Abstract
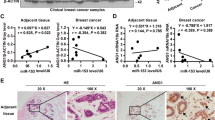
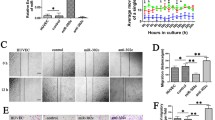
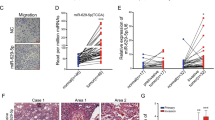
Angiogenesis, a crucial step in tumor growth and metastasis, is regulated by various pro- or anti-angiogenic factors. Recently, microRNAs have been shown to modulate angiogenic processes by modulating the expression of critical angiogenic factors. However, roles of tumor-derived microRNAs in regulating tumor vascularization remain to be elucidated. In this study, we found that delivery of miR-494 into human vascular endothelial cells (ECs) enhanced the EC migration and promoted angiogenesis. The angiogenic effect of miR-494 was mediated by the targeting of PTEN and the subsequent activation of Akt/eNOS pathway. Importantly, co-culture experiments demonstrated that a lung cancer cell line, A549, secreted and delivered miR-494 into ECs via a microvesicle-mediated route. In addition, we found that the expression of miR-494 was induced in the tumor cells in response to hypoxia, likely via a HIF-1α-mediated mechanism. Furthermore, a specific miR-494 antagomiR effectively inhibited angiogenesis and attenuated the growth of tumor xenografts in nude mice. Taken together, these results demonstrated that miR-494 is a novel tumor-derived paracrine signal to promote angiogenesis and tumor growth under hypoxic condition.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Wang Y, Lee CG (2009) MicroRNA and cancer—focus on apoptosis. J Cell Mol Med 13(1):12–23. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00510.x
Stenvang J, Petri A, Lindow M, Obad S, Kauppinen S (2012) Inhibition of microRNA function by antimiR oligonucleotides. Silence 3(1):1. doi:10.1186/1758-907X-3-1
Jones K, Nourse JP, Keane C, Bhatnagar A, Gandhi MK (2014) Plasma microRNA are disease response biomarkers in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 20(1):253–264. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1024
Ries J, Vairaktaris E, Agaimy A, Kintopp R, Baran C, Neukam FW, Nkenke E (2014) miR-186, miR-3651 and miR-494: potential biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma extracted from whole blood. Oncol Rep 31(3):1429–1436. doi:10.3892/or.2014.2983
Lim L, Balakrishnan A, Huskey N, Jones KD, Jodari M, Ng R, Song G, Riordan J, Anderton B, Cheung ST, Willenbring H, Dupuy A, Chen X, Brown D, Chang AN, Goga A (2014) MicroRNA-494 within an oncogenic microRNA megacluster regulates G1/S transition in liver tumorigenesis through suppression of mutated in colorectal cancer. Hepatology 59(1):202–215. doi:10.1002/hep.26662
Liu Y, Lai L, Chen Q, Song Y, Xu S, Ma F, Wang X, Wang J, Yu H, Cao X, Wang Q (2012) MicroRNA-494 is required for the accumulation and functions of tumor-expanded myeloid-derived suppressor cells via targeting of PTEN. J Immunol 188(11):5500–5510. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1103505
Weis SM, Cheresh DA (2011) Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med 17(11):1359–1370. doi:10.1038/nm.2537
Zhang Y, Yang P, Wang XF (2014) Microenvironmental regulation of cancer metastasis by miRNAs. Trends Cell Biol 24(3):153–160. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2013.09.007
Wang X, Fang X, Zhou J, Chen Z, Zhao B, Xiao L, Liu A, Li YS, Shyy JY, Guan Y, Chien S, Wang N (2013) Shear stress activation of nuclear receptor PXR in endothelial detoxification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(32):13174–13179. doi:10.1073/pnas.1312065110
Wang N, Verna L, Hardy S, Zhu Y, Ma KS, Birrer MJ, Stemerman MB (1999) c-Jun triggers apoptosis in human vascular endothelial cells. Circ Res 85(5):387–393
Leung EL, Fiscus RR, Tung JW, Tin VP, Cheng LC, Sihoe AD, Fink LM, Ma Y, Wong MP (2010) Non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing CD44 are enriched for stem cell-like properties. PLoS ONE 5(11):e14062. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014062
