Abstract
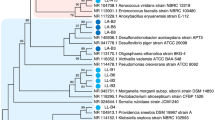
Here we report the effects of starvation and insect age on the diversity of gut microbiota of adult desert locusts, Schistocerca gregaria, using denaturing gradient gel electrophoretic (DGGE) analysis of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Sequencing of excised DGGE bands revealed the presence of only one potentially novel uncultured member of the Gammaproteobacteria in the guts of fed, starved, young or old locusts. Most of the 16S rRNA gene sequences were closely related to known cultured bacterial species. DGGE profiles suggested that bacterial diversity increased with insect age and did not provide evidence for a characteristic locust gut bacterial community. Starved insects are often more prone to disease, probably because they compromise on immune defence. However, the increased diversity of Gammaproteobacteria in starved locusts shown here may improve defence against enteric threats because of the role of gut bacteria in colonization resistance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarestrup FM, Butaye P, Witte W (2002) Non-human reservoirs of Enterococci. In: Gilmore MS (ed) The Enterococci: pathogenesis. Molecular Biology and antibiotic resistance, ASM Press, Washington DC, USA, pp 55–92
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer K-H (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Babendreier D, Joller D, Romeis J, Bigler F, Widmer F (2007) Bacterial community structures in honeybee intestines and their response to two insecticidal proteins. FEMS Micro Ecol 59:600–610
Behar A, Yuval B, Jurkevitch E (2005) Enterobacteria-mediated nitrogen fixation in natural populations of the fruit fly Ceratitis capitata. Mol Ecol 14:2637–2643
Broderick NA, Raffa KF, Goodman RM, Handelsman J (2004) Census of the bacterial community of the gypsy moth larval midgut using culturing and culture-independent methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:293–300
Broderick AA, Raffa KF, Handelsman J (2006) Midgut bacteria required for Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15196–15199
Brummel T, Ching A, Seroude L, Simon AF, Benzer S (2004) Drosophila lifespan enhancement by exogenous bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12974–12979
Charnley AK, Hunt J, Dillon RJ (1985) The germ-free culture of desert locusts, Schistocerca gregaria. J Insect Physiol 31:477–485
Coates ME, Fuller R (1977) The gnotobiotic animal in the study of gut microbiology. In: Clarke RTJ, Bauchop T (eds) Microbial ecology of the gut. Academic Press, London, pp 311–346
Dillon RJ, Charnley AK (1996) Colonization of the guts of germ-free desert locusts, Schistocerca gregaria, by the bacterium Pantoea agglomerans. J Invertebr Pathol 67:11–14
Dillon R, Charnley K (2002) Mutualism between the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria and its gut microbiota. Res Microbiol 153:503–509
Dillon RJ, Dillon VM (2004) The gut bacteria of insects: nonpathogenic interactions. Ann Rev Entomol 49:71–92
Dillon RJ, Vennard CT, Charnley AK (2000) Pheromones—exploitation of gut bacteria in the locust. Nature 403:851
Dillon RJ, Vennard CT, Charnley AK (2002) Gut bacteria produce components of a locust cohesion pheromone. J Appl Microbiol 92:759–763
Dillon RJ, Vennard CT, Buckling A, Charnley AK (2005) Diversity of locust gut bacteria protects against pathogen invasion. Ecology Lett 8:1291–1298
Dillon RJ, Webster G, Weightman AJ, Dillon VM, Blanford S, Charnley AK (2008) Composition of Acridid gut bacterial communities as revealed by 16S rRNA gene analysis. J Invertebr Pathol 97:265–272
Domingo JWS, Kaufman JW, Klug MJ, Holben WE, Harris D, Tiedje JM (1988) Influence of diet on the structure and function of the bacterial hindgut community in crickets. Mol Ecol 7:761–767
Domingo JWS, Kaufman JW, Klug MJ, Tiedje JM (1998) Characterization of the cricket hindgut microbiota with fluorescently labeled rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:752–755
Egert M, Wagner B, Lemke T, Brune A, Friedrich MW (2003) Microbial community structure in midgut and hindgut of the humus-feeding larva of Pachnoda ephippiata (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Appl Environ Micro 69:6659–6668
Gillespie JP, Burnett C, Charnley AK (2000) The immune response of the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria during mycosis of the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae var acridum. J Insect Physiol 46:429–437
Greenberg B (1959) Persistence of bacteria in the developing stages of the housefly. IV. Infectivity of the newly emerged adult. Am J Trop Med Hyg 8:618–622
Haynes S, Darby AC, Daniell TJ, Webster G, van Veen FJF, Godfray HCJ, Prosser JI, Douglas AE (2003) Diversity of bacteria associated with natural aphid populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:7216–7223
