Abstract
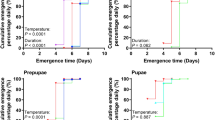
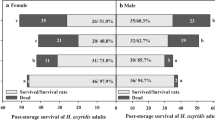
The present study investigated whether long-term cold storage at high relative humidity (RH) affected the quality of the predatory mite Neoseiulus californicus (McGregor) (Acari: Phytoseiidae) in terms of its survival and reproduction. For this purpose, we examined biological traits at the end of storage and during the post-storage period. Mated females three days after adult emergence were stored individually in 1.5-ml vials for 15, 30, 45, 60, or 75 days at 5.0 ± 0.3°C and RH of 99 ± 0.1% under continuous darkness. At the end of the storage period, 94–100% of females had survived when the storage period was ≤30 days, but percent survival decreased with longer storage. After storage, female survival and oviposition rates were equivalent to un-stored females at 24 ± 1°C, RH of 93 ± 2%, and a photoperiod of LD 16:8 h. The quality of progeny (hatchability, survival to adulthood, and sex ratio) of stored females was not affected by storage periods as long as 60 days. These results indicate that storage using the tested method can preserve N. californicus for at least 30 days without any degradation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayram A, Ozcan H, Kornosor S (2005) Effect of cold storage on the performance of Telenomus busseolae Gahan (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), an egg parasitoid of Sesamia nonagrioides (Lefebvre) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Biol Control 35:68–77
Canlas J, Amano H, Ochiai N, Takeda M (2006) Biology and predation of the Japanese strain of Neoseiulus californicus (McGregor) (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Syst Appl Acarol 11:141–157
Castagnoli M, Simoni S (2003) Neoseiulus californicus (McGregor) (Acari Phytoseiidae): survey of biological and behavioral traits of a versatile predator. Redia 86:153–164
Chen WL, Leopold RA, Boetel MA (2008a) Cold storage of adult Gonatocerus ashmeadi (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae) and effects on maternal and progeny fitness. Econ Entomol 101:1760–1770
Chen WL, Leopold RA, Harris MO (2008b) Cold storage effects on maternal and progeny quality of Gonatocerus ashmeadi Girault (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae). Biol Control 46:122–132
Chen H, Opit GP, Sheng P, Zhang H (2011) Maternal and progeny quality of Habrobracon hebetor Say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) after cold storage. Biol Control 58:255–261
Colinet H, Boivin G (2011) Insect parasitoids cold storage: A comprehensive review of factors of variability and consequences. Biol Control 58:83–95
Colinet H, Hance T (2010) Interspecific variation in the response to low temperature storage in different aphid parasitoids. Ann Appl Biol 156:147–156
Colinet H, Hance T, Vernon P (2006) Water relations, fat reserves, survival, and longevity of a cold-exposed parasitic wasp Aphidius colemani (Hymenoptera: Aphidiinae). Environ Entomol 35:228–236
Coudron TA, Ellersieck MR, Shelby KS (2007) Influence of diet on long-term cold storage of the predator Podisus maculiventris (Say) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Biol Control 42:186–195
Escudero LA, Ferragut F (2005) Life-history of predatory mites Neoseiulus californicus and Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on four spider mite species as prey, with special reference to Tetranychus evansi (Acari: Tetranychidae). Biol Control 32:378–384
Etzel LK, Legner EF (1999) Culture and colonisation. In: Bellows TS, Fisher TW (eds) Handbook of biological control: principles and application of biological control. Academic Press, London, UK, pp 125–197
Gaede K (1992) On the water balance of Phytoseiulus persimilis A.-H. and its ecological significance. Exp Appl Acarol 15:181–198
Ghazy NA, Suzuki T, Shah M, Amano H, Ohyama K (2012) Using high relative humidity and low air temperature as a long-term storage strategy for the predatory mite Neoseiulus californicus (Gamasida: Phytoseiidae). Biol Control 60:241–246
Gotoh T, Yamaguchi K, Mori K (2004) Effect of temperature on life history of the predatory mite Amblyseius (Neoseiulus) californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol 32:15–30
Gotoh T, Akizawa T, Watanabe M, Tsuchiya A, Shimazaki S (2005) Cold hardiness of Neoseiulus californicus and N. womersleyi (Acari: Phytoseiidae). J Acarol Soc Jpn 14:93–103
Greco NM, Sanchez NE, Liljesthrom GG (2005) Neoseiulus californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) as a potential control agent of Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae): effect of pest/predator ratio on pest abundance on strawberry. Exp Appl Acarol 37:57–66
Häckermann J, Rott AS, Tschudi-Rein K, Dorn S (2008) Cold stored ectoparasitoid of Cydia fruit moths released under different temperature regimes. BioControl 53:857–867
Kivan M, Kilic N (2005) Effects of storage at low-temperature of various heteropteran host eggs on the egg parasitoid, Trissolcus semistriatus. BioControl 50:589–600
Larentzaki E, Powell G, Copland MJW (2007) Effect of cold storage on survival, production and development of adults and eggs of Franklinothrips vespiformis (Crawford). Biol Control 43:265–270
Lee RE (2010) A primer on insect cold tolerance. In: Denlinger DL, Lee RE (eds) Low temperature biology of insects. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 3–34
Leopold RA (1998) Cold storage of insects for integrated pest management. In: Hallman GJ, Denlinger DL (eds) Temperature sensitivity in insects and application in integrated pest management. Westview Press, Boulder, USA, pp 235–267
Lysyk TJ (2004) Effects of cold storage on development and survival of three species of parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) of house fly, Musca domestica L. Environ Entomol 33:823–831
Morewood WD (1992) Cold storage of Phytoseiulus persimilis (Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol 13:231–236
Nicoli G, Galazzi D (1998) Quality control of cold stored Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Boll Ist Ent ‘‘G Grandi’’ Univ Bologna, Italia 52:61–73
Pitcher SA, Hoffmann MP, Gardner J, Wright MG, Kuhar TP (2002) Cold storage of Trichogramma ostriniae reared on Sitotroga cerealella eggs. BioControl 47:525–535
Rhodes EM, Liburd OE (2006) Evaluation of predatory mites and acramite for control of twospotted spider mites in strawberries in north central Florida. Econ Entomol 99:1291–1298
Riddick EW, Wu Z (2010) Potential long-term storage of the predatory mite Phytoseiulus persimilis. BioControl 55:639–644
Tezze AA, Botto EN (2004) Effect of cold storage on the quality of Trichogramma nerudai (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Biol Control 30:11–16
Uckan F, Gulel A (2001) The effects of cold storage on the adult longevity, fecundity and sex ratio of Apanteles galleriae Wilkinson (Hym:Braconidae). Turk J Zool 25:187–191
van Lenteren JC, Tommasini MG (1999) Mass production, storage, shipment and quality control of natural enemies. In: Albajes R, Gullino ML, van Lenteren JC, Elad Y (eds) Integrated pest and disease management in greenhouse crops. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 276–294
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (No. 21580062) and by JSPS Fellows (22-2650). The authors would like to thank Dr. T. Kozai for his kind support and M. Ohyama for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Patrick De Clercq
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghazy, N.A., Suzuki, T., Shah, M. et al. Effect of long-term cold storage of the predatory mite Neoseiulus californicus at high relative humidity on post-storage biological traits. BioControl 57, 635–641 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-012-9441-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-012-9441-7