Szot CS, Buchanan CF, Freeman JW, Rylander MN (2013) In vitro angiogenesis induced by tumor-endothelial cell co-culture in bilayered, collagen I hydrogel bioengineered tumors. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 19(11):864–874. doi:10.1089/ten.TEC.2012.0684
Zhu TS, Costello MA, Talsma CE, Flack CG, Crowley JG, Hamm LL, He X, Hervey-Jumper SL, Heth JA, Muraszko KM, DiMeco F, Vescovi AL, Fan X (2011) Endothelial cells create a stem cell niche in glioblastoma by providing NOTCH ligands that nurture self-renewal of cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res 71(18):6061–6072. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4269
Tang Z, Wang Y, Fan Y, Zhu Y, Chien S, Wang N (2008) Suppression of c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation inhibits neointimal formation in balloon-injured rat arteries. Circulation 118(7):764–772. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.761932
Liu Y, Tian XY, Mao G, Fang X, Fung ML, Shyy JY, Huang Y, Wang N (2012) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ameliorates pulmonary arterial hypertension by inhibiting 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor. Hypertension 60(6):1471–1478. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.198887
Liu W, Li JJ, Liu M, Zhang H, Wang N (2015) PPAR-gamma promotes endothelial cell migration By inducing the expression of Sema3g. J Cell Biochem 116(4):514–523. doi:10.1002/jcb.24994
Grange C, Tapparo M, Collino F, Vitillo L, Damasco C, Deregibus MC, Tetta C, Bussolati B, Camussi G (2011) Microvesicles released from human renal cancer stem cells stimulate angiogenesis and formation of lung premetastatic niche. Cancer Res 71(15):5346–5356. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0241
Nagasu T, Yoshimatsu K, Rowell C, Lewis MD, Garcia AM (1995) Inhibition of human tumor xenograft growth by treatment with the farnesyl transferase inhibitor B956. Cancer Res 55(22):5310–5314
Bao S, Wu Q, Sathornsumetee S, Hao Y, Li Z, Hjelmeland AB, Shi Q, McLendon RE, Bigner DD, Rich JN (2006) Stem cell-like glioma cells promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res 66(16):7843–7848. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1010
Wang X, Zhang X, Ren XP, Chen J, Liu H, Yang J, Medvedovic M, Hu Z, Fan GC (2010) MicroRNA-494 targeting both proapoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury. Circulation 122(13):1308–1318. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.964684
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Rak J (2009) Microvesicles: messengers and mediators of tumor progression. Cell Cycle 8(13):2014–2018
Muralidharan-Chari V, Clancy JW, Sedgwick A, D’Souza-Schorey C (2010) Microvesicles: mediators of extracellular communication during cancer progression. J Cell Sci 123(Pt 10):1603–1611. doi:10.1242/jcs.064386
Valenti R, Huber V, Iero M, Filipazzi P, Parmiani G, Rivoltini L (2007) Tumor-released microvesicles as vehicles of immunosuppression. Cancer Res 67(7):2912–2915. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0520
D’Souza-Schorey C, Clancy JW (2012) Tumor-derived microvesicles: shedding light on novel microenvironment modulators and prospective cancer biomarkers. Genes Dev 26(12):1287–1299. doi:10.1101/gad.192351.112
Yamada N, Tsujimura N, Kumazaki M, Shinohara H, Taniguchi K, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T, Akao Y (2014) Colorectal cancer cell-derived microvesicles containing microRNA-1246 promote angiogenesis by activating Smad 1/5/8 signaling elicited by PML down-regulation in endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839(11):1256–1272. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.09.002
Liu L, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Greenlee AR, Han Z (2010) Overexpressed miR-494 down-regulates PTEN gene expression in cells transformed by anti-benzo(a)pyrene-trans-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide. Life Sci 86(5–6):192–198. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2009.12.002
