Abstract
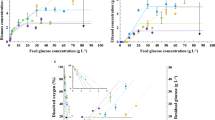
Quasi steady state growth of Lactococcus lactis IL 1403 was studied in glucose-limited A-stat cultivation experiments with acceleration rates (a) from 0.003 to 0.06 h−2 after initial stabilization of the cultures in chemostat at D = 0.2–0.3 h−1. It was shown that the high limit of quasi steady state growth rate depended on the acceleration rate used—at an acceleration rate 0.003 h−2 the quasi steady state growth was observed until μ crit = 0.59 h−1, which is also the μ max value for the culture. Lower values of μ crit were observed at higher acceleration rates. The steady state growth of bacteria stabilized at dilution rate 0.2 h−1 was immediately disrupted after initiating acceleration at the highest acceleration rate studied—0.06 h−2. Observation was made that differences [Δ(μ − D)] of the specific growth rates from pre-programmed dilution rates were the lowest using an acceleration rate of 0.003 h−2 (< 4% of preset changing growth rate). The adaptability of cells to follow preprogrammed growth rate was found to decrease with increasing dilution rate—it was shown that lower acceleration rates should be applied at higher growth rates to maintain the culture in the quasi steady state. The critical specific growth rate and the biomass yields based on glucose consumption were higher if the medium contained S 0 = 5 g L−1 glucose instead of S 0 = 10 g L−1. It was assumed that this was due to the inhibitory effect of lactate accumulating at higher concentrations in the latter cultures. Parallel A-stat experiments at the same acceleration and dilution rates showed good reproducibility—Δ(μ − D) was less than 5%, standard deviations of biomass yields per ATP produced (Y ATP), and biomass yields per glucose consumed (Y XS) were less than 15%.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa MJ, Hoogakker J, Wijffels RH (2003) Optimisation of cultivation parameters in photobioreactors for microalgae cultivation using the A-stat technique. Biomol Eng 20:115–123. doi:10.1016/S1389-0344(03)00033-9
Bolotin A, Wincker P, Mauger S, Jailon O, Malame K, Weissenbach J, Ehrlich SD, Sorokin A (2001) The complete genome sequence of the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis IL1403. Genet Res 11:731–753
Even S, Lindley ND, Cocaign-Bousquet M (2003) Transcriptional, translational, and metabolic regulation of glycolysis in Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris MG 1363 grown in continuous acidic cultures. Microbiol 149:1935–1944. doi:10.1099/mic.0.26146-0
Jensen P, Hammer K (1993) Minimal requirements for the exponential growth of Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:4363–4366
Jensen NBS, Melchiorsen CR, Jokumsen KV, Villadsen J (2001) Metabolic behavior of Lactococcus lactis MG1363 in microaerobic continuous cultivation at a low dilution rate. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2677–2682. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.6.2677-2682.2001
Kasemets K, Drews M, Nisamedtinov I, Adamberg K, Paalme T (2003) Modification of A-stat for the characterization of microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 55:187–2003. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(03)00143-X
Kask S, Laht TM, Pall T, Paalme T (1999) A study on growth characteristics and nutrient consumption of Lactobacillus plantarum in A-stat culture. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 75:309–320. doi:10.1023/A:1001868005416
KEGG metabolic pathways: http://www.genome.ad.jp/kegg/metabolism.html (8/23/06-3/5/07)
Novak L, Loubiere P (2000) The metabolic network of Lactococcus lactis: distribution of 14C-labeled substrates between catabolic and anabolic pathways. J Bacteriol 182:1136–1143. doi:10.1128/JB.182.4.1136-1143.2000
Oliveira AP, Nielsen J, Förster J (2005) Modeling Lactococcus lactis using a genome-scale flux model. BMC Microbiol 5:39. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-5-39
Paalme T, Kahru A, Elken R, Vanatalu K, Tiisma K, Vilu R (1995) The computer controlled continuous culture of Escherichia coli with smooth change of dilution rate. J Microbiol Methods 24:145–153. doi:10.1016/0167-7012(95)00064-X
Paalme T, Elken R, Vilu R, Korhola M (1997) Growth efficiency of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on glucose/ethanol media with smooth change in the dilution rate (A-stat). Enzyme Microb Technol 20:174–181. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(96)00114-7
Teusink B, Wiersma A, Molenaar D, Francke C, de Vos WM, Siezen RJ, Smid EJ (2006) Analysis of growth of Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 on a complex medium using a genome-scale metabolic model. J Biol Chem 281:40041–40048. doi:10.1074/jbc.M606263200
Thomas TD, Ellwood DC, Longyear MC (1979) Change from homo- to heterolactic fermentation by Streptococcus lactis resulting from glucose limitation in anaerobic chemostat cultures. J Bacteriol 138:109–117
van der Sluis C, Westerink BH, Dijkstal MM, Castelein SJ, van Boxtel AJB, Guiseppin MLF, Tramper J, Wijffels RH (2001) Estimation of steady-state culture characteristics during acceleration-stats with yeasts. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:267–275. doi:10.1002/bit.1181
Vinter T, Paalme T, Vilu R (1992) “FermExpert”-an expert system for studies and optimization of processes of microbial synthesis. In: Karim MN, Stephanopolous G (eds) Modeling and control of biotechnical processes. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 467–470
Acknowledgments
The financial support for this research was provided by the Enterprise Estonia project EU22704, and Ministry of Education, Estonia, through the grant SF0142497s03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adamberg, K., Lahtvee, PJ., Valgepea, K. et al. Quasi steady state growth of Lactococcus lactis in glucose-limited acceleration stat (A-stat) cultures. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 95, 219–226 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-009-9305-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-009-9305-z