Hunt J, Charnley AK (1981) Abundance and distribution of the gut flora of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J Invertbr Pathol 38:378–385
Indiragandhi P, Anandham R, Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhalis S, Kim GH, Saravanan US, Sa T (2007) Prothiofos-resistant, prothiofos-susceptible and field caught populations of diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella and their potential for antagonism towards entomopathogenic fungi and host insect nutrition. J Appl Microbiol 103:2664–2675
Jensen S, Ovreas L, Bergh O, Torsvik V (2004) Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial communities associated with larvae of the Atlantic halibut propose succession from a uniform normal flora. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:728–736
Kaufman MG, Walker ED, Odelson DA, Klug MJ (2000) Microbial community ecology and insect nutrition. Am Entomol 46:173–185
Lehman RM, Lundgren JC, Petzke LM (2009) Bacterial communities associated with the digestive tract of the predatory ground beetle, Poecilus chalcites, and their modification by laboratory rearing and antibiotic treatment. Microb Ecol 57:349–358
McCaig AE, Embley TM, Prosser JI (1994) Molecular analysis of enrichment cultures of marine ammonia oxidisers. FEMS Lett 120:363–368
McCaig AE, Glover AL, Prosser JI (2001) Numerical analysis of grassland bacterial community structure under different land management regimens by using 16S ribosomal DNA sequence data and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis banding patterns. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4554–4559
Miller SG, Miller RD (1996) Infectious Enterococcus from Heliothis virescens X H. subflexa backcross hybrids (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 89:420–427
Müller T, Ulrich A, Ott E-M, Müller M (2001) Identification of plant-associated enterococci. J Appl Microbiol 91:268–278
Munch A, Stingl L, Jung K, Heermann R (2008) Photorhabdus luminescens genes induced upon insect infection. BMC Genomics 9:17
Murrell A, Dobson SJ, Yang X, Lacey L, Barker SC (2003) A survey of bacterial diversity in ticks, lice and fleas from Australia. Parasitol Res 89:326–334
Muyzer G, Dewaal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial-populations by denaturing gradient gel-electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes-coding for 16S Ribosomal-RNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Normander B, Prosser JI (2000) Bacterial origin and community composition in the barley phytosphere as a function of habitat and presowing conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4372–4377
Okhuma M, Kudo T (1996) Phylogenetic diversity of the intestinal bacterial community in the termite Reticulitermes speratus. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:461–468
Reeson AF, Jankovic T, Kasper ML, Rogers S, Austin AD (2003) Application of 16S rDNA-DGGE to examine the microbial ecology associated with a social wasp Vespula germanica. Insect Mol Biol 12:85–91
Ryu JH, Kim SH, Lee HY, Bai JY, Nam YD, Bae JW, Lee DG, Shin SC, Ha EM, Lee WJ (2008) Innate immune homeostasis by the homeobox gene Caudal and commensal-gut mutualism in Drosophila. Science 319:777–782
Simpson JM, Kocherginskaya SA, Aminov RI, Skerlos LT, Bradley TM, Mackie RI, White BA (2002) Comparative microbial diversity in the gastrointestinal tracts of food animal species. Integ Comp Biol 42:327–331
Stevenson JP (1966) The bacterial flora of laboratory stocks of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J Invertebr Pathol 8:205–211
Von Wintzergerode F, Gobel UB, Stackebrandt E (1997) Determination of microbial diversity in environmental samples: pitfalls of PCR-based rRNA analysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21:213–229
Webster G, Embley TM, Prosser JI (2002) Grassland management regimens reduce small-scale heterogeneity and species diversity of beta-proteobacterial ammonia oxidizer populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:20–30
Webster G, Newberry CJ, Fry JC, Weightman AJ (2003) Assessment of bacterial community structure in the deep sub-seafloor biosphere by 16S rDNA-based techniques: a cautionary tale. J Microbiol Methods 55:155–164
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank BBSRC for the grant to AKC and RJD that funded the work and Chris Vennard for rearing the locusts. We thank Dr. Emiru Seyoum for providing the locusts from Addis Ababa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dillon, R.J., Webster, G., Weightman, A.J. et al. Diversity of gut microbiota increases with aging and starvation in the desert locust. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 97, 69–77 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-009-9389-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-009-9389-5