Shiojima I, Walsh K (2002) Role of Akt signaling in vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis. Circ Res 90(12):1243–1250
Liao D, Johnson RS (2007) Hypoxia: a key regulator of angiogenesis in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26(2):281–290. doi:10.1007/s10555-007-9066-y
Voellenkle C, Rooij J, Guffanti A, Brini E, Fasanaro P, Isaia E, Croft L, David M, Capogrossi MC, Moles A, Felsani A, Martelli F (2012) Deep-sequencing of endothelial cells exposed to hypoxia reveals the complexity of known and novel microRNAs. RNA 18(3):472–484. doi:10.1261/rna.027615.111
Cha ST, Chen PS, Johansson G, Chu CY, Wang MY, Jeng YM, Yu SL, Chen JS, Chang KJ, Jee SH, Tan CT, Lin MT, Kuo ML (2010) MicroRNA-519c suppresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression and tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res 70(7):2675–2685. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2448
Puissegur MP, Mazure NM, Bertero T, Pradelli L, Grosso S, Robbe-Sermesant K, Maurin T, Lebrigand K, Cardinaud B, Hofman V, Fourre S, Magnone V, Ricci JE, Pouyssegur J, Gounon P, Hofman P, Barbry P, Mari B (2011) miR-210 is overexpressed in late stages of lung cancer and mediates mitochondrial alterations associated with modulation of HIF-1 activity. Cell Death Differ 18(3):465–478. doi:10.1038/cdd.2010.119
Ghosh G, Subramanian IV, Adhikari N, Zhang X, Joshi HP, Basi D, Chandrashekhar YS, Hall JL, Roy S, Zeng Y, Ramakrishnan S (2010) Hypoxia-induced microRNA-424 expression in human endothelial cells regulates HIF-alpha isoforms and promotes angiogenesis. J Clin Invest 120(11):4141–4154. doi:10.1172/JCI42980
Chan YC, Khanna S, Roy S, Sen CK (2011) miR-200b targets Ets-1 and is down-regulated by hypoxia to induce angiogenic response of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 286(3):2047–2056. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.158790
Liu LZ, Li C, Chen Q, Jing Y, Carpenter R, Jiang Y, Kung HF, Lai L, Jiang BH (2011) MiR-21 induced angiogenesis through AKT and ERK activation and HIF-1alpha expression. PLoS ONE 6(4):e19139. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019139
Seok JK, Lee SH, Kim MJ, Lee YM (2014) MicroRNA-382 induced by HIF-1alpha is an angiogenic miR targeting the tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog. Nucleic Acids Res 42(12):8062–8072. doi:10.1093/nar/gku515
Romano G, Acunzo M, Garofalo M, Di Leva G, Cascione L, Zanca C, Bolon B, Condorelli G, Croce CM (2012) MiR-494 is regulated by ERK1/2 and modulates TRAIL-induced apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer through BIM down-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(41):16570–16575. doi:10.1073/pnas.1207917109
Wang J, Chen H, Liao Y, Chen N, Liu T, Zhang H, Zhang H (2015) Expression and clinical evidence of miR-494 and PTEN in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3416-0
Cui FM, Li JX, Chen Q, Du HB, Zhang SY, Nie JH, Cao JP, Zhou PK, Hei TK, Tong J (2013) Radon-induced alterations in micro-RNA expression profiles in transformed BEAS2B cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A 76(2):107–119. doi:10.1080/15287394.2013.738176
He W, Li Y, Chen X, Lu L, Tang B, Wang Z, Pan Y, Cai S, He Y, Ke Z (2014) miR-494 acts as an anti-oncogene in gastric carcinoma by targeting c-myc. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29(7):1427–1434. doi:10.1111/jgh.12558
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of China (#30881220108005, 31430045 and 81470373) and the Provincial Office of Science and Technology, Shaanxi (2011KTCQ03-14).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, G., Liu, Y., Fang, X. et al. Tumor-derived microRNA-494 promotes angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Angiogenesis 18, 373–382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-015-9474-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-015-9474-5