3), 329–339 (1998)
Regli, C., Huggenberger, P., Rauber, M.: Interpretation of drill core and georadar data of coarse gravel deposits. J. Hydrol. 255, 234–252 (2002)
Revol-Muller, C., Peyrin, F., Carrillon, Y., Odet, C.: Automated 3D growing algorithm based on an assessment function. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 23(1-3), 137–150 (2002)
Ritzi, R.W., Behavior of indicator variograms and transition probabilities in relation to the variance in lengths of hydrofacies. Water Resour. Res. 36(11), 3375–3381 (2000)
Rubin, Y., Lunt, I.A., Bridge, J.S.: Spatial variability in river sediments and its link with river channel geometry. Water Resour. Res. 42, W06D16 (2006)
Scheibe, T.D., Freyberg, D.L.: Use of sedimentological information for geometric simulation of natural porous media structure. Water Resour. Res. 31(12), 3259–3270 (1995)
Sensors & Software: Technical Manual 25, Pulse-EKKO 100 Run, User’s Guide v1.2. Sensors and Software, Ontario (1999)
Vandenberghe, J., van Overmeeren, R.A.: Ground penetrating radar images of selected fluvial deposits in the Netherlands. Sediment. Geol. 128, 245–270 (1999)
Wan, S., Higgins, W.E.: Symmetric region growing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 12(9), 1007–1015 (2003)
Weissmann, G. S., Carle, S.F., Fogg, G.E.: Three-dimensional hydrofacies modeling based on soil surveys and transition probability geostatistics. Water Resour. Res. 35(6), 1761–1770 (1999)
Weissmann, G.S., Fogg, G.E.: Multi-scale alluvial fan heterogeneity modeled with transition probability geostatistics in a sequence stratigraphic framework. J. Hydrol. 226(1–2), 48–65 (1999)
Weissmann, G.S., Zhang, Y., Fogg, G.E., Mount, J.F.: Influence of incised-valley-fill deposits on hydrogeology of a stream-dominated alluvial fan. In: Bridge, J.J., Hyndman, D.W. (eds.) Aquifer Characterization, pp. 15–28. SEPM special publication No. 80 (2004)
Xu, W., Cumming, I.: A region-growing algorithm for InSAR phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 37(1), 124–134 (1999)
Zheng, C., Gorelick, S.M.: Analysis of solute transport in flow fields influenced by preferential flowpaths at the decimeter scale. Ground Water 41(2), 142–155 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engdahl, N.B., Weissmann, G.S. & Bonal, N.D. An integrated approach to shallow aquifer characterization: combining geophysics and geostatistics. Comput Geosci 14, 217–229 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-009-9145-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-009-9145-y